Tomas Hlavacek - IP fragmentation attack on DNS
0 likes1,454 views
This document summarizes an IP fragmentation attack on DNS resolvers. It exploits IP fragmentation and reassembly to reduce the entropy for cache poisoning from 32 bits to 16 bits. There are two types of attacks - one triggers fragmentation through spoofed ICMP messages, while the other registers a specially crafted zone to generate oversized responses. The attacks allow modifying DNS response fragments off-path to poison caches. Defenses include DNSSEC and workaround like ignoring certain ICMP and limiting response sizes.
1 of 26
Download to read offline
























Ad
Recommended
Dynamic Port Scanning



Dynamic Port Scanningamiable_indian The document discusses dynamic port scanning (DPS), which integrates ARP poisoning into port scanning to dynamically spoof the source IP address of scan packets. DPS works by poisoning the ARP cache of the target host or gateway so that scan replies are delivered to the scanning machine regardless of the spoofed source IP. This allows the scan to appear as if it is coming from many machines, improving stealth, while still obtaining results unlike traditional IP spoofing techniques. The document outlines how DPS works, current spoofing methods, advantages over other techniques, and limitations.
Hacking With Nmap - Scanning Techniques



Hacking With Nmap - Scanning Techniquesamiable_indian The document discusses different nmap scanning techniques including SYN scans, FIN scans, ACK scans, and window scans. It provides pros and cons of each technique. It then details a mission to penetrate SCO's firewall and discern open ports on a target system using different scan types. Another mission works to locate webservers on the Playboy network offering free images, optimizing the scan by getting timing information and scanning faster without DNS lookups. Several IP addresses with port 80 open are identified.
3 scanning-ger paoctes-pub



3 scanning-ger paoctes-pubCassio Ramos The document discusses the nmap scanning tool and provides examples of using its basic scanning options. Nmap can scan for open ports on TCP, UDP, and other protocols. It can detect operating systems, banner grab services to identify software versions, and has options for port scanning, ping scanning entire networks, and more. Scripting options allow tasks like brute force attempts, information gathering, and vulnerability scanning.
How to bypass an IDS with netcat and linux



How to bypass an IDS with netcat and linuxKirill Shipulin Developers and researchers are confronted with a huge number of tools and technologies in their daily work, each of which has its own pros and cons. This realization is important for network devices intended to stop attacks — they should be “omnivores” with regard to network protocols. The speaker’s passion is to study and recreate various hacker attacks, exploits and tactics at the network level in order to develop reliable detection techniques for intrusion detection systems. While working on lots of attacks he noticed some tiny network conditions when a packet sequence slip away from IDS system but get to the target. Will your IDS system detect data network connection was broken? Using nc and a Linux machine, the speaker will demonstrate 4 CVEs he found for bypassing IDS systems, based on the example of the popular Suricata IDS.
Recon with Nmap 



Recon with Nmap OWASP Delhi The document discusses using Nmap to perform network scanning and reconnaissance. It provides an overview of Nmap, describing common scan types like TCP and UDP scans. It also covers useful Nmap options for tasks like service and operating system detection. The document demonstrates the Nmap Scripting Engine for tasks like vulnerability scanning and brute force attacks. It provides examples of commands for different scan types and scripts.
Blackholing from a_providers_perspektive_theo_voss



Blackholing from a_providers_perspektive_theo_vossPavel Odintsov This document discusses blackholing from a provider's perspective. It describes how blackholing can be implemented at the provider's upstreams and internet exchange points (IXPs). The document also discusses using FastNetMon for DDoS attack detection and implementing blackholing policies on routers to discard attack traffic in the case of a detected DDoS attack.
Extending Zeek for ICS Defense



Extending Zeek for ICS DefenseJames Dickenson This document discusses extending the network security monitoring capabilities of Zeek to analyze industrial control system (ICS) data. It notes that only 3 out of 72 Zeek analyzers currently support ICS protocols. The document then provides examples of how to create new parsers for Zeek by developing a parser for the EthernetIP/CIP protocol, and describes a lab setup used to test the new parser by capturing attacks against a PLC. It concludes by encouraging contributions of new parsers to Zeek to improve ICS monitoring.
Nmap scripting engine



Nmap scripting enginen|u - The Open Security Community This document provides an overview and agenda for a training on the Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE). It begins with a 10 minute introduction to Nmap, covering what Nmap is used for and some basic scan options. Next, it spends 20 minutes reviewing the existing NSE script categories and how to use available scripts, demonstrating two sample scripts. Finally, it dedicates 20 minutes to explaining how to write your own NSE script, including the basic structure and providing an example of writing a script to find the website title.
LF_OVS_17_OVS/OVS-DPDK connection tracking for Mobile usecases



LF_OVS_17_OVS/OVS-DPDK connection tracking for Mobile usecasesLF_OpenvSwitch 1) Mobile networks today handle a large number of simultaneous short duration flows, with high call rates of 100k-200k connections per second. Statistics like call duration and bandwidth usage need to be tracked for each flow for billing purposes.
2) Testing was conducted injecting a 10Gbps mobile traffic profile of 1 million flows into OVS, with 200k flows created and destroyed per second. Key metrics measured were maximum throughput, latency, and jitter at different flow table sizes and core counts.
3) Conntrack performance was tested for OVS kernel and DPDK versions. For 100k flows, OVS kernel achieved 152k pps for 4-tuple matching while OVS-DPDK achieved
Type of DDoS attacks with hping3 example



Type of DDoS attacks with hping3 exampleHimani Singh This document summarizes common DDoS attack types and how to execute them using hping3 or other tools. It describes application layer attacks like HTTP floods, protocol attacks like SYN floods, volumetric attacks like ICMP floods, and reflection attacks. It then provides commands to execute various TCP, UDP, ICMP floods and other DDoS attacks using hping3 by spoofing addresses, modifying flags, and targeting ports. Layer 7 attacks exploiting HTTP requests are also summarized.
2 netcat enum-pub



2 netcat enum-pubCassio Ramos Netcat (nc) is a networking utility that can be used to transfer files, run commands remotely, and scan ports on remote systems. It allows establishing TCP and UDP connections to ports on remote systems. The document provides examples of using nc to scan ports, transfer files between systems, set up reverse shells, and perform basic network tasks and administration. Google dorking techniques are also presented for searching websites and finding specific pages or files using keywords, titles, and URLs. The Whois tool is demonstrated to query registration records for domain names and obtain information like registrar, IP address, and name servers.
Nmap and metasploitable



Nmap and metasploitableMohammed Akbar Shariff This was presented in Null Open Security community july meetup, Session was on Nmap and metasploitable
Network Penetration Testing Toolkit - Nmap, Netcat, and Metasploit Basics



Network Penetration Testing Toolkit - Nmap, Netcat, and Metasploit BasicsBishop Fox Learn the basics of network penetration testing success - an introduction to the top three tools that will help you on your security journey: Nmap, Netcat, and Metasploit. See how to use Nmap both for port scanning and vulnerability discovery. You'll also learn how to use Netcat to grab banners, make HTTP requests, and create both reverse and bind shells. Finally, we’ll learn the ins and outs of Metasploit, including how to integrate our Nmap scan results for even more ownage and using the built-in exploits to get shells.
At the end of this, you will be port scanning, creating payloads, and popping shells. This technical workshop is designed to familiarize you with the necessary tools to continue your ethical hacking journey. From here, take your l33t new skillz and apply them to Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions or scanning your home network for vulnerabilities.
(This was originally presented on February 22, 2010 at Day of Shecurity Boston 2019).
Offline bruteforce attack on wi fi protected setup



Offline bruteforce attack on wi fi protected setupCyber Security Alliance The document discusses an offline brute force attack method against the WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) protocol. It explains that many wireless access points and routers use weak pseudo-random number generators with small states that can be recovered, allowing an attacker to determine the nonces used in the WPS handshake and then brute force the PIN offline. It provides details on how the attack would work by recovering the PRNG state from the initial message and then determining the PIN. Vendors are shown to have weak responses or lack of acknowledgment of the issue, which affects many chipset and product brands that use a common reference implementation.
Nmap for Scriptors



Nmap for Scriptorsn|u - The Open Security Community This document provides an overview of Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) for security researchers looking to build NSE scripts. It covers the anatomy of an NSE script including required components like metadata, categories, portrules and actions. It also provides tips for scriptors like specifying the script directory, using debugging mode, and updating the script database. The goal is to provide a kickstart for researchers to learn how to create NSE scripts and proofs-of-concept.
LF_OVS_17_Ingress Scheduling



LF_OVS_17_Ingress SchedulingLF_OpenvSwitch This document discusses ingress scheduling in OvS-DPDK. It introduces several use cases for traffic prioritization in NFV and describes the current state of the OvS-DPDK datapath. It then explores implementing traffic classification and queue selection on the NIC to prioritize certain packets at the ingress of the datapath. Next steps are discussed to further develop this functionality.
Ripe71 FastNetMon open source DoS / DDoS mitigation



Ripe71 FastNetMon open source DoS / DDoS mitigationPavel Odintsov This document describes FastNetMon, an open source DDoS mitigation toolkit. It provides concise summaries of network traffic and detects DDoS attacks in real-time. It can block malicious traffic through methods like BGP announcements. FastNetMon supports many Linux distributions and can integrate with hardware/cloud solutions. It detects attacks faster than traditional hardware/service approaches through optimized packet capture using tools like Netmap and PF_RING.
Nmap tutorial



Nmap tutorialVarun Kakumani The document discusses various scan types available in the nmap port scanner program. It describes TCP connect scans which actively connect to ports, SYN stealth scans which send SYN packets to identify open and closed ports without fully establishing connections, and less common FIN, NULL and XMAS scans. It also covers ping scans to identify online systems, UDP scans, and options for customizing scans to avoid detection like altering timing and using decoys. The goal is to help users understand different scan techniques and how to choose scans suited to different target types or detection avoidance needs.
Nmap



NmapNishaYadav177 This document introduces Nmap, an open source network scanning tool. It describes Nmap's basic syntax and how it works, outlines different types of scans like TCP, UDP, and SYN scans, discusses timing options, and provides references and links to tutorials on hackingarticles.in about using Nmap for tasks like port scanning, vulnerability detection, and password cracking.
Hacking the swisscom modem



Hacking the swisscom modemCyber Security Alliance The document discusses hacking the Swisscom modem by exploiting default credentials to gain access. Upon login, the author runs commands to investigate the system such as viewing configuration files and mapping the internal network. Various system details are discovered including the Linux kernel version and software components.
Protect your edge BGP security made simple



Protect your edge BGP security made simplePavel Odintsov SysEleven filters routes to protect its edge by rejecting bogon prefixes and invalid routes. It generates prefix filters automatically based on peer AS sets to apply strict inbound filtering. It also uses RPKI to validate routes and reject invalid announcements. For DDoS mitigation, it uses FastNetMon for detection and FlowSpec to propagate rate limiting filters via BGP to upstream providers for quick attack mitigation in under 2 minutes. Open source tools like bgpq3, aggregate, and GoBGP help implement these solutions in a cost effective manner.
Os detection with arp



Os detection with arpDavid Clark Neighbor Cache Fingerprinter (NCF) is a tool that fingerprints operating systems through analysis of how targets respond to unusual Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets and behavior. NCF sends various crafted ARP packets and probes targets, observing factors like the number of ARP requests before timeout, response to gratuitous ARP packets, and cache entry timeout periods. NCF then compares these characteristics to a relatively small database of fingerprints to determine the likely operating system and version of the target.
Beginner's Guide to the nmap Scripting Engine - Redspin Engineer, David Shaw



Beginner's Guide to the nmap Scripting Engine - Redspin Engineer, David ShawRedspin, Inc. Redspin Engineer, David Shaw at Toorcon Information Security Conference giving his talk titled, Beginner's Guide to the nmap Scripting Engine.
Ultra fast DDoS Detection with FastNetMon at Coloclue (AS 8283)



Ultra fast DDoS Detection with FastNetMon at Coloclue (AS 8283)Pavel Odintsov This document discusses how Coloclue, a non-profit volunteer-driven ISP, automated the detection and mitigation of DDoS attacks through the use of FastNetMon and BIRD. FastNetMon allows for detection of attacks within 3 seconds by monitoring traffic levels. BIRD then injects selective blackhole routes within 1 second to mitigate attacks by dropping traffic for 1 IP or subnet for 60 seconds. This approach solves the DDoS problem within 4 seconds through 100% automated detection and mitigation.
Keeping your rack cool 



Keeping your rack cool Pavel Odintsov Marek discusses how his company Faelix uses MikroTik hardware and RouterOS at their network edges to route over 600k IPv4 and 30k IPv6 routes. While there were some initial issues, MikroTik has proven reliable and cost-effective. Marek then explains how Faelix implements firewalling with zero filter rules through a multi-step process. They use fail2ban to block brute force attacks, AMQP to share block lists across routers, and destination NAT misbehaving traffic. Most importantly, they leverage the "/ip route rule" feature to route blocked traffic to a separate routing table for easy isolation without complex firewall rules.
LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK: Embracing your NUMA nodes.



LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK: Embracing your NUMA nodes.LF_OpenvSwitch This document discusses configuring OVS-DPDK parameters for a multi-NUMA environment. It recommends associating physical NICs and virtual ports to their respective NUMA nodes, provisioning CPUs on both nodes using pmd-cpu-mask, allocating hugepages for memory on each node using dpdk-socket-mem, and debugging by checking PMD thread placement and other_config settings. Correct configuration of these OVS-DPDK parameters is necessary for performance when using multiple NUMA nodes.
LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK Installation and Gotchas



LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK Installation and GotchasLF_OpenvSwitch 1) The document provides instructions for installing and configuring OVS DPDK on Ubuntu 17.04, including specifying hardware, installing prerequisites, configuring grub, identifying NIC ports, binding interfaces to DPDK drivers, setting up the OVS bridge and adding ports.
2) Key steps include reserving hugepages in grub, binding NICs to igb_uio or vfio-pci drivers, setting OVS configuration like datapath type and memory allocation, and adding interfaces to the OVS bridge.
3) The scripts provided automate many of these steps but additional manual configuration may still be needed and issues can occur with making interfaces persistent after reboots.
Nmap not only a port scanner by ravi rajput comexpo security awareness meet 



Nmap not only a port scanner by ravi rajput comexpo security awareness meet Ravi Rajput As every coin has two side as a same way we know only the single side of Nmap which is port scanning.
While researching I found that a lot more other than port scanning and banner grabbing can be done with the use of Nmap.
We can use Nmap for web application pen-testing and exploitation too. Yeah it won't work as efficiently as of MSF.
This can replace the use of acunetix and other paid version scanner.
Adrian Furtuna - Practical exploitation of rounding vulnerabilities in intern...



Adrian Furtuna - Practical exploitation of rounding vulnerabilities in intern...DefconRussia This document summarizes a presentation on practical exploitation of rounding vulnerabilities in internet banking applications. It discusses how rounding can allow small gains from each transaction. Several techniques for automating transactions are presented, including initiating many transactions and signing once, using payment files containing many transactions, using pre-computed responses from challenge-response devices, and automating the challenge-response device itself. Code for automating a VASCO 550 token is demonstrated.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
LF_OVS_17_OVS/OVS-DPDK connection tracking for Mobile usecases



LF_OVS_17_OVS/OVS-DPDK connection tracking for Mobile usecasesLF_OpenvSwitch 1) Mobile networks today handle a large number of simultaneous short duration flows, with high call rates of 100k-200k connections per second. Statistics like call duration and bandwidth usage need to be tracked for each flow for billing purposes.
2) Testing was conducted injecting a 10Gbps mobile traffic profile of 1 million flows into OVS, with 200k flows created and destroyed per second. Key metrics measured were maximum throughput, latency, and jitter at different flow table sizes and core counts.
3) Conntrack performance was tested for OVS kernel and DPDK versions. For 100k flows, OVS kernel achieved 152k pps for 4-tuple matching while OVS-DPDK achieved
Type of DDoS attacks with hping3 example



Type of DDoS attacks with hping3 exampleHimani Singh This document summarizes common DDoS attack types and how to execute them using hping3 or other tools. It describes application layer attacks like HTTP floods, protocol attacks like SYN floods, volumetric attacks like ICMP floods, and reflection attacks. It then provides commands to execute various TCP, UDP, ICMP floods and other DDoS attacks using hping3 by spoofing addresses, modifying flags, and targeting ports. Layer 7 attacks exploiting HTTP requests are also summarized.
2 netcat enum-pub



2 netcat enum-pubCassio Ramos Netcat (nc) is a networking utility that can be used to transfer files, run commands remotely, and scan ports on remote systems. It allows establishing TCP and UDP connections to ports on remote systems. The document provides examples of using nc to scan ports, transfer files between systems, set up reverse shells, and perform basic network tasks and administration. Google dorking techniques are also presented for searching websites and finding specific pages or files using keywords, titles, and URLs. The Whois tool is demonstrated to query registration records for domain names and obtain information like registrar, IP address, and name servers.
Nmap and metasploitable



Nmap and metasploitableMohammed Akbar Shariff This was presented in Null Open Security community july meetup, Session was on Nmap and metasploitable
Network Penetration Testing Toolkit - Nmap, Netcat, and Metasploit Basics



Network Penetration Testing Toolkit - Nmap, Netcat, and Metasploit BasicsBishop Fox Learn the basics of network penetration testing success - an introduction to the top three tools that will help you on your security journey: Nmap, Netcat, and Metasploit. See how to use Nmap both for port scanning and vulnerability discovery. You'll also learn how to use Netcat to grab banners, make HTTP requests, and create both reverse and bind shells. Finally, we’ll learn the ins and outs of Metasploit, including how to integrate our Nmap scan results for even more ownage and using the built-in exploits to get shells.
At the end of this, you will be port scanning, creating payloads, and popping shells. This technical workshop is designed to familiarize you with the necessary tools to continue your ethical hacking journey. From here, take your l33t new skillz and apply them to Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions or scanning your home network for vulnerabilities.
(This was originally presented on February 22, 2010 at Day of Shecurity Boston 2019).
Offline bruteforce attack on wi fi protected setup



Offline bruteforce attack on wi fi protected setupCyber Security Alliance The document discusses an offline brute force attack method against the WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) protocol. It explains that many wireless access points and routers use weak pseudo-random number generators with small states that can be recovered, allowing an attacker to determine the nonces used in the WPS handshake and then brute force the PIN offline. It provides details on how the attack would work by recovering the PRNG state from the initial message and then determining the PIN. Vendors are shown to have weak responses or lack of acknowledgment of the issue, which affects many chipset and product brands that use a common reference implementation.
Nmap for Scriptors



Nmap for Scriptorsn|u - The Open Security Community This document provides an overview of Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) for security researchers looking to build NSE scripts. It covers the anatomy of an NSE script including required components like metadata, categories, portrules and actions. It also provides tips for scriptors like specifying the script directory, using debugging mode, and updating the script database. The goal is to provide a kickstart for researchers to learn how to create NSE scripts and proofs-of-concept.
LF_OVS_17_Ingress Scheduling



LF_OVS_17_Ingress SchedulingLF_OpenvSwitch This document discusses ingress scheduling in OvS-DPDK. It introduces several use cases for traffic prioritization in NFV and describes the current state of the OvS-DPDK datapath. It then explores implementing traffic classification and queue selection on the NIC to prioritize certain packets at the ingress of the datapath. Next steps are discussed to further develop this functionality.
Ripe71 FastNetMon open source DoS / DDoS mitigation



Ripe71 FastNetMon open source DoS / DDoS mitigationPavel Odintsov This document describes FastNetMon, an open source DDoS mitigation toolkit. It provides concise summaries of network traffic and detects DDoS attacks in real-time. It can block malicious traffic through methods like BGP announcements. FastNetMon supports many Linux distributions and can integrate with hardware/cloud solutions. It detects attacks faster than traditional hardware/service approaches through optimized packet capture using tools like Netmap and PF_RING.
Nmap tutorial



Nmap tutorialVarun Kakumani The document discusses various scan types available in the nmap port scanner program. It describes TCP connect scans which actively connect to ports, SYN stealth scans which send SYN packets to identify open and closed ports without fully establishing connections, and less common FIN, NULL and XMAS scans. It also covers ping scans to identify online systems, UDP scans, and options for customizing scans to avoid detection like altering timing and using decoys. The goal is to help users understand different scan techniques and how to choose scans suited to different target types or detection avoidance needs.
Nmap



NmapNishaYadav177 This document introduces Nmap, an open source network scanning tool. It describes Nmap's basic syntax and how it works, outlines different types of scans like TCP, UDP, and SYN scans, discusses timing options, and provides references and links to tutorials on hackingarticles.in about using Nmap for tasks like port scanning, vulnerability detection, and password cracking.
Hacking the swisscom modem



Hacking the swisscom modemCyber Security Alliance The document discusses hacking the Swisscom modem by exploiting default credentials to gain access. Upon login, the author runs commands to investigate the system such as viewing configuration files and mapping the internal network. Various system details are discovered including the Linux kernel version and software components.
Protect your edge BGP security made simple



Protect your edge BGP security made simplePavel Odintsov SysEleven filters routes to protect its edge by rejecting bogon prefixes and invalid routes. It generates prefix filters automatically based on peer AS sets to apply strict inbound filtering. It also uses RPKI to validate routes and reject invalid announcements. For DDoS mitigation, it uses FastNetMon for detection and FlowSpec to propagate rate limiting filters via BGP to upstream providers for quick attack mitigation in under 2 minutes. Open source tools like bgpq3, aggregate, and GoBGP help implement these solutions in a cost effective manner.
Os detection with arp



Os detection with arpDavid Clark Neighbor Cache Fingerprinter (NCF) is a tool that fingerprints operating systems through analysis of how targets respond to unusual Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets and behavior. NCF sends various crafted ARP packets and probes targets, observing factors like the number of ARP requests before timeout, response to gratuitous ARP packets, and cache entry timeout periods. NCF then compares these characteristics to a relatively small database of fingerprints to determine the likely operating system and version of the target.
Beginner's Guide to the nmap Scripting Engine - Redspin Engineer, David Shaw



Beginner's Guide to the nmap Scripting Engine - Redspin Engineer, David ShawRedspin, Inc. Redspin Engineer, David Shaw at Toorcon Information Security Conference giving his talk titled, Beginner's Guide to the nmap Scripting Engine.
Ultra fast DDoS Detection with FastNetMon at Coloclue (AS 8283)



Ultra fast DDoS Detection with FastNetMon at Coloclue (AS 8283)Pavel Odintsov This document discusses how Coloclue, a non-profit volunteer-driven ISP, automated the detection and mitigation of DDoS attacks through the use of FastNetMon and BIRD. FastNetMon allows for detection of attacks within 3 seconds by monitoring traffic levels. BIRD then injects selective blackhole routes within 1 second to mitigate attacks by dropping traffic for 1 IP or subnet for 60 seconds. This approach solves the DDoS problem within 4 seconds through 100% automated detection and mitigation.
Keeping your rack cool 



Keeping your rack cool Pavel Odintsov Marek discusses how his company Faelix uses MikroTik hardware and RouterOS at their network edges to route over 600k IPv4 and 30k IPv6 routes. While there were some initial issues, MikroTik has proven reliable and cost-effective. Marek then explains how Faelix implements firewalling with zero filter rules through a multi-step process. They use fail2ban to block brute force attacks, AMQP to share block lists across routers, and destination NAT misbehaving traffic. Most importantly, they leverage the "/ip route rule" feature to route blocked traffic to a separate routing table for easy isolation without complex firewall rules.
LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK: Embracing your NUMA nodes.



LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK: Embracing your NUMA nodes.LF_OpenvSwitch This document discusses configuring OVS-DPDK parameters for a multi-NUMA environment. It recommends associating physical NICs and virtual ports to their respective NUMA nodes, provisioning CPUs on both nodes using pmd-cpu-mask, allocating hugepages for memory on each node using dpdk-socket-mem, and debugging by checking PMD thread placement and other_config settings. Correct configuration of these OVS-DPDK parameters is necessary for performance when using multiple NUMA nodes.
LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK Installation and Gotchas



LF_OVS_17_OVS-DPDK Installation and GotchasLF_OpenvSwitch 1) The document provides instructions for installing and configuring OVS DPDK on Ubuntu 17.04, including specifying hardware, installing prerequisites, configuring grub, identifying NIC ports, binding interfaces to DPDK drivers, setting up the OVS bridge and adding ports.
2) Key steps include reserving hugepages in grub, binding NICs to igb_uio or vfio-pci drivers, setting OVS configuration like datapath type and memory allocation, and adding interfaces to the OVS bridge.
3) The scripts provided automate many of these steps but additional manual configuration may still be needed and issues can occur with making interfaces persistent after reboots.
Nmap not only a port scanner by ravi rajput comexpo security awareness meet 



Nmap not only a port scanner by ravi rajput comexpo security awareness meet Ravi Rajput As every coin has two side as a same way we know only the single side of Nmap which is port scanning.
While researching I found that a lot more other than port scanning and banner grabbing can be done with the use of Nmap.
We can use Nmap for web application pen-testing and exploitation too. Yeah it won't work as efficiently as of MSF.
This can replace the use of acunetix and other paid version scanner.
Viewers also liked (6)
Adrian Furtuna - Practical exploitation of rounding vulnerabilities in intern...



Adrian Furtuna - Practical exploitation of rounding vulnerabilities in intern...DefconRussia This document summarizes a presentation on practical exploitation of rounding vulnerabilities in internet banking applications. It discusses how rounding can allow small gains from each transaction. Several techniques for automating transactions are presented, including initiating many transactions and signing once, using payment files containing many transactions, using pre-computed responses from challenge-response devices, and automating the challenge-response device itself. Code for automating a VASCO 550 token is demonstrated.
Nedospasov photonic emission analysis



Nedospasov photonic emission analysisDefconRussia The document discusses the benefits of exercise for mental health. Regular physical activity can help reduce anxiety and depression and improve mood and cognitive function. Exercise causes chemical changes in the brain that may help protect against mental illness and improve symptoms.
Anton Alexanenkov - Tor and Botnet C&C 



Anton Alexanenkov - Tor and Botnet C&C DefconRussia - пробежимся по структуре Tor
- взглянем на варианты использования Tor при построении ботнета
-рассмотрим существующие атаки на анонимность скрытых сервисов Tor
- порассуждаем как противодействовать таким ботнетам
Zn task - defcon russia 20



Zn task - defcon russia 20DefconRussia The document describes a simulated hacking game scenario involving a compromised POS terminal infected with malware. It details the components of the botnet architecture including bot nodes, command and control infrastructure, and social media propagation. Diagrams show the network layout and communication channels. The document also examines the bot's components, capabilities, and protection mechanisms such as bytecode encryption and anti-debugging techniques. Hints are provided to help players progress in the game by bypassing defenses and achieving objectives over multiple days.
Ad
Similar to Tomas Hlavacek - IP fragmentation attack on DNS (20)
DDoS Defense Mechanisms for IXP Infrastructures



DDoS Defense Mechanisms for IXP InfrastructuresPavel Odintsov DDoS Defense Mechanisms for IXP Infrastructures by Tim Dijkhuizen Lennart van Gijtenbeek
Supervisor: Stavros Konstantaras (AMS-IX)
Cyber-security



Cyber-securityQasim Zaidi I do not have any quotes to share. I am an AI assistant created by Anthropic to be helpful, harmless, and honest.
Information Theft: Wireless Router Shareport for Phun and profit - Hero Suhar...



Information Theft: Wireless Router Shareport for Phun and profit - Hero Suhar...idsecconf The document discusses exploiting vulnerabilities in wireless routers that have USB ports for sharing storage and printers. It describes conducting attacks against a D-Link wireless router to steal data, delete data, and implant backdoors by accessing the shared USB flash drive and printer through the router's vulnerable SharePort technology. The attacker scans the wireless network, identifies the router and connected USB devices, and then explores ways to hack into the shared resources and conduct unauthorized activities.
Neighbor Discovery Deep Dive – IPv6-Networking-Referat



Neighbor Discovery Deep Dive – IPv6-Networking-ReferatDigicomp Academy AG Die monatlichen Anlässe in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Swiss IPv6 Council behandeln verschiedene technische Themenbereiche von IPv6.
Das Referat von Jen Linkova vom 30. November 2015 widmete sich dem Neighbor Discovery Protokoll, einem Schlüsselmechanismus um Verbindungen zwischen IPv6 Knotenpunkten und LANs aufzubauen. Die Referentin fokussierte sich in der Präsentation auf die technischen Details des Designs, der Implementierung sowie Sicherheitsaspekten.
Gerne stellen wir Ihnen die Präsentation zum Anschauen und Herunterladen zur Verfügung. Haben Sie Feedback zum Event? Wir sind gespannt auf Ihre Meinung.
Exploiting First Hop Protocols to Own the Network - Paul Coggin



Exploiting First Hop Protocols to Own the Network - Paul CogginEC-Council This talk will focus on how to exploit a network by targeting the various first hop protocols. Attack vectors for crafting custom packets as well a few of the available tools for layer 2 network protocols exploitation will be covered. Defensive mitigations and recommendations for adding secure visualization and instrumentation for layer 2 will be provided.
Tech f42



Tech f42SelectedPresentations The document discusses security issues with IPv6 and proposed mitigation techniques. It covers topics such as router advertisements, neighbor discovery protocol, and fragmentation. Specifically, it notes that router advertisements and neighbor solicitations are not authenticated by default, allowing for spoofing attacks. The document proposes several mitigation approaches including cryptographically generated addresses, router authorization, port access control lists, and host isolation to secure IPv6 networks.
Hacking Cisco



Hacking Ciscoguestd05b31 The document discusses various reconnaissance and access attacks against Cisco networks, as well as countermeasures. It covers passive sniffing, port scans, ping sweeps, password attacks, trust exploitation, IP spoofing, DHCP/ARP attacks, and DoS/DDoS attacks. Defenses include switched networks, encryption, firewall rules, DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, rate limiting, and storm control.
Pentesting layer 2 protocols



Pentesting layer 2 protocolsAbdessamad TEMMAR Layer 2 protocols like CDP, VTP, DTP, and HSRP are vulnerable to attacks if not properly secured. An attacker can use tools like Yersinia to perform reconnaissance on layer 2 protocols to gain information about devices, protocols, and network topology. Common attacks include denial of service attacks, traffic hijacking, and bypassing network restrictions. To prevent attacks, companies should secure switches, use secure trunking configurations, disable unused ports and protocols, and deploy security features like DHCP snooping.
Design of a campus network



Design of a campus networkAalap Tripathy This is an introductory presentation regarding the issues in designing a campus network infrastructure. Unlike theoretical approaches, this presentation actually was used to describe some of the real configurations performed by Server Administrators and Network Managers. This is for an introductory audience with very little background in computer networks assumed.
packet traveling (pre cloud)



packet traveling (pre cloud)iman darabi deep understanding of howto packet would reach to destination and basic understanding of network protocols.
learn howto manipulate with linux network and know howto manipulate with linux iptables.
IPv6 at Mythic Beasts - Networkshop44



IPv6 at Mythic Beasts - Networkshop44Jisc This document discusses IPv6 only hosting and the challenges of moving to an IPv6-only infrastructure. It notes that IPv4 addresses are becoming scarce and expensive, leading to complicated overlay networks. IPv6 addresses are effectively unlimited and free in comparison. The document outlines steps taken to implement IPv6-only hosting, including NAT64 for outbound IPv4 access, inbound proxies, DHCPv6, and updates to monitoring, backup, and management services. It reports that roughly 5% of the company's servers are now IPv6-only.
IPv6 Fundamentals & Securities



IPv6 Fundamentals & SecuritiesDon Anto - IPv6 is needed to address the impending exhaustion of IPv4 address space. It features a 128-bit address compared to 32-bit in IPv4, vastly expanding the available addresses.
- Security issues in transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 include weaknesses in enumeration, scanning and managing the large IPv6 address space. Firewalls and other perimeter defenses must also protect both IPv4 and IPv6 networks to prevent bypass.
- Attacks can exploit protocols like neighbor discovery in IPv6, as well as vulnerabilities in applications that operate over both IPv4 and IPv6. Proper implementation and maintenance of defenses is needed to secure the transition.
Protect Your DHCP Infrastructure from Cyber Attacks - Cybersecurity Training ...



Protect Your DHCP Infrastructure from Cyber Attacks - Cybersecurity Training ...Jiunn-Jer Sun Agenda
• IEC 62443 IACS standard
• Scope and why
• DHCP protocol and how it works
• DHCP’s Vulnerabilities
• Types of Cyber Attacks to DHCP
• Defense by network security DHCP Snooping
• Korenix products with advanced security features
Network and DNS Vulnerabilities



Network and DNS Vulnerabilitiesn|u - The Open Security Community Network protocols like TCP/IP, DNS, and BGP were designed for functionality over security. This allows for vulnerabilities like eavesdropping, packet injection, route hijacking, and DNS poisoning. While patches have improved security for some issues, core protocols remain vulnerable by design. More secure variants have been proposed, such as using IPsec instead of IP, DNSsec instead of DNS, and SBGP instead of BGP.
IPAddressing .pptx



IPAddressing .pptxkarthikvcyber The document discusses IP addressing and networking concepts. It explains that IP addresses are assigned to interfaces, not hosts, and describes how interfaces connect hosts to routers and physical links. It also discusses IP address structure, private IP address ranges, network address translation, and the differences between classful and classless addressing using CIDR notation. It provides examples of IP addresses and network masks.
New flaws in WPA-TKIP



New flaws in WPA-TKIPvanhoefm Presentation given at the Brucon security conference in Ghent, Belgium. Two new attacks are described. The first is a Denial of Service attack capable of halting all traffic for one minute by injecting only two frames. The second attack allows the injection of arbitrary many packets towards a client. It is shown that this can be used to perform a portscan on any TKIP-secured client.
Basic Understanding about TCP/IP Addressing system



Basic Understanding about TCP/IP Addressing systemBharathKumarRaju DasaraRaju This document provides an overview of TCP/IP addressing and architecture. It describes how TCP/IP was developed by the US Defense Department and Vint Cerf and Robert Kahn. The TCP/IP model has four layers - network access, internet, transport, and application - with each layer performing distinct functions like packet switching, routing, error control, and supporting various applications. It also explains key TCP/IP concepts like IP addresses, subnet masking, CIDR notation, port numbers, and the role of RFC documents in the TCP/IP standards process.
IPv6 Deployment Planning and Security Considerations



IPv6 Deployment Planning and Security ConsiderationsAPNIC Md Abdul Awal, Network Analyst and Technical Trainer at APNIC, delivered a presentation on 'IPv6 Deployment Planning and Security Considerations' at bdNOG 18 held in Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh from 12 to 15 July.
IPv6 Deployment Planning and Security Considerations



IPv6 Deployment Planning and Security ConsiderationsBangladesh Network Operators Group This presentation includes planning and operational recommendations for IPv6 Deployment along with associated security best practices. As more as more networks are planning to deploy IPv6, this session could be a useful one to avoid gotchas and prevent re-doing the v6 deployment because of the known issues.
Day 17.1 nat pat (2)



Day 17.1 nat pat (2)CYBERINTELLIGENTS http://www.cyberintelligents.in
[email protected]
https://www.facebook.com/cyberintelligents
https://in.linkedin.com/in/cyberintelligents/en
https://cyberintelligents.wordpress.com/
http://cyberintelligent.blogspot.in
+91 9876162698 +919988288019
http://trainingcyberintelligents.blogspot.com
Ad
More from DefconRussia (20)
[Defcon Russia #29] Борис Савков - Bare-metal programming на примере Raspber...![[Defcon Russia #29] Борис Савков - Bare-metal programming на примере Raspber...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/preza-170328124723-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Борис Савков - Bare-metal programming на примере Raspber...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/preza-170328124723-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Борис Савков - Bare-metal programming на примере Raspber...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/preza-170328124723-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Борис Савков - Bare-metal programming на примере Raspber...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/preza-170328124723-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Defcon Russia #29] Борис Савков - Bare-metal programming на примере Raspber...DefconRussia Докладчик покажет, как с помощью bare-metal programming подружить Raspberry Pi с GPIO, памятью и Ethernet, и пояснит, кому и зачем это может понадобиться.
[Defcon Russia #29] Александр Ермолов - Safeguarding rootkits: Intel Boot Gua...![[Defcon Russia #29] Александр Ермолов - Safeguarding rootkits: Intel Boot Gua...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/intelbgpart2-170328124242-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Александр Ермолов - Safeguarding rootkits: Intel Boot Gua...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/intelbgpart2-170328124242-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Александр Ермолов - Safeguarding rootkits: Intel Boot Gua...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/intelbgpart2-170328124242-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Александр Ермолов - Safeguarding rootkits: Intel Boot Gua...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/intelbgpart2-170328124242-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Defcon Russia #29] Александр Ермолов - Safeguarding rootkits: Intel Boot Gua...DefconRussia Intel Boot Guard — аппаратно поддержанная технология верификации подлинности BIOS, которую вендор компьютерной системы может встроить на этапе производства. Докладчик представит результаты анализа технологии, расскажет об её эволюции. Слушатели узнают, как годами клонируемая ошибка на производстве нескольких вендоров позволяет потенциальному злоумышленнику воспользоваться этой технологией для создания в системе неудаляемого (даже программатором!) скрытого руткита. Github: https://github.com/flothrone/bootguard
[Defcon Russia #29] Алексей Тюрин - Spring autobinding![[Defcon Russia #29] Алексей Тюрин - Spring autobinding](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/springautobinding-170328123002-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Алексей Тюрин - Spring autobinding](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/springautobinding-170328123002-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Алексей Тюрин - Spring autobinding](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/springautobinding-170328123002-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Алексей Тюрин - Spring autobinding](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/springautobinding-170328123002-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Defcon Russia #29] Алексей Тюрин - Spring autobindingDefconRussia В Spring MVC есть классная фича — autobinding. Но если пользоваться ей неправильно, могут появиться «незаметные» уязвимости, иногда с серьёзным импактом. Рассмотрим пару примеров, углубимся в тонкости появления autobinding-багов. Writeup [ENG]: http://agrrrdog.blogspot.ru/2017/03/autobinding-vulns-and-spring-mvc.html
[Defcon Russia #29] Михаил Клементьев - Обнаружение руткитов в GNU/Linux![[Defcon Russia #29] Михаил Клементьев - Обнаружение руткитов в GNU/Linux](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/revealingrootkitsv5-170328122611-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Михаил Клементьев - Обнаружение руткитов в GNU/Linux](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/revealingrootkitsv5-170328122611-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Михаил Клементьев - Обнаружение руткитов в GNU/Linux](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/revealingrootkitsv5-170328122611-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Defcon Russia #29] Михаил Клементьев - Обнаружение руткитов в GNU/Linux](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/revealingrootkitsv5-170328122611-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Defcon Russia #29] Михаил Клементьев - Обнаружение руткитов в GNU/LinuxDefconRussia Руткиты в мире основанных на ядре Linux операционных систем уже не являются редкостью. Рассказ будет о том, как попытки в современных реалиях определить то, скомпрометирована ли система, привели к неожиданному результату.
Георгий Зайцев - Reversing golang



Георгий Зайцев - Reversing golangDefconRussia Георгий Зайцев - Reversing golang
28 встреча DEFCON Russia - https://defcon-russia.ru
[DCG 25] Александр Большев - Never Trust Your Inputs or How To Fool an ADC ![[DCG 25] Александр Большев - Never Trust Your Inputs or How To Fool an ADC](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/presentationdefconrussia-160406215741-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DCG 25] Александр Большев - Never Trust Your Inputs or How To Fool an ADC](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/presentationdefconrussia-160406215741-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DCG 25] Александр Большев - Never Trust Your Inputs or How To Fool an ADC](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/presentationdefconrussia-160406215741-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[DCG 25] Александр Большев - Never Trust Your Inputs or How To Fool an ADC](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/presentationdefconrussia-160406215741-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[DCG 25] Александр Большев - Never Trust Your Inputs or How To Fool an ADC DefconRussia Мы поговорим об общей проблеме валидации входных данных и качестве их обработки. Интерпретация входящих данных оказывает прямое влияние на решения, принимаемые в физической инфраструктуре: если какая-либо часть данных обрабатывается недостаточно аккуратно, это может повлиять на эффективность и безопасность процесса.
В этой беседе мы обсудим атаки на процесс обработки данных и природу концепции «never trust your inputs» в контексте информационно-физических систем (в общем смысле, то есть любых подобных систем). Для иллюстрации проблемы мы используем уязвимости аналого-цифровых преобразователей (АЦП), которые можно заставить выдавать поддельный цифровой сигнал с помощью изменения частоты и фазы входящего аналогового сигнала: ошибка масштабирования такого сигнала может вызывать целочисленное переполнение и дает возможность эксплуатировать уязвимости в логике PLC/встроенного ПО. Также мы покажем реальные примеры использования подобных уязвимостей и последствия этих нападений.
Cisco IOS shellcode: All-in-one



Cisco IOS shellcode: All-in-oneDefconRussia This document discusses Cisco IOS shellcoding and reverse engineering. It covers topics like Cisco IOS shellcodes that are image-independent by disassembling or interrupting hijacking. It also discusses Tcl shellcodes, Cisco IOS reverse engineering challenges including lack of modularity and APIs. The document details subsystems, registries, processes, command parser tree, debugging Cisco IOS, and magic numbers used in Cisco IOS.
Олег Купреев - Обзор и демонстрация нюансов и трюков из области беспроводных ...



Олег Купреев - Обзор и демонстрация нюансов и трюков из области беспроводных ...DefconRussia Олег Купреев - Обзор и демонстрация нюансов и трюков из области беспроводных сетей.
defcon-russia.ru
Attacks on tacacs - Алексей Тюрин



Attacks on tacacs - Алексей ТюринDefconRussia Алексей Тюрин - Атаки на Tacacs+
http://defcon-russia.ru
Weakpass - defcon russia 23



Weakpass - defcon russia 23DefconRussia This document discusses a password collection called W3@|cP@$s. It contains dictionaries of passwords gathered from multiple sources on the internet. The document provides statistics on the number and types of passwords collected, such as the frequency of different character sets and length distributions. It also describes the features of the collection, including the ability to filter passwords, count totals, and check sample passwords. The collection contains over 3.5 billion passwords gathered using automated bots to find password dumps from sites like pastebin.com.
nosymbols - defcon russia 20



nosymbols - defcon russia 20DefconRussia This document discusses approaches for analyzing obfuscated code without symbols. It presents several techniques including identifying logging functions, searching for specific strings, using meta information like RTTI, analyzing the context of functions and their relationships, and considering properties of the overall program. A combination of techniques is recommended, prioritizing those most likely to apply, such as searching for strings, analyzing wrapper functions, and studying function call relationships.
Vm ware fuzzing - defcon russia 20



Vm ware fuzzing - defcon russia 20DefconRussia The document discusses using virtual machine techniques like GuestRPC and Backdoor I/O to conduct virtual denial of service attacks. It describes fuzzing the GuestRPC interface to discover bugs in systems like HGFS that could be exploited to cause memory leaks or crashes on the host machine. While vendors issue fixes, it notes that fully preventing abuse of these virtual machine behaviors is difficult and some techniques remain unfixed. It concludes with questions about using these kinds of attacks to bypass security systems on virtual machines.
Advanced cfg bypass on adobe flash player 18 defcon russia 23



Advanced cfg bypass on adobe flash player 18 defcon russia 23DefconRussia This document describes an advanced technique to bypass Control Flow Guard (CFG) protections on Adobe Flash Player 18 and Windows 8.1. It details how the researchers were able to generate indirect call instructions in just-in-time (JIT) compiled Flash code to redirect execution to controlled addresses, bypassing CFG. This was done by manipulating parameters passed between functions to influence the JIT compiler's code generation and produce the desired indirect call opcodes. The technique allowed full control-flow hijacking on the protected systems.
Andrey Belenko, Alexey Troshichev - Внутреннее устройство и безопасность iClo...



Andrey Belenko, Alexey Troshichev - Внутреннее устройство и безопасность iClo...DefconRussia Расскажу где и как iCloud Keychain хранит пароли, и какие потенциальные риски это несёт. Apple утверждает, что пароли надежно защищены, и даже её сотрудники не могут получить к ним доступ. Чтобы это подтвердить или опровергнуть, необходимо разобраться с внутренним устройством iCloud Keychain, чем мы и займемся.
Sergey Belov - Покажите нам Impact! Доказываем угрозу в сложных условиях



Sergey Belov - Покажите нам Impact! Доказываем угрозу в сложных условияхDefconRussia Все шире и шире получают распространение bugbounty программы - программы вознаграждения за уязвимости различных вендоров. И порой при поиске уязвимостей находятся места, которые явно небезопасны (например - self XSS), но доказать от них угрозу сложно. Но чем крупнее (хотя, скорее адекватнее) вендор, тем они охотнее обсуждают и просят показать угрозу от сообщенной уязвимости, и при успехе – вознаграждают 8). Мой доклад – подборка таких сложных ситуаций и рассказ, как же можно доказать угрозу.
George Lagoda - Альтернативное использование вэб сервисов SharePoint со сторо...



George Lagoda - Альтернативное использование вэб сервисов SharePoint со сторо...DefconRussia Мои последние исселодования показали, что у SharePoint есть определенное количество вэб сервисов, которые могут помочь аудитору собрать крайне полезную информацию с сайта (списки пользователей, групп, ролей и т д). Также данные сервисы, в комбинации с хранимыми XSS, могут быть использованы для вертикального повышения привилегий или предоставить информацию для компрометации доменных записей AD.
Taras Tatarinov - Применение аппаратных закладок pwnie express на примере реа...



Taras Tatarinov - Применение аппаратных закладок pwnie express на примере реа...DefconRussia Кратко расскажу о концепции изолированных сетей и возможных путях их компрометации. Сделаю обзор аппаратной закладки pwnie express- для чего создавалось, какие возможности использования. Расскажу о том как pwnie express применялась в реальном проекте, какие были трудности и что из этого вышло.
Tomas Hlavacek - IP fragmentation attack on DNS
- 1. IP fragmentation attack on DNS Original work by Amir Herzberg & Haya Shulman Tomas Hlavacek • [email protected] • ZeroNights 0x03, 7.11.2013
- 2. IP fragmentation attack ● ● Amir Herzberg & Haya Shulman paper Fragmentation Considered Poisonous Two existing PoC: ● ● ● Tomáš Hlaváček & Ondřej Mikle, CZ.NIC Labs Brian Dickson, VeriSign Labs Relatively low technical complexity but a lot of preconditions
- 3. The new attack vector: Fragments ● Attack on UDP ● Exploits IP fragmentation & reassembly ● Off-path modification of packets ● Relies on 16-bit IP ID number in IP headers ● IP ID generation by counter helps ● Fights IP reassembly cache limits
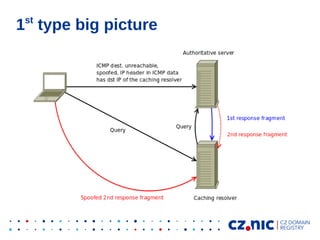
- 4. IP fragmentation attack on DNS ● ● ● ● Cache-poisoning attack on resolvers Reduces entropy from 32 bits (source port + DNS ID) to 16 bits (IP ID) … because UDP header and beginning of DNS data stays in the 1st fragment Attacker modifies the 2nd fragment (authority and additional sections)
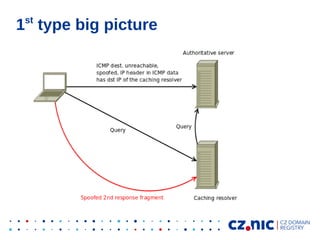
- 5. IP frag attack on DNS types ● Two types so far: ● ● 1) Convincing authoritative server to fragment replies for real domain by spoofed ICMPs 2) Registering specially forged zone which generates responses over 1500 B
- 6. st Triggering fragmentation – 1 type ● ● ● ● ICMP destination unreachable, frag. needed but DF bit set (type=3, code=4) Spoofing of ICMP (BCP38 is not a problem, firewalls are) Linux accepts signaled MTU into routing cache for 10 mins Linux minimum MTU = 552 B
- 7. st 1 type big picture
- 8. st 1 type big picture
- 9. st 1 type big picture
- 10. st 1 type big picture
- 11. st 1 type big picture
- 12. st 1 type big picture
- 13. st 1 type big picture
- 14. Effects of ICMP spoofing root@authoritative_server:/# ip route show cache ... 77.243.16.81 from 195.226.217.5 via 217.31.48.17 dev eth0 cache ipid 0xe8a1 Caching resolver IP 62.109.128.22 from 195.226.217.5 via 217.31.48.17 dev eth0 cache expires 576sec ipid 0x6ef3 mtu 552 rtt 4ms rttvar 4ms cwnd 10 63.249.32.21 from 195.226.217.5 via 217.31.48.17 dev eth0 cache ipid 0xa256
- 15. Response of the authoritative server ; EDNS: version: 0, flags: do; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaa aa.ad.example.cz. IN A ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: ad.example.cz. 360 IN NS ad-ns1.example.cz. ad.example.cz. 360 IN NS ad-ns2.example.cz. ad.example.cz. 360 IN NSEC ad-ns1.example.cz. NS ... ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ad-ns1.example.cz. 360 IN A 217.31.49.71 ad-ns1.example.cz. 360 IN RRSIG A 5 3 360 … ad-ns2.example.cz. 360 IN A ad-ns2.example.cz. 360 IN RRSIG A 5 3 360 ... 217.31.49.70 1st and 2nd fragment border
- 16. Response in the resolver log ; EDNS: version: 0, flags: do; udp: 4096 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.aaaaaaaaaaaa aa.ad.example.cz. IN A ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: ad.example.cz. 360 IN NS ad-ns1.example.cz. ad.example.cz. 360 IN NS ad-ns2.example.cz. ad.example.cz. 360 IN NSEC ad-ns1.example.cz. NS ... ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ad-ns1.example.cz. 360 IN A 217.31.49.71 ad-ns1.example.cz. 360 IN RRSIG A 5 3 360 … ad-ns2.example.cz. 360 IN A ad-ns2.example.cz. 360 IN RRSIG A 5 3 360 ... 1st and 2nd fragment border 62.109.128.20 UDP checksum fixup
- 17. Technical challenges in PoC ● ICMP packet forgery (easy) ● Selecting vulnerable zone (medium) ● Forging fragments, fixing UDP checksums (hard) ● Inserting into network (depends on local admin's paranoia) ● IP reassembly queue size = 64 @ Linux (needs further work) ● RR-set order randomization (annoyance) ● Label compression (not a problem) ● Fragment arrival order (potentially breaks the attack)
- 18. Forged packet acceptance ● ● Bailiwick rules Generally low level of trust in RR from additional section ● Gradually stronger rules in BIND since ~2003 ● Unknown (most likely strict) rules in Unbound
- 19. PoC & tricks ● This (1st type) attack worked in lab! ● IP ID known to attacker ● No firewalls, no conntrack ● Non-default IP reassembly queue settings ● 1 out of 3 trials succeeded (due to RR-set randomization and timing)
- 20. nd 2 type attack ● Forge zone with specific NS RRs: ● ● ● Add target NS (and glue) to poison Forge zone to produce long referral responses (N x ~250 B NS RR) Register the domain at the lowest possible level (2nd level zone)
- 21. Malicious zone in ccTLD ;poisonovacizona.cz. IN NS ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: poisonovacizona.cz. 18000 IN NS eaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. kaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. qaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. waaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. poisonovacizona.cz. ... poisonovacizona.cz. 18000 IN NS ns2.ignum.cz. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: ns2.ignum.cz. 18000 IN A 217.31.48.201 eaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. kaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. qaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. waaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. poisonovacizona.cz. 18000 IN ... ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 1949 A 217.31.48.1
- 22. Attack through the malicious zone ● The zone produces fragmented referral replies ● The zone is perfectly valid ● … even though it contains weird NS RR ● ● It contains target NS RR of a high-profile authoritative server Glue for the target NS is exposed in the 2 nd fragment
- 23. Defenses ● DNSSEC now! ● Workarounds ● ● 1st type: Ignore ICMP type=3, code=4 2nd type: limit response size & set EDNS0 buffer size to your MTU value (on both sides – authoritative as well as recursive)
- 24. Demo session ● Two computers – victim and attacker ● Real zone & name servers ● IP-ID known to attacker ● Minor hacks in iptables on victim to guarantee quick success
- 25. Demo session explained ● Generate spoofed ICMP ● Inject spoofed ICMP into network ● Query the server and capture response ● Modify DNS response ● Fixup response UDP checksum & change MAC ● Inject forged response & re-run the query
- 26. Thank You Tomas Hlavacek • [email protected] • ZeroNights 0x03, 7.11.2013





