Virtualization with KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)
- 1. Virtualization with (KVM) Kernel-based Virtual Machine Thomas Korber Bruce Rogers Consultant and Trainer Consulting Software Engineer B1 Systems GmbH Novell, Inc. [email protected] [email protected]
- 2. KVM First release in early 2007 Originally developed by Qumranet Included in Linux kernel release 2.6.20 GPL v2 2 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 3. KVM – Full Virtualization • Relies on AMD's AMD-V or Intel's VT-x virtualization technologies • Implemented as kernel modules – kvm.ko: provides virtualization infrastructure – kvm_amd.ko and kvm_intel.ko: hardware platform specific modules for the hardware virtualization technologies • => Vanilla Linux kernel becomes virtual machine monitor, which can use any kernel infrastructure without modifications • => KVM virtual machines become regular user-space processes 3 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 4. KVM Architecture Adds “Guest Mode” to Traditional Kernel and User Modes Guest Userspace Processes Userspace Userspace Guest Kernel Process Process ... (e.g. Linux Kernel) QEMU-KVM Linux Kernel KVM (Module) Hardware Support, vitualization technologies for x86 (AMD-V/ Intel-VT) 4 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved. Source: “Virtualization with KVM” training, B1 Systems GmbH
- 5. Supported Hardware Any i386/x86_64 CPUs that have AMD-V or VT-x: => Almost any server CPU sold in the last couple years 5 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 6. Supported Hardware (Continued) Utilizes the following additional hardware virtualization features: VPID / ASID VT-d/IOMMU HAP (EPT/NTP) VMX Unrestricted Guest SR-IOV 6 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 7. QEMU • Community project founded in 2003 • Emulates PC hardware and CPUs • Since v 0.10.0 support for KVM VMM • Modified qemu-kvm is user space tool for KVM • Communication with KVM via /dev/kvm 7 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 8. KVM Features Supports 32 and 64 bit guests (on 64 bit hosts) Supports hardware virtualization features Paravirtualized drivers (virtio): blk, net, clock, balloon Snapshots Delta images of virtual machines PCI passthrough Kernel samepage merging 8 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 9. KVM Features (continued) Sound support CPU, memory and disk over-commit Live migration CPU and device hotplug Non-kvm (emulation only) mode PXE boot 9 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 10. KVM - Supported Guest Systems Solaris, OpenSolaris Linux BSD Windows BSD Unix 10 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 11. KVM Guests Supported by Novell (I) ® Linux - both 32 and 64 bit • SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 (level 3 supported) • SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP3 (level 3 supported) • SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 SP4 (level 3 supported) • SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop 11 SP1 (technical preview) • Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (best effort) • Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (best effort) 11 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 12. KVM Guests Supported by Novell (II) ® Microsoft Windows – both 32 and 64 bit (“best effort” support only) • Microsoft Windows 2003 SP2+ plus PV drivers • Microsoft Windows 2008+ plus PV drivers • Microsoft Windows XP SP3+ plus PV drivers • Microsoft Windows Vista SP1+ plus PV drivers 12 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 13. Supported Limits Host RAM and CPU limits are the same with or without kvm modules loaded Guest RAM size: 512 GB Virtual CPUs per guest: 16 NICs per guest: 8 Block devices per guest: 4 emulated, 20 para-virtual (virtio-blk) Maximum number of guests: total vCPUs <= 8 times total CPU cores in Host 13 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 14. Xen and KVM: A Comparison Xen KVM • VMM implementation of • Kernel module its own; hypervisor • Kernel as I/O dispatcher and management domain • Uses kernel as VMM • Maintained and supported as a patch to mainline • In upstream kernel kernel by Novell ® • Supports fully virtualized and paravirtualized Vms • Only supports fully virtualized VMs 14 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 15. Virtualization in SUSE Linux ® Enterprise Server 11 SP1 • SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 will ship with both virtualization solutions (KVM and Xen) • Xen is the primary solution, being the proven enterprise-ready open source hypervisor • Long term, Novell expects KVM eventually to ® become equivalent to Xen • Toolset shipped in SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 supports both Xen and KVM 15 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 16. Setting up KVM on SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP1 ®
- 17. Demo Setup • Storage server and installation source: – SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 GA x86_64 ® – Logical volume as iSCSI target for OCFS2 file system – Installation sources (SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 Beta5 and SUSE Linux Enterprise High Availability Extension Server 11 SP1 Beta5) exported via HTTP • 2 KVM hosts – SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 Beta5 x86_64 – Logical volume for DRBD; DRBD primary/primary setup 17 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 18. Demo Setup – Shared Storage Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 FC or iSCSI OCFS2 18 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 19. Demo Setup – Replicated Storage Node 1 Node 2 TCP/IP DRBD Local Disk Local Disk 19 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 20. Packages • KVM, libvirt and virt-manager as GUI zypper in kvm virt-manager • (optional) packages for shared storage: – server: iscsitarget – KVM hosts: open-iscsi, ocfs2-tools, ocfs2-tools-o2cb or – KVM hosts: drbd, drbd-kmp-default 20 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 21. iSCSI Setup • Storage Server: storage:~ # cat /etc/ietd.conf | grep -v "#" Target iqn.2009-11.b1-systems.de:lv_share Lun 0 Path=/dev/vg_system/lv_share,Type=fileio • KVM Hosts: node1:~ # iscsiadm -m discovery -tst -p storage 192.168.2.35:3260,1 iqn.2009-11.b1- systems.de:lv_share node1:~ # iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2009-11.b1- systems.de:lv_share -p 192.168.2.35 -l 21 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 22. DRBD Setup - /etc/drbd.conf (I) Create /etc/drbd.conf and have the identical file on both nodes node1:~ # cat /etc/drbd.conf global { usage-count no; } resource r0 { protocol C; syncer { rate 40M; } net { allow-two-primaries; } startup { become-primary-on both; } 22 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 23. DRBD Setup - /etc/drbd.conf (II) on node1 { device /dev/drbd0; disk /dev/mapper/storage-lv_drbd; address 192.168.2.31:7791; meta-disk internal; } on node2 { device /dev/drbd0; disk /dev/mapper/storage-lv_drbd; address 192.168.2.32:7791; meta-disk internal; } } 23 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 24. DRBD Setup On both nodes: node1:~ # modprobe drbd && rcdrbd start node1:~ # drbdadm create r0 On first node: node1:~ # drbdadm -- --overwrite-data-of-peer primary r0 On second node: node1:~ # drbdadm primary r0 On either node: node1:~ # cat /proc/drbd 24 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 25. OCFS2 Setup (I) node1:~ # vi /etc/ocfs2/cluster.conf node: name = node1 cluster = ocfs2 number = 0 ip_address = 192.168.2.31 ip_port = 7777 node: name = node2 cluster = ocfs2 number = 1 ip_address = 192.168.2.32 ip_port = 7777 cluster: name = ocfs2 node_count = 2 25 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 26. OCFS2 Setup (II) node1:~ # rco2cb configure Configuring the O2CB driver. This will configure the on-boot properties of the O2CB driver. Load O2CB driver on boot (y/n) [y]: Cluster stack backing O2CB [o2cb]: Cluster to start on boot (Enter "none" to clear) [ocfs2]: Specify heartbeat dead threshold (>=7) [31]: Specify network idle timeout in ms (>=5000) [30000]: Specify network keepalive delay in ms (>=1000) [2000]: Specify network reconnect delay in ms (>=2000) [2000]: Writing O2CB configuration: OK Loading filesystem "configfs": OK Mounting configfs filesystem at /sys/kernel/config: OK Loading stack plugin "o2cb": OK Loading filesystem "ocfs2_dlmfs": OK Mounting ocfs2_dlmfs filesystem at /dlm: OK Setting cluster stack "o2cb": OK Starting O2CB cluster ocfs2: OK 26 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
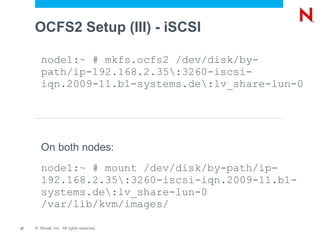
- 27. OCFS2 Setup (III) - iSCSI node1:~ # mkfs.ocfs2 /dev/disk/by- path/ip-192.168.2.35:3260-iscsi- iqn.2009-11.b1-systems.de:lv_share-lun-0 On both nodes: node1:~ # mount /dev/disk/by-path/ip- 192.168.2.35:3260-iscsi-iqn.2009-11.b1- systems.de:lv_share-lun-0 /var/lib/kvm/images/ 27 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 28. OCFS2 Setup (IV) - DRBD node1:~ # mkfs.ocfs2 /dev/drbd0 On both nodes: node1:~ # mount /dev/drbd0 /var/lib/kvm/images 28 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 29. KVM VM Installation – GUI 29 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 30. KVM VM Installation: CLI • qemu-img create /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img 5G • qemu-kvm -hda /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img -cdrom /srv/isos/SLES-11-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso -boot d -m 512 [installation of a “physical computer”] • qemu-kvm -hda /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img -m 512 30 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 31. KVM – Installation With vm-install Unattended installation: vm-install --background --vm- settings=/foo/bar/vm-template.xml --os- settings=/foo/bar/autoinst.xml … 31 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 32. KVM – Networking • Usermode network stack – Default setup – No root permissions needed – Integrated DHCP, DNS, SMB and DNS • TAP device • Bridged mode (comparable to default Xen network setup) 32 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 33. KVM – Networking (II) Example: bridged setup node1:~ # cat /etc/libvirt/qemu/sles11.xml cat /etc/libvirt/qemu/networks/default.xml <network> <name>default</name> [...] <bridge name="br0" /> [...] </network> 33 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 34. KVM – Selected Image Formats Name Compression Snapshot Encryption Deltas raw qcow2 X X X X vmdk X 34 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 35. KVM – Converting, Compressing and Encrypting Images • qemu-img convert -O qcow2 /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_qcow2_disk1.img • qemu-img convert -c -O qcow2 /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_qcow2_disk1.img /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_qcow2_compr_disk1.img • qemu-img convert -e -O qcow2 /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_qcow2_compr_disk1.img /var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_qcow2_compr_encr_disk1.img 35 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 36. Virt-Manager – Hardware Configuration 36 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 37. KVM – Snapshots • qemu-img snapshot -l image.img • qemu-img snapshot -a snapshot image.img • qemu-img snapshot -c snapshot image.img • qemu-img snapshot -d snapshot image.img 37 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 38. KVM – Live Migration • CLI: qemu-kvm -incoming tcp:0:4444 (qemu) migrate -d tcp:192.168.3.34:4444 • Via libvirt and virt-manger instances 38 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 39. Demo
- 41. Unpublished Work of Novell, Inc. All Rights Reserved. This work is an unpublished work and contains confidential, proprietary, and trade secret information of Novell, Inc. Access to this work is restricted to Novell employees who have a need to know to perform tasks within the scope of their assignments. No part of this work may be practiced, performed, copied, distributed, revised, modified, translated, abridged, condensed, expanded, collected, or adapted without the prior written consent of Novell, Inc. Any use or exploitation of this work without authorization could subject the perpetrator to criminal and civil liability. General Disclaimer This document is not to be construed as a promise by any participating company to develop, deliver, or market a product. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. Novell, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents of this document, and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. The development, release, and timing of features or functionality described for Novell products remains at the sole discretion of Novell. Further, Novell, Inc. reserves the right to revise this document and to make changes to its content, at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes. All Novell marks referenced in this presentation are trademarks or registered trademarks of Novell, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

























![OCFS2 Setup (II)
node1:~ # rco2cb configure
Configuring the O2CB driver.
This will configure the on-boot properties of the O2CB driver.
Load O2CB driver on boot (y/n) [y]:
Cluster stack backing O2CB [o2cb]:
Cluster to start on boot (Enter "none" to clear) [ocfs2]:
Specify heartbeat dead threshold (>=7) [31]:
Specify network idle timeout in ms (>=5000) [30000]:
Specify network keepalive delay in ms (>=1000) [2000]:
Specify network reconnect delay in ms (>=2000) [2000]:
Writing O2CB configuration: OK
Loading filesystem "configfs": OK
Mounting configfs filesystem at /sys/kernel/config: OK
Loading stack plugin "o2cb": OK
Loading filesystem "ocfs2_dlmfs": OK
Mounting ocfs2_dlmfs filesystem at /dlm: OK
Setting cluster stack "o2cb": OK
Starting O2CB cluster ocfs2: OK
26 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/els305-100323102407-phpapp02/85/Virtualization-with-KVM-Kernel-based-Virtual-Machine-26-320.jpg)


![KVM VM Installation: CLI
• qemu-img create
/var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img 5G
• qemu-kvm -hda
/var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img
-cdrom /srv/isos/SLES-11-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso
-boot d -m 512
[installation of a “physical computer”]
• qemu-kvm -hda
/var/lib/kvm/images/sles11_raw_disk1.img -m 512
30 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/els305-100323102407-phpapp02/85/Virtualization-with-KVM-Kernel-based-Virtual-Machine-30-320.jpg)


![KVM – Networking (II)
Example: bridged setup
node1:~ # cat
/etc/libvirt/qemu/sles11.xml
cat
/etc/libvirt/qemu/networks/default.xml
<network>
<name>default</name>
[...]
<bridge name="br0" />
[...]
</network>
33 © Novell, Inc. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/els305-100323102407-phpapp02/85/Virtualization-with-KVM-Kernel-based-Virtual-Machine-33-320.jpg)







