Ad
Top 100 Java Interview Questions with Detailed Answers
- 1. Top 100 Java Interview Questions With Detailed Answers Are you a Java professional preparing for an interview? If yes, you’ve reached the right page. Yes! We’ve got you covered with Top 100 Java interview questions with detailed answers. As a Java professional, it is required to be familiar with various Java technologies while going for an interview. In this Java interview questions blog, we have compiled a definitive set of most commonly asked Java interview questions and answers for freshers as well as experienced professionals to help them crack the Java interview. Millions of developers and a huge number of devices worldwide are using Java. Java is everywhere!! We have divided this list of Java interview questions into 9 sections to make it easier for you to easily prepare each section. So, let’s start with the first section Core Java Interview Questions and Answers. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !1
- 2. Core Java Interview Questions In this section, we’ve not only covered the core Java interview questions for freshers but you will also find the core Java interview questions for experienced professionals. If you are an aspirant freshers, determined enough to become a Java professional or want to bring your Java development career one level up, these Core Java interview questions will help you reach the goal. If you have come across any other Java interview question, please post it in the comment section. 1. Can you explain class and object with a Java example? Answer – Class and Object both are the basis of Object Oriented Programming, and the concept of class and object revolves around the real-world entities. Class – A class in Java can be defined as a template or program construct that is used to create objects, and also its methods and data types. The declaration of a class may include various components such as class name, body, modifiers, interface (not mandatory), and superclass (not mandatory). Let’s consider an example of class i.e. Student Class Student { WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !2
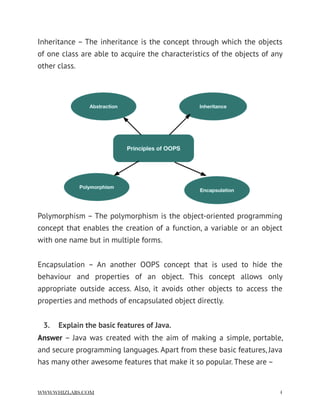
- 3. // instance variables declaration // methods definition } Object – An object is known as the basic unit of Object Oriented programming. It is a program construct that has state, behavior, and identity. Many objects are created in a Java program that interacts by invoking methods. Let’s consider the object of the Student class, that will be a specific student. Student amaira = new Student ( ); It means one of the students of Student class is referred by ‘amaira’ 2. What are the basic concepts/principles of OOPS? Answer – The Object-Oriented Programming System is based on the four basic principles, these are – Abstraction – The abstraction is the concept of representing essential features by hiding internal details or features. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !3
- 4. Inheritance – The inheritance is the concept through which the objects of one class are able to acquire the characteristics of the objects of any other class. Polymorphism – The polymorphism is the object-oriented programming concept that enables the creation of a function, a variable or an object with one name but in multiple forms. Encapsulation – An another OOPS concept that is used to hide the behaviour and properties of an object. This concept allows only appropriate outside access. Also, it avoids other objects to access the properties and methods of encapsulated object directly. 3. Explain the basic features of Java. Answer – Java was created with the aim of making a simple, portable, and secure programming languages. Apart from these basic features, Java has many other awesome features that make it so popular. These are – WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !4
- 5. • Java is a simple programming language • Java is distributed • Java is faster i.e. high-performance • Java is dynamic in nature • Java is multithreaded • Java is robust in nature • Java is highly portable language • Java is independent of platform • Java provides high-level security • Java is architecture neutral • Java is an object-oriented programming language 4. How is Java an object-oriented language? Answer – Being an object-oriented programming language is an important feature of Java. Let’s understand what makes it object-oriented. • Java follows Object Oriented programming model • Java is focused on the modular approach • Java follows the concept of abstraction • Java strictly follows object-oriented principle encapsulation • Java is based on the inheritance i.e. object-oriented concept • Java follows the object-oriented principle of polymorphism 5. How will you compile a Java program? Answer – In order to compile a Java program, follow the steps mentioned below – WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !5
- 6. 1. Save the source code file with .java extension. For example – student.java 2. Javac compiler will then create a bytecode version of the source file i.e. Student.class 3. The bytecode is the executable code and thus executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), also known as Java runtime systems. 6. What does “public static void main (String args [ ] )“ signify? Explain. Answer – • “public” is the access specifier • “static” is the access modifier that allows main ( ) method to be invoked without creating any instance of the class • “void” is the return type that specifies that the main ( ) method won’t return any value • main ( ) is the pre-defined method that is called in the beginning of a java program • “String args [ ]” are the arguments of the type String, when a Java program is run, the Java application accepts it. 7. What does “System.out.println ( )” specify? Answer – “System” is the pre-defined class in Java that gives access to the system “out” is the output stream WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !6
- 7. “println” is the method that is used to print line on the console i.e. println is the console output statement 8. What do you know about JVM? Answer – The full form of JVM is the Java Virtual Machine. Some important features of Java Virtual Machine are – • JVM is platform dependent • JVM is the runtime system of Java • JVM acts as an interpreter for the bytecode • JVM is responsible to maintain the security of the system • JVM is the what actually provides the environment for execution 9. Define garbage collection. Answer – In Java, garbage collection is used to free up the memory. It is done by clearing/deleting those objects which are no more required by any program. Two steps are involved in the process of garbage collection – Step 1: Garbage Object Collection This step involves the grouping and collection of all the objects that are not referenced by any program. The garbage collector uses various methods for the collection of garbage objects such as system.gc( ) or runtime.gc( ) Step 2: Run Finalize Method WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !7
- 8. After the collection of objects, the next step is to free the memory space by deleting the objects that has been gathered by the garbage collector. Then, Finalize method is executed in order to delete all the objects that are dynamically created. 10. Define polymorphism. Answer – The meaning of word polymorphism is – one name and many forms. Polymorphism refers to the characteristic of methods to act differently on the basis of the calling object. Followings are the key features of polymorphism – • It allows the use of one interface to implement various methods • It supports method overloading i.e. allows the use of multiple methods with same name but different arguments. • It supports method overriding I.e. allows the use of multiple methods with same name, same argument, and return type. 11. What do you know about constructor? Answer – A constructor can be defined as a block of code very similar to the method that is called on the creation of an instant of the object. The features of the constructor are as follows – • The name of the constructor is same as that of the name of the class. • It doesn’t have any return type. • It is not considered as the class member like other methods. • It is invoked automatically when a new instance of an object is created. • It can not be inherited like other methods of the class. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !8
- 9. • It is not compulsory to create a constructor for the class. Advanced Java Interview Questions In the second section, we cover the advanced Java interview questions and answers for freshers as well as experienced professionals. If you are looking for some advanced Java interview questions to crack the Java interview and get a better job, these advanced Java interview questions for experienced are only for you. If you have any other Java interview questions for freshers or experienced professionals, please post in the comment section. 12. What are the different Access Specifiers in Java? Answer – Access Specifiers are used to setting the access level of the classes and the methods, fields, and constructors in the classes. There are four different types of Access Specifiers in Java – • Public – The classes, fields, and methods defined by public access specifier, are accessible by every class. • Private – The fields and methods defined by private access specifier are accessible within the same class to which those fields and methods belong. The private fields and methods can’t even be inherited by any subclasses. • Protected – The fields and methods defined by protected access specifier are accessible only in the class to which those fields and methods belong. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !9
- 10. • Default – Default means no specifier. When the methods, fields, and classes are not defined by any access specifier, then those methods, fields, and classes are accessible in the package to which those methods, fields, and classes belong. 13.. What are the different method signatures in Java? Answer – A method inside a class is the sequence of statement to perform a specific task. Method Signatures: A number of parameters such as method name, return type, access specifiers etc. constitute the method signature. The various elements of the method signature are – Method name – Method name is the mandatory signature, such as display ( ) Return type – Return type of the method is also the mandatory method signature, it can be void, int, float, string etc. Access Modifier – It is the method signature that is not compulsory to be defined. It can be synchronized, static, etc. Access Specifier – Not mandatory method signature; access specifier can be private, public, protected etc. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !10
- 11. Parameters – A method may either have or not parameters; these are given in parenthesis such as (String name, int number); A few examples of methods with the signatures are – public static void getFinalName (String Name) { } Void displaySum ( ) { } public synchronized int getSalary (double grossSalary) { } 14. What is a thread? What do you know about its lifecycle? Answer – A thread is an execution in the program which follows the single flow of control. The life cycle of thread comprises of the five states, that are being mentioned below – Newborn state – When an instance of the thread is created, the thread is considered to be in this newborn state. In this state, the thread is not considered alive, and the state exists before the start ( ) method is invoked. Runnable state – The life of the thread starts from this state i.e. runnable state. When the start ( ) function is invoked, the thread enters in the runnable state. Running state – When the thread enters the runnable state, it is ready to run and start the program execution. When the thread is actually in the execution phase, it is said to be in the running state. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !11
- 12. Blocked state – During the running state, the thread may have to wait for the resources that are being used by any another thread. During the waiting phase, the thread is known to be in the blocked state. Dead state – When the execution of the program is done and the run ( ) method is completed, the thread is said to be in the dead state. After this state, a thread cannot be in execute or run again. 15. What are the Applets? Answer – Applets are the small Java programs that can be sent from one computer to the other computer over the network with the use of Applet Viewer that supports Java. Applets have following properties – WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !12
- 13. • Being a Java program, an applet can be run in a web browser • It has the set of whole Java API • Applets are known to be the fully functional Java application • Applets offer a high-level security, called sandbox security • Applets follow the security ruled of the web browser 16. Mention the situations when you will prefer to use interfaces and when abstract classes. Answer – It depends when a Java programmer will use interfaces and when abstract class. Let’s discuss both one by one – Abstract Classes are used – • When you need to make multiple implementations of the same kind with common behaviour • In order to create inheritance hierarchies (already planned) • When you have to leave the implementation task on the inheriting subclass by enabling the generalised form of abstraction Interface is used – • When you need multiple classes to use some methods that are not to be included in the class • When multiple implementations share the signatures of method or program design is changed frequently 17. How are the source code files named in Java? WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !13
- 14. Answer – The name of the Java source code file is same as that of the public class or interface, defined by programmer during writing the program code. It is restricted that source code won’t contain more than one public class or interface. While naming a Java source code file, there may be occurrence of two different cases – Case 1: When there is no public class or interface in the source code file – Although it is mandatory that source code file will contain only one public class or interface but it may not contain any public class or interface. In this case, the java source code file will be named something else except its interfaces and classes. Case 2: When there is one public class or interface in the source code file – It is the case when one public class or inheritance occur in the source code file. In this case, the name of the java source code file will be same as that of the public class or interface that has been defined in the program code. 18. What do you mean by the nested class? Answer – In general, the meaning of nested means one in another. In Java, a nested class means a class within another class i.e. the class that is declared inside an another class is the nested class. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !14
- 15. Some times, the nested class is also known as the inner class. The Syntax is – class Parent_class { //code class Nested_class { //code } } Advantages of nested class in Java • Permitted to access all the methods and data members (including private) of the outer class • As it groups interfaces and classes in one place, thus develops easily maintainable and readable code • Less code is required to be written WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !15
- 16. 19. Does Java support networking? Answer – Yes, Java supports networking. There are two types of classes in Java to support networking i.e. low-level and high-level. These classes control the network applications programming. As Java is platform independent in nature, Java networking is also platform independent. The classes to support Java networking are – • Low-level classes – These classes support socket programming like DataramSocket, Socket, and ServerSocket classes. • High-level classes – These classes provide support for URLEncoder, web programming URL, and URL connection. 20. Is there any alternative to inheritance? Explain. Answer – Yes, there is an alternative to inheritance in Java; Delegation. Followings are the important points about delegation – • Delegation specifies that there exists an instance of any class that works as the instance variable and used to send messages to that instance of the class. • Delegation is comparatively safer than that of the inheritance as the programmer doesn’t need to think about the forwarded message. As the instance belongs to the existing known class and doesn’t make you accept all the methods of superclass, only the selected and required methods can be provided. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !16
- 17. • Due to delegation, the programmer have to write more code. Also, it is harder to reuse the delegation unlike inheritance as it is not a subclass. 21. What is the difference between JDK, JVM, and JRE? Answer – The difference between JDK, JVM, and JRE is as follows: JDK – JDK stands for Java Development Kit. JDK is the most commonly used software development environment for Java programmers. It is meant for the development of Java applications and applets. It consists of Java Runtime Environment, a compiler (javac), an interpreter (Java), an archiver (jar), a generator for documentation (Javadoc), and some other tools that are required in the development of Java applications. JVM – JVM is an acronym for JavaVirtual Machine. It acts as an interpreter for the byte code. It is the real runtime system of Java and provides an environment for the execution of Java programs and applications. Most important, Java Virtual Machine is independent of the platform. JRE – JRE is the Java Runtime Environment, also known as Java RTE. It is the Java Virtual Machine implementation that is responsible for the execution of Java applications. It provides everything that is required for the execution of a Java application. It comprises of the Java Virtual Machine, supporting files, and core classes. 22. What is the difference between WAR and JAR files? WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !17
- 18. Answer –The difference between WAR and JAR files is being described in the following table – 23. What exactly happens when an object is created in Java? Answer – When an object is created in Java, a number of things happen in a specific sequence to ensure whether the object has been created properly, these are – 1. Memory Allocation – The memory is allocated for the storage of all the instance variables and the other data of object and its superclasses that are related to implementation. 2. Initialization – After memory allocation, the objects are declared and initialized with their default values. 3. Constructor – Next, the constructors call other constructors for its superclasses. java.lang.Object is the base class for all the objects in Java, so this process is repeated continuously until the constructor for java.lang.Object is called. WAR Files JAR Files 1. The term WAR files stand for the Web Archive Files. 1. The term JAR files stand for the Java Archive Files. 2. WAR files are responsible for the storage of Java classes, XML, and JavaServer pages. 2. Java files allow the aggregation and storage of multiple Java files into a single file. 3. WAR files are mainly used for the purpose of web applications. 3. JAR files are mainly used to handle Java classes in a library. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !18
- 19. 4. Execution – In this step, the initialization of all the instance variable takes place and the initialisation blocks are executed. After that the execution of the body of the constructor takes place. JDBC Java Interview Questions In the third section, here we cover the JDBC Java interview questions and answers. Go through these basic and advanced JDBC Java interview questions and broaden your knowledge to crack the interview. If you have any other JDBC Java interview questions, please post in the comment section. 24. What do you know about JDBC? JDBC is a Java API that is responsible for the connection and execution of Java query with the database. JDBC API uses JDBC drivers to create a connection between database and the query. JDBC API can be used to access data from any relational database. 25. What are the steps to connect a Java application with the database using JDBC? Answer – Followings are the steps that will connect a Java application with the database using JDBC: Step 1: Registration of the driver class using forName( ) method of the Class class. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !19
- 20. Step 2: Creation of connection object using getConnection( ) method of the DriverManager class. Step 3: Creation of statement object using createStatement( ) method. Of the connection interface. Step 4: Execution of the query using executeQuery( ) method of the Statement interface. Step 5: Closure of the connection object using close( ) method of the Connection interface. 26. Name different types of JDBC statements in Java. Answer – Following are the 3 different types of JDBC statements in Java: 1. Statement 2. CallableStatement 3. PreparedStatement 27. How will you store an image in database? Answer – In Java, the images can be stored in a database with the setBinaryStream( ) method of the Prepared Statement interface. This method will set the Binary information into the parameterIndex. The syntax is – Public void setBinaryStream(Int paramIndex,InputStream stream) WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !20
- 21. Throws SQLException 28. How are the stored functions and procedures executed in Java? Answer – In Java, the stored functions and procedures are executed with the help of CallableStatement interface. 29. Name the various components of JDBC API. There are various components of JDBC API are classes and interfaces that are stored in java.sql package, these are – Classes – Blob, DriveManager, Types, Clob, SQLException etc. Interfaces – Statement, Connection, ResultSet, PreparedStatement, DatabaseMetaData, ResultSetMetaData, CallableStatement etc. 30. What is the batch processing technique in JDBC? Answer – In Java, the batch processing technique is used to perform the execution of multiple queries at the same time. During batch processing, the grouping of related SQL statements is done into a batch and then performs their execution instead of performing the execution of a single query. In this way, the batch processing results in faster execution of queries and improved performance. 31. What do you know about Connection interface in JDBC API? Answer – The Connection interface is used for the maintenance of a session with the database. It can also be used for the management of transactions. It contains various factory methods that returns the WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !21
- 22. instance of CallableStatement, Statement, PreparedStatement, and DatabaseMetaData. 32. Differentiate statements execute, executeQuery, and executeUpdate. Answer – The difference between execute, executeQuery, and executeUpdate is as follows – execute (String query) – The execute statement is used to perform the execution of SQL query. When the result is an ResultSet, it returns TRUE, e.g. returns TRUE value for Update or Insert queries. getResultSet( ) method is used to get the ResultSet and getUpdateCount( ) is method is used to get the value of update count. executeQuery(String query) – The executeQuery statement is used for the execution of Select queries and to return the ResultSet. The value of ResultSet is never set to null even when no matching record is found for the query. executeQuery method should be used for the execution of Select queries as it cannot be used for insert and update queries. It throws java.sql.SQLException if someone executes update/insert query with the message that executeQuery method cannot be used for update/insert. executeUpdate (String query) – The execute update statement is used for the execution of DML (i.e. Insert, Update, and Delete) statements and also for DDL statements those don’t return any value. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !22
- 23. For DML statements the return value is int and equals to the DML statements row count. While in case of DDL statements, the return value is 0. So, the execute( ) method is used only if you don’t know the type of query statement else the use of executeQuery( ) and executeUpdate( ) methods is preferred. 33. Name the interface that performs transaction management in JDBC. Answer – The Connection interface performs the transaction management in JDBC. It provides various methods such as rollback( ), commit( ) etc. that helps in transaction management in JDBC. String Handling Java Interview Questions The fourth section covers the String handling Java interview questions and answers. Preparing through these String Java interview questions will be highly helpful to crack the Java interview. If you have any other String-based Java interview questions, please post in the comment section, we’ll cover them up. 34. Why are the string objects immutable in Java? Answer – In general, the meaning of term immutable is unchangeable i.e. that cannot be changed. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !23
- 24. String objects are immutable in Java which means once the string objects are created, it is not possible to change its value. String objects are immutable as Java is based on the concept of string literal. To understand this, consider that 5 references are there, all of which refers to the one object called “naira”. In this case, if the value of the object is changed by one reference variable, it will also affect the value of the other reference variables. This is the reason why string objects are immutable in Java. 35. What are the different ways to create String objects in Java? Answer – There are two ways to create String objects in Java: • By String Literal String object using String literal is created by using double quotes. For example – String s=“hello”; Every time, when you create a string literal, JVM checks string constant pool to find if the string already exists. If the string already exists, it will return a reference to the pooled instance. If the string is not already there in the pool, JVM creates the new string and store it in the pool. Now consider, String s1=“hey”; WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !24
- 25. String s2=“hey”; Here, the second statement will not create the new instance as the first statement has already created that. • By New Keyword This is an another method to create String objects in Java using new keyword. For example – String s=new String(“Niharika”); This statement will create two objects and one reference variable. In this case, JVM creates a new string object in a heap memory and the literal “Niharika” will be stored in the constant pool of the string. The variable s refers to the String object in the heap. 36. Differentiate StringBuilder and StringBuffer in Java. Answer – The basic difference between StringBuilder and StringBuffer is given as – StringBuffer – It is a user mutable string i.e. its value can be changed any time after it has been created. The objects that are created using StringBuffer, are stored in the heap and StringBuffer is thread safe. StringBuilder – It is also a user mutable string i.e. its value can be changed any time after it has been created. StringBuilder also stores the WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !25
- 26. objects in heap like StringBuffer but the main difference is that StringBuilder is not thread safe. 37. How will you create an immutable class in Java? Answer – There are a number of immutable classes in Java such as Boolean, Integer, Float, Long, Double, Short, Byte, String etc. To sum up, String class and all the wrapper classes are immutable. An immutable Index StringBuffer StringBuilder Modifiable Yes, it can be modified or changed i.e. mutable No, it can’t be modified or changed i.e. immutable Storage Area Objects created through StringBuffer are stored in heap. The objects created through StringBuilder are stored in heap. Thread Safe Yes, it is thread safe. No, it is not thread safe. Synchroniz ation All the methods in StringBuffer are synchronized Methods are not synchronized in StringBuilder Method Access A method can access only one thread at a time A method can access multiple threads simultaneously at a time Performan ce StringBuffer is slower than StringBuilder even while calling the same methods of a class StringBuilder is faster when it comes to calling the same methods of a class Conversion StringBuffer to String conversion can be done by using toString ( ) method, + “” or String.valueOf ( ) method StringBuilder to String conversion can be done by using toString ( ) method. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !26
- 27. class can also be created by creating a final class containing final data members. A class is said to be final when • The class itself is final i.e. it is not possible to create its subclasses. • It has a final instance variable i.e. it is not possible to change its value after the creation of an object. • There are no setter methods i.e. there will not be any option to change the value of instance variable. For example – public final class Student { Final String idNumber; public Employee(String idNumber) { this.idNumber = idNumber; } public String getidNumber( ) WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !27
- 28. { return idNumber; } } This is a final class with name Student that contains one parameterised constructor, one final data member, and a getter method. 38. Why does the Java use the concept of string literal? Answer – Java uses the concept of string literal as it makes Java more memory efficient. It is because the concept of string literal doesn’t create a new String object if that is already existing in the String constant pool. It avoids the redundant storage and thus saves memory. 39. How many String objects the following code will create? Explain. • String s1 = “Hello”; • String s2 = “Hello”; • String s3 = “Hello”; • String s4 = “Hello”; • String s5 = “Hello”; Answer – The given code will create only one String object. Explanation – Only the first statement will create the String object “Hello”. For the next statements, as the string is already there in the WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !28
- 29. constant pool, JVM will not create any instance instead will return a reference to the pooled instance. 40. What is the main difference between string and stringbuffer object? Answer – The main difference between string and stringbuffer object can be explained in terms of the mutability. String object is immutable while StringBuffer object is mutable. 41. What is the use of toString() method in Java? Answer – The toString() method returns the object representation. Whenever an object is printed, Java complier will invoke the toString() method for that object. This overriding of toString() method will return the desired output on the basis of your implementation. Exception Handling Java Interview Questions The fifth section covers the Exception handling Java interview questions and answers. Preparing through these Exception Handling Java interview questions will be highly helpful to crack the Java interview. If you have any other Exception-based Java interview questions, please post in the comment section, we’ll cover them up. 42. What is exception handling? WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !29
- 30. Answer – Exception handling can be defined as the process of handling runtime errors such as IO, Remote, ClassNotFound, Remote etc. The exceptions may effect the normal execution of application, that’s why the exception handling is used. Importance of exception handling Exception handling is very important while creating Java programs and applications. It is important as it helps to maintain the normal flow of the application avoiding any disruption (i.e. runtime error). 43. What is an exception? How is it different from error? Answer – In general terms, exception is something that creates abnormal condition. In Java, the runtime errors are known as exceptions. These are the events or conditions, thrown at the runtime and affects the normal flow of a program. Difference between Exception and Error – The exceptions are the recoverable conditions that thrown at runtime while errors are the irrecoverable conditions that are also thrown at runtime. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !30
- 31. The example of exception is FilenotFoundException that will be thrown when the particular file is not found or that does not exist. The example of error is OutofMemory. 44. Name the keywords that are used to handle exceptions in Java. Answer – The Java exceptions are handled by the use of five keywords: throw throws finally try catch 45. Differentiate checked exception and unchecked exception. Answer – The differences between checked exception and unchecked exception are as follows: Checked Exception Unchecked Exception The checked exceptions are those which are checked at the compile time. The unchecked exceptions are those which are not checked at the compile time. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !31
- 32. 46. Explain the hierarchy of exception in Java. Answer – The hierarchy of exception in Java can be explained by the following diagram – The parent class of all the Exception and Error classes is the Throwable class. The exceptions are classified into two types – Checked Exceptions and Unchecked Exceptions. Also, the errors are of two types – Assertion Errors and Virtual Machine Errors. 47. Explain some of the methods of Exception class in Java. Answer – The specific methods used to handle exception handling are not present in the Exception class andlasses but all the exception These exceptions are thrown by the classes that extend Throwable class except RuntimeException. These exceptions are thrown by the classes that extend RuntimeException. The examples are SQLException, IOException etc. The examples are NullPointerException, Arithmetic Exception etc. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !32
- 33. handler methods are defined in the parent class i.e. Throwable. Some of the methods that are used for exception handling are: String toString( ) – The information about Throwable is returned by this method in String format. The output String of this method contains a localized message along with the name of the Throwable class. String getMessage( ) – The result of this method is the message String of Throwable. Synchronized Throwable getCause( )- The output of this method specifies the cause null id or the exception. String getLocalizedMessage( ) – This method is overriden by the subclasses to provide specific localized message to the calling program. In Throwable class, this method is implemented just by using getMessage( ) method which returns the exception message. void printStackTrace( ) – This method is used to print the information about stack trace. This is an overloaded method. In order to write stack trace information to the stream or file, we can pass PrintWriter or PrintStream as argument of this method. 48. Write some statements the will create custom Exceptions. Answer – The custom exceptions can be created by extending the Exception class or its subclasses. Example 1: WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !33
- 34. class NewException extends ArithmeticException{ } //this will create Unchecked Exception Example 2: class NewException extends Exception { } //this will create Checked Exception Example 3: Class NewException extends IOException { } //this will create Checked Exception 49. Is it possible to use try block without catch block? WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !34
- 35. Answer – Yes, it is possible to use try block without catch block. It is not always required that the try block should be followed by a catch block. Try block can also be followed by a finally block. And the exceptions that are to be thrown should be declared in the throws clause of the method. 50. In which case the finally block will not be executed? Answer – In case of the program exit, the finally block will not be executed. So, when the program exits either by causing a serious error that may cause the abortion of the process or by calling System.exit() method, it will stop the finally block from execution. 51. Differentiate throw and throws. Answer – The main differences between throw and throws are as follows – Throw Throws 1. Throw is used to trigger the expectation. 1. Throws is used for the declaration of an expectation. 2. Throw is used inside the method body 2. Throws is used in the method signature. 3. Throw is followed by the instance of exception class, such as Throw new ArithmeticException (“Arithmetic Exception”); 3. Throws is followed by the name of exception class, such as Throws ArithmeticException; WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !35
- 36. 52. How will you differentiate final, finalize, and finally? Answer – The difference between final, finalize, and finally is as follows – Final – In Java, Final is a keyword that is used to define constants. Once a class is declared as final, it can not be divided into subclasses. Once a field is marked as final, its value becomes constant that cannot be reset. When a method is declared as final, subclasses cannot override that method. Finalize ( ) – Finalize method in Java is associated with the garbage collection. The finalize method is automatically invoked before the garbage value collection. Finally – Finally block in Java is used with the try and catch blocks (except when try block uses System.exit(0) call) The finally block is meant for the unexpected error. It executes the last clause mentioned in the try catch block. 4. Using throw, one exception can be handled at a time. 4. Using throws, multiple exceptions can be declared at the same time. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !36
- 37. The finally block contains a set of statements thats execution does not depend on the exception caught by the previous catch block. Servlet Java Interview Questions Here in sixth section, we cover the list of Servlet Java interview questions for the freshers and as well as professionals. If there is any Servlet-based Java interview question, you want to find the answer, post it in the comment section and our expert team will respond with the detailed answer. 53. What do you know about Servlet? Answer – Servlet in Java is server side technology that provides support for the data persistence and dynamic response and thus enhance the web servers capabilities. Some important points about Java Servlets are – • There are two types of packages i.e. javax.servlet and java.servlet.http that provides classes and interfaces to write own servlets. • javax.servlet.Servlet interface is responsible to define the methods for servlet lifecycle, so it is mandatory for all the servlets to implement java.servlet.Servlet interface. • Java Servlet API provides GenericServlet class that can be extended during the implementation of any generic service. • The HttpServlet class contains methods to handle HTTP specific services i.e. doPost( ) and doGet( ). WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !37
- 38. • As the http protocols are mainly used to access the web applications, HttpServlet class is extended. 54. What are the different stages in a servlet lifecycle? Answer – The lifecycle of a servlet comprises of the 5 stages: Loading – The servlet class is loaded Instant Creation – The servlet instance is created Initialization – Init method is invoked and the servlet becomes ready Service Request – Service method is invoked to perform any task Destruction – invocation of destroy method and the destruction of servlet WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !38
- 39. 55. Explain the working of cookies in Servlets. Answer – Cookies are the text that are sent to the client by server, and is saved at client side. Servlet APIs contain javax.servlet.http.Cookie class which implements Cloneable and Serializable interfaces an thus provides cookies support. HttpServletRequest getCookies( ) method is used to get the array of cookies from the request. HttpServletResponse addCookie (Cookie c) method is used to attach the cookie in response header. As there is no need to add cookie to the request, no method is there to add or set cookie to the request. Similarly, there is no getter method for the cookies in servlet. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !39
- 40. 56. What are the various methods to manage session in Servlets? Answer – Session is a state of conversation between the server and the client. It may consist of a number of requests and responses between the server and the client. Session is maintained through session id (that is the unique info about the session). The session id is passed between client and server during every request and response. There are different methods for the management of sessions in servlets – Cookies URL Rewriting HTML Hidden Field User Authentication Session Management API 57. Differentiate between Get and Post methods. Answer – The difference between Get and Post methods is as follows – Get Method Post Method Get method is used to request data from a particular resource i.e. server Post method is used to return the requested data to a particular resource i.e. client WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !40
- 41. 58. Differentiate ServletConfig and ServletContext. Answer – In servlet, the difference between ServletConfig and ServletContext is as follows – The request data is sent in the header, so only the limited data can be sent The response data is sent in the body, so large amount of data can be sent doGet method of servlet handles the Get method doPost method of servlet handles the Post method Get method is no secure as the data is visible in the URL Post method is secured as the data is not visible in the URL It is possible to bookmark Get method It is not possible to bookmark Get method Get method is idempotent i.e. it provides same result on the multiple executions Post method is non-idempotent i.e. it provides different results on the multiple executions The Get method is most commonly used and is more efficient as compared to the Post method The Post method is less used and is even less efficient as compared to the Get method ServletConfig ServletContext It denotes single servlet It denotes the complete set of running web application, and is same for all the servlets The scope of ServletConfig is servlet wide as it is defined within the servlet section of the web.xml file The scope of ServletContext is application wide as it is define outside the servlet section of the web.xml file getServletConfig( ) method provides the config object getServletContext( ) provides the context object WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !41
- 42. 59. What do you understand by servlet collaboration? Answer – The communication between two servlets is known as the servlet collaboration. The different methods through which servlets communicate like sendRedirect( ) method, RequestDispacher interface and others. 60. How will you differentiate sendRedirect( ) method and forward( ) method? Answer – The difference between sendRedirect( ) and forward( ) method is as follows – 61. What is the meaning of session tracking? Answer – Session indicates a specific time interval in servlet while session tracking is a method to manage or maintain the user state, also known as session management in servlet. It belongs to a specific servlet so acts as a local parameter It belongs to the whole web application so acts as a global parameter sendRedirect( ) method forward( ) method sendRedirect( ) method uses browser URL bar so, always sends a new request forward( ) method sends the existing request from a servlet to the resource of another servlet The scope of sendRedirect( ) method is not only within the server but also outside of the server The scope of forward( ) method id within the server I.e. it can’t work outside the server sendRedirect( ) method works at the client side forward( ) method works at the server side WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !42
- 43. As the http protocol is stateless due to which every request generated by a user is consider it is required to maintain the state using any of the session tracking techniques. The session tracking is done to recognize a particular user. 62. Explain cookies in servlet. Answer – Cookie is defined as a small piece of information that continues to remain between the requests of multiple clients. Cookie has a name, value, and some other attributes version number, domains and path qualifiers, comment, and a maximum age. A cookie can be persistent, that remains valid for multiple sessions or non-persistent that remains valid only for one session. Hibernate Java Interview Questions Here in seventh section, we’ll cover the list of Hibernate Java interview questions. If there are any Hibernate Java interview questions, you want to find the answer, just post it in the comment section and our expert team will respond with the detailed answer. 63. What do you know about hibernate framework? Answer – Hibernate is a lightweight, open source, ORM tool. The hibernate framework is meant to simplify the Java application development in order to interact with the database. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !43
- 44. The hibernate framework has many advantages, these are: • Hibernate framework is lightweight and open source under LGPL licence. • Hibernate framework uses Hibernate Query Language (HQL) that is independent of database. • Due to the use of cache, the performance of hibernate framework is very fast. • It make complex joins simpler so it is easy to retrieve data from multiple tables. • Hibernate framework facilitates the automatic creation of tables of the database. • With the Query cache supporting feature, hibernate framework provides status of database and statistics of query. 64. Define ORM. Answer – Object Relation Mapping (ORM) is a technique of programming used for the mapping of data with the data stored in the database. An ORM tools makes the process of data access, data creation, and data manipulation simpler. The Object Relation Mapping tool uses JDBC APIs to create an interaction with the database. 65. What do you know about Hibernate Query Language (HQL)? WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !44
- 45. Answer – Hibernate Query Language is an object oriented query language that is much similar to the Structured Query Language. Hibernate Query Language (HQL) has some advantages over Structured Query Language (SQL), these are – • HQL is independent of database; no need to change the HQL query if database is changed • The previous knowledge or experience with SQL is not required to work with HQL • It is easier and simpler to write query with HQL as compared to SQL 66. Name the core interfaces of Hibernate. Answer – There are six core interfaces in the hibernate framework, these are: • Session • SessionFactory • Configuration • Criteria • Query • Transaction 67. Differentiate first level cache from second level cache. Answer – The first level cache is different form second level cache in hibernate. The differences between the two are: WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !45
- 46. 68. How many states of object are there in hibernate? Answer – There are 3 states of object in hibernate: 1. Transient – When the object is created, it is said to be in the transient state. In the transient state, the object does not have any primary key. Also, the session is not created for the object in this state. 2. Persistent – When the session is created for the object and is open, the object is said to be in persistent state. This state starts when the instance of the object is saved in the database or retrieved from the database. 3. Detached – When the session of the object is closed, the object is said to be in detached state. The object can also reach to the persistent state again after this state if you invoke update() or lock() method. 69. Name the different types of association mapping in hibernate. Answer – There are four different types of association mapping in hibernate. • One to One First Level Cache Second Level Cache The first level cache is associated with the Session interface of hibernate. The second level cache is associated with the SessionFactory interface of hibernate. The first level cache is by default enabled. The second level cache is not by default enabled. It is required to enable it manually. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !46
- 47. • Many to One • One to Many • Many to Many 70. Differentiate persist() and save() method of session of the hibernate. Answer – Following is the difference between persist() and save() method of session of the hibernate. 71. Name the different strategies for inheritance mapping in hibernate. Answer – There are three different types of strategies for inheritance mapping in hibernate: • Table per subclass; the tables are created according to the class but related to the foreign key • Table per hierarchy; only one table is created to map the whole hierarchy • Table per concrete class; tables are created according to the class. persist( ) save( ) The persist( ) method does not return anything. The save( ) method returns the instance identifier. The syntax of persist( ) method is – public void persist(Object a) The syntax of save( ) method is – public Serializable save(Object a) It’s return type if void. It’s return type is Serializable. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !47
- 48. 72. How will you make a class immutable in hibernate? Answer - By default, a class is set to be mutable with the true value of mutable i.e. mutable = “true”. In order to make a class immutable, you will require to mark the value of mutable false i.e. mutable = “false”. 73. Differentiate merge() and update() method. Answer – The difference between merge() and update() method is as follows: 74. What do you know about lazy loading in hibernate? Answer – Lazy loading is a technique that is used to improve the performance in hibernate. It results in faster performance by loading the child object on the basis of demand. Lazy loading is by default enabled in Hibernate 3 and later versions. It means you don’t require to set the value of lazy to true I.e. lazy = “true”. It specifies that you won’t require to load child objects if the parent object has already been loaded. merge() method update() method The merge method is used to combine something. The update method is used to edit something. The merge method is used when the state of the session is not known. The update method is used when the session is not in the persistent state. It is used to make the modifications at any time. It is only used inside the session. It doesn’t throw an error when session is in detached state. It throws an error when session is in detached state. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !48
- 49. Spring Java Interview Questions In the eighth section, here we cover the Spring Java interview questions and answers. Go through these basic and advanced Spring framework Java interview questions and broaden your knowledge to crack the interview. If you have any other Spring-based Java interview questions, please post in the comment section. 75. Define Spring and explain the advantages of spring framework. Answer – Spring is a lightweight, integrated, and loosely coupled framework that is used for the development of the enterprise applications with Java programming. Sometimes the Spring framework is considered to be the framework of frameworks as it supports many frameworks such as Hibernate, Struts, EJB, Tapestry, JSF etc. Followings are the advantages of spring framework – • Lightweight • Integrated • Loose Coupling • Predefined Templates • Easy Testing • Faster Development • Declarative Support • Powerful Abstraction 76. What are the various Spring Modules? WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !49
- 50. Answer – The spring framework is consisted of various modules which are grouped as Test, Spring Core Container, Instrumentation, Aspects, AOP, Web (MVC/Remoting), and Data Access/Integration. Let’s know more about these modules of spring framework – Test – The test layer is responsible to provide the testing support with the testNG and JUnit modules. Core Container – The spring core container is composed of three modules, these are – Context – It supports EJB, Internationalization, Basic Remoting, and JMS. Core and Beans – It provides Dependency Injection and IOC features. Expression Language – It provides support to accessing indexers and collections, getting and setting property values, arithmetic and logical operators, method invocation, named variables, object retrieval by name and others. Instrumentation, Aspects, and AOP – The instrumentation module is meant to support to the class loader and class instrumentation implementations. The aspects module is made to support the integration by means of the AspectJ. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !50
- 51. The AOP module is known to provide support to the implementation of the aspect-oriented programming to make use of pointcuts, advices etc. for the decoupling of the code. Web (MVC/Remoting) – This layer of spring framework is composed of Web, Web-Struts, Web-Servlet, and Web-Portlet modules which are used to provide support for the development of web applications in Java. Data Access/ Integration – This group in spring framework includes OXM, JDBC, JMS, ORM, and Transaction modules which are made to provide support for the database interaction. 77. Explain Autowiring in Spring. Answer – Autowiring is a programming technique that helps programmer to automatically inject the bean without writing any injection logic explicitly. The code for the bean injection (with the help of dependency injection) is – <bean id= “emp” class= “com.javapoint.Student” autowire= byFName” /> There are different autowiring modes in spring, these are – Name of Autowiring Module Details constructor It performs the injection of bean using constructor. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !51
- 52. 78. Explain various bean scopes in Spring. Answer – The spring framework contains 5 bean scopes that are explained below: 79. Mention some Spring annotations you have used. Answer – Here are the spring annotations that I’ve used in my Java projects: @ResponseBody – to send Object as response. It was mainly used for sending JSON and XML data as response. byName It performs the injection of bean on the basis of the name of the property by using setter method. byType It performs the injection of the bean on the basis of the type of the property by using setter method. no This mode specifies that the autowiring is disable. It is the default mode of the autowiring. Name of the Scope Description session The instance of the bean is created as per the HTTP session. request The instance of the bean is created as per the HTTP request. prototype The instance of the bean is created at the time when it is requested. globalses sion The instance of the bean is created as per the global session of HTTP. singleton The instance of the bean is created only once and is returned by the IOC container. Singleton is the default spring scope. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !52
- 53. @Controller – used for controller classes @PathVariable – to map dynamic values from URI to handler method arguments @RequestMapping – to configure URI mapping in controller handler methods @Qualifier – for avoiding confusion among multiple instances of bean type @Autowired – to autowire dependencies in beans @ Scope – for the configuration of the scope of bean in spring @Service – used for service classes @ComponentScan, @Configuration, and @Bean – used for the configurations based on Java @Aspect, @After, @Before, PointCut, and @Around – for the configuration of advices and aspects 80. Have you ever integrated Spring framework with Hibernate framework? Explain. Answer – Yes, I have integrated Spring framework with Hibernate framework by using Spring ORM module. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !53
- 54. While using Hibernate 3+ where current session is provided by SessionFactory, HibernateDaoSupport and usingHibernateTemplate classes should be avoided. Instead, DAO pattern was used along with dependency injection for the purpose of integration. Spring ORM was used over Hibernate boiler-plate code in order to implement transaction management 81. What do you know about IOC? Explain in detail. Answer – IOC is an abbreviation for Inversion of Control, it is a design pattern that is used to provide loose coupling. it is a container that is responsible for instantiation, configuration, and assembly of the objects. It retrieves information from XML files and then works. It is used for the removal of the dependencies from the program. IOC container is responsible to perform the following functions – For the instantiation of the application class For the configuration of the object In order to assemble the object’s dependencies Sample IOC Code: public class Student{ WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !54
- 55. Name name; Student(Name name){ This.address=address; } } 82. Explain how is exception handling performed in Spring framework. Answer – There are different ways to handle exceptions in spring framework: Global Exception Handler – The exceptions can be handled by defining global exception handler. The global exception handler can be defined by using @ControllerAdvice annotation with the class. Controller based – In this, the exception handler method is defined in the controller classes. The annotation @ExceptionHandler is used for controller based exception handling. Implementation of HandlerExceptionResolver – In static pages, it is required to handle the generic exceptions. For this, the HandlerExceptionResolver interface in Spring framework is implemented for creating global exception handler. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !55
- 56. 83. State the advantages of JdbcTemplate in Spring. Answer – Followings are the advantages of JdbcTemplate in Spring: • JdbcTemplate provides various methods using those you can directly write the queries. In this way, JdbcTemplate saves the a lot of time as well as work. • When you use JdbcTemplate class, you don’t require to create statement, connection, close connection, start transaction, and commit transaction for the execution of various queries. So, JdbcTemplate class allows the programmer to perform direct execution of the query. 84. Name the different types of advice in Spring Aspect Orient Programming (AOP). Answer – The Spring AOP provides of five types of advices, these are – • Around Advice • Throws Advice • After Advice • After Returning Advice • Before Advice 85. Differentiate between ApplicationContext and BeanFactory. Answer – The difference between ApplicationContext and beanFactory is as follows: ApplicationContext BeanFactory WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !56
- 57. JSP Java Interview Questions In this ninth section, we cover the JSP Java interview questions and answers. Go through these JSP Java interview questions and prepare yourself for the Java interview. If you have any other JSP Java interview questions, please post in the comment section. 86. What is JSP? Answer – Java Server Pages (JSP) is a Java technology that is used to develop web applications. It offers some more functionality and features than servlet i.e. JSTL, expression language, custom tags etc. so it is considered as the extension of servlet technology. The ApplicationContext is an advanced spring container. The BeanFactory is a basic spring container. The ApplicationContext is the extension of the BeanFactory interface. The BeanFactory interface is not an extended interface. ApplicationContext interface provides some additional facilities – message resource handling, integration with spring AOP, and many others. BeanFactory interface provides the basic facilities. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !57
- 58. A Java Server Page is composed of JSP tags along with HTML tags. It is easy to maintain JSP pages as it does not combine development and designing. Advantages of JSP – • Easy to maintain • Additional functionality • Faster development • Less coding 87. Explain the lifecycle of a JSP page. Answer – The lifecycle of a JSP page involves following phases – JSP Page Translation JSP Page Compilation Class file loading by class loader (Classloading) Creation of generated servlet object (Instantiation) Invocation of jspInit( ) method by container (Initialization) Invocation of jspService( ) method by container (Request Processing) Invocation of jspDestroy( ) method by container (Destroy) WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !58
- 59. 88. What do you know about JSP Implicit Objects? Answer – JSP Implicit Objects are those which are created by the web container and can be used by any of the JSP page. In Java, nine JSP Implicit Objects are there. Following table covers all the JSP implicit object with their types. 89. What do you know about JSTL? Answer – JSTL stands for JSP Standard Tag Library that contains a set of tags for the development of JSP pages. • JSTL has the following advantages – • Code Reusability • Fast Development • Avoids the use of scriptlet tags 90. What are the different types of JSTL tags? Answer – There are 5 types of JSTL tags – Object Name Object Type request HttpServletRequest page Object pageContext PageContext application ServletContext session HttpSession out JspWriter config ServletConfig exception Throwable response HttpServletResponse WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !59
- 60. Core Tags: The JSTL core tags help in URL management, variable support, flow control etc. The prefix c used for core tags. The URL for core tags is http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core XML Tags: The JSTL XML tags help in transformation, flow control etc. The prefix x used for core tags. The URL for XML tags is http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/xml Function Tags: The JSTL function tags are used to provide support for string length and string manipulation. The prefix fn used for function tags. The URL for function tags is http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions SQL Tags: WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !60
- 61. The JSTL SQL tags are used to provide SQL support for the development of JSP pages. The prefix sql used for SQL tags. The URL for SQL tags is http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/sql Formatting Tags: The JSTL formatting tags are used to provide support for message, number, and date formatting etc. The prefix fmt used for formatting tags. The URL for formatting tags is http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt 91. Have you ever heard about EL in JSP? Answer – In JSP, EL means Expression Language. The EL is used in order to make the objects accessibility simpler in JSP. The expression language provides a number of objects such as session, sessionScope, applicationScope, param, request, requestScope and many others. These objects can be directly used in JSP in a simple manner. 92. Differentiate between Java beans and Java custom tags. Answer – The difference between Java beans and Java custom tags is as follows: WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !61
- 62. 93. Name the tags that are used in the development of Java beans. Answer – Three tags are used for the development of Java beans, these are: jsp:useBean Jsp:getProperty jsp:setProperty 94. Write the statement that disables session in JSP. Answer – The statement that disables session in JSP is: <%@ page session=“fasle” %> 95. H ow a r e t h e co n t ex t . g e t Re q u e s t D i s p a t c h e r ( ) a n d request.getRequestDispatcher() different in terms of use? Java Beans Java Custom Tags Java beans cannot manipulate JSP content. Java custom tags can manipulate JSP content. It is simple to set up Java beans. It is comparatively harder to set up Java custom tags. Java beans are helpful to reduce the complex operations into simpler form. Java custom tags are helpful to reduce the complex operations into simpler form. Java beans is available in all 1.x versions of JSP. Java custom tags can only be used in JSP 1.1 WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !62
- 63. Answer – In order to create context.getRequestDispatcher(path), it relative path of the resource is required to be given while in order to create request.getRequestDispatcher(path) absolute path of the resource is required to be given alongwith. 96. Name the directive used in JSP custom tag. How will you perform the exception handling in JSP? Answer – The directive used in JSP custom tag is JSP tag lib directive. The exceptions in JSP can be handled in two different ways: 1. By the errorPage element of web.xml file 2. By the errorPage element of page directive 97. What is the use of JSP in MVC model? Answer – JSP performs the role of the view in Model View Controller. It is used for the purpose of presentation in MVC model. The MVC is meant to deal with the calling of business classes and model to get the data. After that, this received data is presented to JSP to render to the client. 98. Name the various scope values for <jsp:useBean> tag. Answer – The scope value represents the bean scope i.e. scope of the bean. There are four different scopes of the bean. • page • session • request WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !63
- 64. • application The default value of bean scope is page. 99. Differentiate between include action and include directive. Answer – The difference between include action and include directive is as follows: 100.Did you find JSP technology extensible? Answer – Yes, I found JSP technology extensible. The JSP technology is considered extensible as it comes with custom tags or actions that are encapsulated within tag libraries. Cover Up So here we reach the end of the Java interview questions blog. The questions and answers covered in this Java Interview Questions blog are the frequently-asked Java interview questions that the recruiters ask to Java Professional in a Java interview. These are the Java Interview Questions that will definitely help you ace your job interview. Include Action Include Directive It includes content at the time of request. It includes content at the time of page translation. It does not include the original content. It includes the original content. Include action invokes the include( ) method of the Vendor provided class. Include directive doesn’t invoke any method. Using include action is better for the dynamic pages. Using include directive is better for the static pages. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !64
- 65. Whizlabs is pioneering the online certification training industry and have helped more than 3 million professionals too advance their career. We are aimed to help you in your journey to build a bright career, so apart from these Java interview questions, we provide Oracle Java certifications online course and practice tests. Our study and practice material is best- in the industry and will help you become an Oracle Java certified. Wish you the luck for your Java interview! Any Query, Please write us here. ____________All The Best____________ © Copyright 2018. Whizlabs Software Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved. WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !65





![1. Save the source code file with .java extension. For example –
student.java
2. Javac compiler will then create a bytecode version of the source file
i.e. Student.class
3. The bytecode is the executable code and thus executed by the Java
Virtual Machine (JVM), also known as Java runtime systems.
6. What does “public static void main (String args [ ] )“ signify?
Explain.
Answer –
• “public” is the access specifier
• “static” is the access modifier that allows main ( ) method to be
invoked without creating any instance of the class
• “void” is the return type that specifies that the main ( ) method
won’t return any value
• main ( ) is the pre-defined method that is called in the beginning of
a java program
• “String args [ ]” are the arguments of the type String, when a Java
program is run, the Java application accepts it.
7. What does “System.out.println ( )” specify?
Answer –
“System” is the pre-defined class in Java that gives access to the system
“out” is the output stream
WWW.WHIZLABS.COM !6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whizlabsjavainterviewquestions-180629093202/85/Top-100-Java-Interview-Questions-with-Detailed-Answers-6-320.jpg)















































































































































