Ad
Version Control with Git
- 1. Version Control with Git Luigi De Russis Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Politecnico di Torino [email protected]
- 2. How do you share and save data? “I’m working solo… and I only have one computer” What I need: - backup; - different saved versions; - early and frequently saving. What I can use: - external hard drives; - dedicated folder; - Dropbox folder; - … 2
- 3. How do you share and save data? “I’m working solo… and I only have one computer” What if… - … I forget to save a specific version and then I need it? - … I delete/loose a previous version? 3
- 4. How do you share and save data? “I’m working solo… and I have more than one computer” What I need: - backup; - different saved versions; - early and frequently saving; - conventions on file names. What I can use: - USB memory sticks; - external hard drives; - Dropbox folder; - shared folder; - … 4
- 5. How do you share and save data? “I’m working solo… and I have more than one computer” What if… - … I forget to save a specific version and then I need it? - … I delete/loose a previous version? - … I have different projects in the “shared” workspace? - … I forget to copy one version between computers? 5
- 6. How do you share and save data? “I’m working in team” What I need: - backup; - different saved versions; - early and frequently saving; - shared conventions on file names. What I can use: - USB memory sticks; - external hard drives; - Dropbox folder; - e-mails; - … 6
- 7. How do you share and save data? “I’m working in team” What if… - … a team member forgets to save a specific version and then someone else needs it? - … someone deletes/looses a version? - … someone forgets to share a specific version of the projects? Other issues: - who has the latest version? - who has the right to edit? - how to ensure that everyone sees up-to-date versions of everything? - how to handle conflicts? 7
- 8. Version Control Systems Record changes to a file or a set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later Three generations: 1. Local (RCS, SCCS) 2. Centralized (CVS, Subversion, Team Foundation Server) NOW 3. Distributed (Git, Mercurial) 8
- 9. Basic Concepts Repository ◦ place where you store all your work ◦ contains every version of your work that has ever existed files directories layout history ◦ can be shared by the whole team 9
- 10. Basic Concepts Working copy ◦ a snapshot of the repository used for… working ◦ the place where changes happens ◦ private, not shared by the team ◦ it also contains some metadata so that it can keep track of the state of things has a file been modified? is this file new? has a file been deleted? 10
- 11. Basic Concepts Commit ◦ the operation that modifies the repository ◦ atomically performed by modern version control tools the integrity of the repository is assured ◦ it is typical to provide a log message (or comment) when you commit to explain the changes you have made the message becomes part of the history of the repository 11
- 12. Basic Concepts Update ◦ update the working copy with respect to the repository apply changes from the repository merge such changes with the ones you have made to your working copy, if necessary 12
- 13. Centralized Version Control one central repository client-server relationship Linguaggi e Ambienti Multimediali A 13
- 14. Distributed Version Control clients and server have the full copy of the repository ◦ local repositories clone a remote repository possible to have more than one server Linguaggi e Ambienti Multimediali A 14
- 15. More Basic Concepts Push ◦ copy changesets from a local repository instance to a remote one synchronization between two repository instances 15
- 16. More Basic Concepts Pull ◦ copy changesets from a remote repository instance to a local one synchronization between two repository instances 16
- 17. Git Distributed Version Control System Born ◦ on 2005 for the Linux kernel project ◦ to be used via command line Website: http://git-scm.com Highlights: ◦ free and open source ◦ strong support for non-linear development ◦ fully distributed ◦ efficient handling of large projects ◦ cryptographic authentication of history 17
- 18. Projects using Git Perl 18
- 19. Getting started with Git Standard installations ◦ http://git-scm.com/download On Windows, you can also use Git Extensions ◦ http://code.google.com/p/gitextensions/ For this course, Git is ◦ included in RailsInstaller ◦ integrated in Aptana Studio 3 19
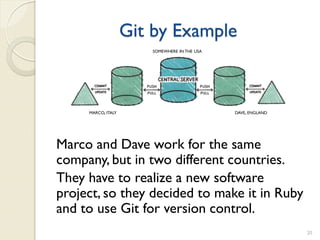
- 20. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Marco and Dave work for the same company, but in two different countries. They have to realize a new software project, so they decided to make it in Ruby and to use Git for version control. 20
- 21. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Marco starts the project by creating a new Git repository on the central server. He goes into the project directory and types: git init --bare myproject.git to initialize an empty git repository for the project. 21
- 22. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND When the central repository is ready, Dave clones it on his computer: git clone http://centralserver.com/myproject.git 22
- 23. Git by Example git clone http://centralserver.com/myproject.git creates a directory named myproject initializes a .git directory inside it pulls down all the data for that repository checks out a working copy of the latest version If you want to clone the repository into a directory with another name, you can specify that as: git clone http://centralserver.com/myproject.git projectOne 23
- 24. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Dave writes some code in the myproject folder. Before committing, Dave needs to really put the created file under version control, by adding the file to the Staging area: git add main.rb 24
- 25. The Staging area STAGING AREA A sort of loading dock It can contain things that are neither in the working copy nor in the repository instance Also called “index” 25
- 26. The Staging area: an example STAGING AREA Imagine to modify an existing file in the working copy The file is marked as “modified” 26
- 27. The Staging area: an example ADD STAGING AREA Before committing, the modified file needs to be “staged” ◦ i.e., add a snapshot of it in the staging area Modified data has been marked in its current version to go into the next commit snapshot 27
- 28. The Staging area: an example STAGING AREA Then, changes can be “committed” ◦ i.e., take the file from the staging area and store permanently the snapshot in the local repository 28
- 29. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND After adding main.rb to the Staging area, Dave can commit the file to the local repository: git commit -a -m “initial implementation” 29
- 30. Git by Example git commit -a -m “initial implementation” store the current snapshot in the local repository -a ◦ also perform an add for modified files ◦ useless at this point -m “put a message here” ◦ perform the commit with a log message ◦ useful to know what you have committed If Dave wants permanently to exclude from version control some files in the project folder, he can add them in the .gitignore file 30
- 31. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Now Dave can push the data to the remote repository: git push origin master where origin is the remote name and master is the branch name 31
- 32. Git by Example git push origin master Git pushes only to matching branches ◦ for every branch that exists on the local side, the remote side is updated if a branch of the same name already exists there ◦ you have to push the branch explicitly the first time Alternative command: ◦ git push --all After the first time, you can simply use: ◦ git push 32
- 33. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND After cloning the remote repository, Marco can pull the data: git pull Now Marco has the code! 33
- 34. Pull and Fetch in Git Fetch ◦ copy changesets from a remote repository FETCH instance to a local one ◦ previously, we called it “pull” Pull ◦ perform fetch ◦ update the working copy 34
- 35. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Marco wants to check the log to see the details: git log The result will be something like: commit bcb39bee268a92a6d2930cc8a27ec3402ebecf0d Author: Dave <[email protected]> Date: Wed Mar 28 10:06:13 2012 initial implementation 35
- 36. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Marco wants to check the log to see the details: git log The result will be something like: commit bcb39bee268a92a6d2930cc8a27ec3402ebecf0d Author: Dave <[email protected]> SHA-1 hash for data integrity Date: Wed Mar 28 10:06:13 2012 initial implementation 36
- 37. Git by Example At this point, Marco edits the source code and saves To see the pending changes, he can use: ◦ git status To see the difference between his version and the previous one, he can use: ◦ git diff (--cached, to include staged files) Marco decides to commit and to push his work git commit -a -m “added new functionalites” 37
- 38. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Meanwhile, Dave has been found some bugs in the code. After fixing them, he commits: git commit -a -m “bug fixing” 38
- 39. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND Dave tries to push his changes git push but something goes wrong: To http://centralserver.com/myproject ! [rejected] master -> master (non-fast-forward) error: failed to push some refs to ‘http://centralserver.com/myproject’ 39
- 40. Git by Example What happens? ◦ Git is not allowing Dave to push his change because Marco has already pushed something to the master branch Solution: ◦ Dave has to do a pull, to bring in changes before pushing its modifications Two possible scenarios: ◦ merging of files goes smoothly; ◦ merging of files generates conflicts. 40
- 41. Git by Example Merge with conflicts From http://centralserver.com/myproject b19f36c..b77378f master -> origin/master Auto-merging main.rb CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in main.rb Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result. Git includes both Marco’s code and Dave’s code with conflict markers to delimit things <<<<<<< HEAD # Marco’s code here ======= # Dave’s code here >>>>>>> b77378f6eb0af44468be36a085c3fe06a80e0322 41
- 42. Git by Example SOMEWHERE IN THE USA MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND After (manually) resolving these conflicts, Dave can push the changes: git push 42
- 43. Other useful commands Operations on files ◦ Remove: git rm [filename] ◦ Move/rename: git mv [file-from] [file-to] ◦ Unstage some staged files: git reset HEAD [filename-list] ◦ Unmodify a modified file: git checkout -- [filename] Operations on remotes ◦ List: git remote (-v, to show the URLs) ◦ Add: git remote add [shortname] [url] ◦ Inspect: git remote show [remote-name] ◦ Rename: git remote rename [old-name] [new-name] ◦ Remove: git remote rm [remote-name] Change the last commit ◦ git commit --amend 43
- 44. Tags and Branches in a nutshell Local and remote Do not push automatically [Image from http://nvie.com/posts/a-successful-git-branching-model/] 44
- 45. Tags and Branches in a nutshell Tags ◦ useful to mark release points ◦ two types: lightweight annotated (more complete) ◦ commands: git tag, shows the available existing tags git tag [tag-name], creates a lightweight tag git tag -a [tag-name] -m [message]‚ creates an annotated tag tag show [tag-name], shows the tag data 45
- 46. Tags and Branches in a nutshell Branches ◦ used to develop features isolated from each other ◦ the master branch is the “default” branch when you create a repository ◦ you should use other branches for development and merge them back to the master branch upon completion ◦ really lightweight in Git ◦ commands: git branch [branch-name], create a new branch git branch, lists all existing branches git checkout [branch-name], switches to the selected branch git branch -d [branch-name], removes the selected branch 46
- 47. Hosted Git To have (at least) one remote repository Alternative: to set up your Git server Most popular: ◦ Github https://github.com/ ◦ Bitbucket https://bitbucket.org/ ◦ Sourceforge http://sourceforge.net/ ◦ (Microsoft) Codeplex http://www.codeplex.com/ ◦ Google Code http://code.google.com/ 47
- 48. Github Slightly different than other code-hosting sites ◦ instead of being primarily based on the project, it is user-centric ◦ social coding A commercial company ◦ charges for accounts that maintain private repository ◦ free account to host as many open source project as you want 48
- 49. Bitbucket Similar to Github Less famous than Github, right now Mercurial support A commercial company ◦ free private and public repositories for small team (up to 5 private collaborators) ◦ charges for project involving bigger team ◦ free for academia (also for students) unlimited public and private repositories unlimited users for single projects 49
- 50. References Git Reference ◦ http://gitref.org/ Git - the simple guide ◦ http://rogerdudler.github.com/git-guide/ Git User’s Manual ◦ http://schacon.github.com/git/user-manual.html Pro Git (online book) ◦ http://progit.org/book/ Git Magic (online book) ◦ http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~blynn/gitmagic Git Screencast ◦ http://gitcasts.com/ Version Control by Example (online book) ◦ http://www.ericsink.com/vcbe/ 50
- 51. References Learn Git one commit at time ◦ http://gitready.com/ The Git Parable ◦ http://tom.preston-werner.com/2009/05/19/the-git- parable.html Interactive Git Cheatsheet ◦ http://ndpsoftware.com/git-cheatsheet.html A successful Git branching model ◦ http://nvie.com/posts/a-successful-git-branching-model/ Some Git (graphical) clients ◦ http://guides.beanstalkapp.com/version- control/clients.html#git-clients EGit, Eclipse plugin for Git ◦ http://www.eclipse.org/egit/ 51
- 52. License This work is licensed under the Creative Commons “Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike Unported (CC BY- NC-SA 3,0)” License. You are free: ◦ to Share - to copy, distribute and transmit the work ◦ to Remix - to adapt the work Under the following conditions: ◦ Attribution - You must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work). ◦ Noncommercial - You may not use this work for commercial purposes. ◦ Share Alike - If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar license to this one. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ 52






































![Git by Example
SOMEWHERE IN THE USA
MARCO, ITALY DAVE, ENGLAND
Dave tries to push his changes
git push
but something goes wrong:
To http://centralserver.com/myproject
! [rejected] master -> master (non-fast-forward)
error: failed to push some refs to ‘http://centralserver.com/myproject’
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/versioncontrolwithgit-120329115548-phpapp02/85/Version-Control-with-Git-39-320.jpg)



![Other useful commands
Operations on files
◦ Remove: git rm [filename]
◦ Move/rename: git mv [file-from] [file-to]
◦ Unstage some staged files: git reset HEAD [filename-list]
◦ Unmodify a modified file: git checkout -- [filename]
Operations on remotes
◦ List: git remote (-v, to show the URLs)
◦ Add: git remote add [shortname] [url]
◦ Inspect: git remote show [remote-name]
◦ Rename: git remote rename [old-name] [new-name]
◦ Remove: git remote rm [remote-name]
Change the last commit
◦ git commit --amend
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/versioncontrolwithgit-120329115548-phpapp02/85/Version-Control-with-Git-43-320.jpg)
![Tags and Branches in a nutshell
Local and remote
Do not push automatically
[Image from http://nvie.com/posts/a-successful-git-branching-model/]
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/versioncontrolwithgit-120329115548-phpapp02/85/Version-Control-with-Git-44-320.jpg)
![Tags and Branches in a nutshell
Tags
◦ useful to mark release points
◦ two types:
lightweight
annotated (more complete)
◦ commands:
git tag, shows the available existing tags
git tag [tag-name], creates a lightweight tag
git tag -a [tag-name] -m [message]‚ creates an
annotated tag
tag show [tag-name], shows the tag data
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/versioncontrolwithgit-120329115548-phpapp02/85/Version-Control-with-Git-45-320.jpg)
![Tags and Branches in a nutshell
Branches
◦ used to develop features isolated from each other
◦ the master branch is the “default” branch when you
create a repository
◦ you should use other branches for development and
merge them back to the master branch upon
completion
◦ really lightweight in Git
◦ commands:
git branch [branch-name], create a new branch
git branch, lists all existing branches
git checkout [branch-name], switches to the selected branch
git branch -d [branch-name], removes the selected branch
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/versioncontrolwithgit-120329115548-phpapp02/85/Version-Control-with-Git-46-320.jpg)





























































































