Type i and type ii errors
- 2. In the context of testing of hypotheses, there are basically two types of errors we can make:-
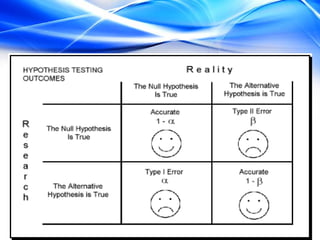
- 3. A type I error, also known as an error of the first kind, occurs when the null hypothesis (H0) is true, but is rejected. A type I error may be compared with a so called false positive. A Type I error occurs when we believe a falsehood. The rate of the type I error is called the size of the test and denoted by the Greek letter α (alpha). It usually equals the significance level of a test. If type I error is fixed at 5 %, it means that there are about 5 chances in 100 that we will reject H0 when H0 is true.
- 4. Type II error, also known as an error of the second kind, occurs when the null hypothesis is false, but erroneously fails to be rejected. Type II error means accepting the hypothesis which should have been rejected. A type II error may be compared with a so-called False Negative. A Type II error is committed when we fail to believe a truth. A type II error occurs when one rejects the alternative hypothesis (fails to reject the null hypothesis) when the alternative hypothesis is true. The rate of the type II error is denoted by the Greek letter β (beta) and related to the power of a test (which equals 1-β ).
- 5. In the tabular form two error can be presented as follows: Null hypothesis (H0) is Null hypothesis (H0) is true false Reject null hypothesis Type I error Correct outcome False positive True positive Fail to reject null Correct outcome Type II error hypothesis True negative False negative
- 7. If there is a diagnostic value distinguish the choice of two means, moving it to decrease type I error will increase type II error (and vice-versa)
- 8. Graphical depiction of the relation between Type I and Type II errors
- 9. What are the differences between Type 1 errors and Type 2 errors? Type 1 Error Type 2 Error A type 1 error is when a statistic A type 2 error is when a statistic calls for the rejection of a null does not give enough evidence to hypothesis which is factually true. reject a null hypothesis even when the null hypothesis should We may reject H0 when H0 is factually be rejected. true is known as Type I error . We may accept H0 when infect H0 is not true is known as Type II Error. A type 1 error is called a false positive. A type 2 error is a false negative. It denoted by the Greek letter α It denoted by the *Beta* (alpha). Alternative hypothesis and type II Null hypothesis and type I error error
- 10. Reducing Type I Errors • Prescriptive testing is used to increase the level of confidence, which in turn reduces Type I errors. The chances of making a Type I error are reduced by increasing the level of confidence.
- 11. Reducing Type II Errors • Descriptive testing is used to better describe the test condition and acceptance criteria, which in turn reduces Type II errors. This increases the number of times we reject the Null hypothesis – with a resulting increase in the number of Type I errors (rejecting H0 when it was really true and should not have been rejected). Therefore, reducing one type of error comes at the expense of increasing the other type of error! THE SAME MEANS CANNOT REDUCE BOTH TYPES OF ERRORS SIMULTANEOUSLY!
- 12. Many statisticians are now adopting a third type of error, a type III, which is where the null hypothesis was rejected for the wrong reason. In an experiment, a researcher might assume a hypothesis and perform research. After analyzing the results statistically, the null is rejected. The problem is, that there may be some relationship between the variables, but it could be for a different reason than stated in the hypothesis. An unknown process may underlie the relationship.