Visual programming lecture
- 1. B Y A Q S A H A Y A T D E P A R T M E N T O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Visual Programming 7/13/2021 1
- 2. Brief History of Visual Basic Evolved from BASIC Beginner’s All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code Developed in mid-1960s 7/13/2021 2
- 3. Visual Basic Evolved into Visual Basic in 1991 Major Features: IDE (Integrated Development Environment) GUI’s Event Handling Object Oriented Programming Exception Handling Rapid Application Development (RAD) 7/13/2021 3
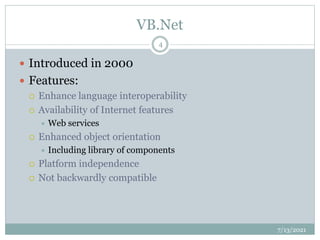
- 4. VB.Net Introduced in 2000 Features: Enhance language interoperability Availability of Internet features Web services Enhanced object orientation Including library of components Platform independence Not backwardly compatible 7/13/2021 4
- 5. .Net Strategy Web Services Applications can be used over the Internet Includes ASP.Net technology Software Reuse Allows programmers to concentrate on their particular specialties without having to implement every component of every application. Universal Data Access Central location for data 7/13/2021 5
- 6. Reusability Building-block approach Central to the OOP concept. Improves performance More reliable programs Avoids reinventing the wheel… 7/13/2021 6
- 7. .Net Framework Manages and executes applications and Web services Contains a class library Framework Class Library or FCL Enforces security Visual programming Microsoft .Net Framework Link 7/13/2021 7
- 8. .Net Framework Layers 7/13/2021 8 VB C++ C# JScript Common Language Specification ASP.NET Windows Forms Data and XML Base Class Library Common Language Runtime Windows COM+ Services
- 9. Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) Contains info about storage of data types Data that have predefined characteristics Ex. Dates, percentages or currency amounts Objects Has been standardized Making it easier to create the .NET Framework for other platforms. 7/13/2021 9
- 10. Common Language Runtime (CLR) Executes Visual Basic .Net programs Programs are compiled into machine-specific instructions using two steps: Program is compiled into Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL). Defines instructions for the CLR Then another compiler in the CLR, called the JIT compiler (just- in-time compiler) translates the MSIL into machine code, for the particular platform, creating a single application 7/13/2021 10
- 11. Why two compilations? Provides Portability between operating systems Interoperability between languages Execution-management features Memory management Security 7/13/2021 11
- 12. Platform Independence .Net framework provides the ability of a program to run (without any modification) across multiple platforms. The .NET Framework is actually a set of classes called base classes. Saves Time and Money! Don’t reinvent the same code for multiple platforms Targets wider audience Avoids the expensive process of porting (converting software from one platform to another) 7/13/2021 12
- 13. Language Interoperability Programs from different languages are all compiled into MSIL The different parts are combined to create one program MSIL allows the .NET Framework to be language independent or .Net compliant .Net programs are not tied to any particular programming language. 7/13/2021 13
- 14. Benefits of Language Interoperability in .Net? VB.Net, C#, Visual C++.Net programmers can all work on same project Old and new components can work together Permits code reusability (code doesn’t have to be rewritten) CLR’s execution-management features Code loading and execution Application isolation Memory management Security 7/13/2021 14
- 15. Exception handling Interoperability Managing security, memory and other features, relieving programmer of these responsibilities Provides huge library of classes providing reusability Framework Class Library (FCL) 7/13/2021 15
- 16. Software Engineering Observation Reuse of existing classes when building new classes and programs saves time, money & effort Reuse also helps in building more reliable and effective systems Why? Because existing classes and components go through extensive testing, debugging and performance tuning. 7/13/2021 16
- 17. Views of VB Between Vista vs Windows 7 & 8 7/13/2021 17 Vista Windows 7 Windows 8
- 19. People Involved in Program Development Programmer Person who solves the problem and writes the instructions for the computer Client The person/organization who is responsible for requesting/purchasing the program User Any person who uses the program 7/13/2021 19
- 20. Designing Your Program Critically important to design before beginning to code Coding first is like putting the cart before the horse. Doesn’t matter the size of the program -- design first! 7/13/2021 20
- 21. Program Planning Steps 1. Analyze – define the problem 2. Design – plan the solution to the problem 3. Design the Interface – select the objects that will be used 4. Code – translate the algorithm into a programming language 5. Debug & Test – locate and remove any errors in the program 6. Complete the documentation – Internal & External 7/13/2021 21
- 22. Key Steps to Creating a Visual Program 7/13/2021 22 Plan the tasks How it should work Design user interface Write the code Debug and Test Document & Distribute How it should look Repeat Steps 1 & 2 Prepare test criteria Put program into use
- 23. Design Process Results Even for a small program, the design process should produce the following results: A concise list of tasks to be performed by the program Deadlines for components Clarification of the dependence of one part of the program on another The criteria for testing the program 7/13/2021 23
- 24. Problem Solving Developing the solution to a problem Algorithm a step by step series of instructions to solve a problem Example: How would you give instructions to someone to find your house? 7/13/2021 24
- 25. Divide-and-Conquer Method Used in problem solving take a large problem and break it into smaller problems Solve the small problems first 7/13/2021 25
- 26. Tools Used in Design Hierarchy Charts/Structure Charts Flowcharts/UML Graphically depict the logical steps to accomplish a task and indicate how the steps relate to each other Pseudocode Uses English-like phrases with some Visual Basic terms to outline the task. Control Structures Sequence Decision/Selection Repetition/Loops/ Iteration 7/13/2021 26
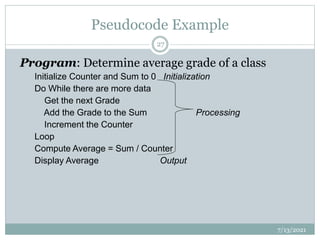
- 27. Pseudocode Example Program: Determine average grade of a class Initialize Counter and Sum to 0 Initialization Do While there are more data Get the next Grade Add the Grade to the Sum Processing Increment the Counter Loop Compute Average = Sum / Counter Display Average Output 7/13/2021 27
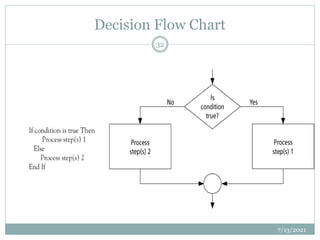
- 31. Statement Structures Sequence Execute instructions one after another Decision Allows us to ask questions and execute different instructions based on result Looping a series of instructions are executed repeatedly 7/13/2021 31
- 34. Visual Programming Benefits Provides the programmer with the ability to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Allows the programmer to write much less code Does not require the programmer to be a Windows expert Provides Rapid Application Development (RAD) – code can be developed faster & cheaper 7/13/2021 34
- 35. Programming Languages-Procedural, Event Driven and Object Oriented Procedural—Cobol, Fortran, Basic Program specifies exact sequence of all operations Event Driven (VB 6.0 and previous) Contain some elements of Object oriented programming but not all User controls sequence Click event Double Click event Change event 7/13/2021 35
- 36. Object Oriented Programming (OOP) (VB .NET) VB is an object-oriented programming language. Means you work with objects in building an application. Examples: Form objects, Button objects, TextBox objects, Label objects, ListBox objects, PictureBox objects, and more. 7/13/2021 36
- 37. VB is also termed an event-driven programming language because you will write program code that responds to events that are controlled by the system user. Example events include: Clicking a button or menu. Opening or Closing a form. Moving the mouse over the top of an object such as a text box. Moving from one text box to another. 7/13/2021 37
- 38. The Object Model In VB you will work with objects, which have properties, methods, and events. Each object is based on a class. Objects equate to Nouns Forms are windows Controls are components contained inside a form Properties equate to Adjectives Color or size of a Form Methods are like Verbs Typical methods include Close, Show and Clear Events occur when the user takes action User clicks a button, User moves a form 7/13/2021 38
- 39. The Object Model Classes are templates used to create a new object Classes contain the definition of all available properties, methods, and events Each new object created is based on a class Creating three new buttons makes each button a instance of the Button class 7/13/2021 39
- 40. Terminology Definition Object A thing – like a noun in English. Examples include forms and controls you place on forms such as buttons, text boxes, and icons. Property Objects have properties – like adjectives in English. Properties describe object behaviors. Examples of properties include Text, Name, BackColor, Font, and Size. Refer to a property by the notation ObjectName.PropertyName (use the .dot notation) – example: TotalDueTextBox.Text or AccountLabel.ForeColor. Method Like a verb in English – these are the actions that objects exhibit. Examples include methods to Show and Hide forms and methods to Print and Close forms. Refer to a method with the notation ObjectName.MethodName – example Me.Close will close the current form. Event Events are actions usually triggered by the system user such as clicking a button; however, events can also be triggered by the actions of objects. For example, closing a form can trigger an event. Class This is a really abstract term – it is a sort of template for an object. For example, all forms belong to the Form class of object. All buttons belong to the Button class of object. Classes include definitions for object properties, methods, and associated events. Each class is assigned an identifying namespace within the .NET Framework Class Library. Each new object you create is defined based on its class – the new object is called a class instance. 7/13/2021 40
- 41. Object Model Analogy Class = automobile Properties = make, model, color, year Object = each individual car Object is also an Instance of the automobile class Methods = start, stop, speedup, slowdown Events = car arrives, car crashes 7/13/2021 41
- 42. Visual Studio .NET Included in Visual Studio .NET 2002, 2003,2005, 2008 ,2010and onword Visual Basic Visual C++ Visual C# (C sharp) Visual J# Visual F# .NET 2.0 Framework or more Visual Studio .NET Editions Standard Professional Enterprise Developer Enterprise Architect Express 7/13/2021 42
- 43. System Requirements Express Edition Supported Operating Systems Windows 7 SP3 (x32) (This package) Windows 7 SP1 (x86 and x64) Windows 8 (x86 and x64) Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 (x64) Windows Server 2012 (x64) Hardware Requirements: 1.6 GHz or faster processor 1 GB of RAM (1.5 GB if running on a virtual machine) 5 GB of available hard disk space 5400 RPM hard drive DirectX 9-capable video card running at 1024 x 768 or higher display resolution 7/13/2021 43
- 44. Visual Studio Environment The Visual Studio environment is where you create and test your projects-in Visual Studio it is called an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) consists of various tools including: Form Designer Editor for entering code Compiler Debugger Object Browser Help facility 7/13/2021 44
- 45. The IDE Initial Screen The Visual Studio IDE with the Start Page open, as it first appears in Windows , with an open project. 7/13/2021 45
- 46. Get Started New Project Opens list of existing projects Recent Projects Contains information on projects recently created or modified Get Started Focuses on using the IDE for creating programs and learning VB. 7/13/2021 46
- 47. New Project Window 7/13/2021 47 Need to rename to something meaningful! Window Form Change Location
- 48. New Project 7/13/2021 48 DO NOT MOVE Properties Window Or Solution Explorer Windows!!!!!
- 49. Visual Studio’s Main Windows Solution Explorer Properties Toolbox 7/13/2021 49
- 50. Solution Explorer Provides access to all of a solution’s files. If it’s not shown in the IDE, click the Solution Explorer icon in the IDE , select View > Other Windows > Solution Explorer or type <Ctrl> <Alt> L. Displays the solution’s contents When a new or existing solution is opened. 7/13/2021 50
- 51. Properties Window 4 Methods to Place Control on Form Double-click Drag and Drop Click, Point, and Click Click, Point, and Drag 7/13/2021 51
- 54. Toolbox 7/13/2021 54 Toolbox window displaying controls for the Common Controls group. The pushpin in the upper right corner is the AutoHide feature and will “stick” the Toolbox to visible if you want it to remain visible during design.
- 55. Auto Hide Hides Toolbox when not in use Vertical push pin icon indicates auto hide is disabled. Click the push pin to make it horizontal and enable auto hide. 7/13/2021 55 push pin
- 57. Modes Design Time--used when designing the user interface and writing code Run Time--used when testing and running a project Break Time--if/when receiving a run-time error or pause error 7/13/2021 57
- 58. VB Application Files One Solution File—think of one solution file equals one project .sln Solution User Options File .suo Form Files .vb Resource File for the Form .resx Project Files .vbproj Project User Options File .vbproj.user Application configuration File .app.config 7/13/2021 58
- 59. Remark Statement Also known as Comment, used for documentation; every procedure should begin with a remark statement providing explanation Non-executable Automatically colored Green in Editor Begins with an apostrophe ( ' ) On a separate line from executable code At the right end of a line of executable code `Display your information 7/13/2021 59
- 60. Notation To reference object's properties and events in code Object dot Property Form.Text, TextBox.Text Object dot Method/Function/Subroutine Form.Hide( ), TextBox.Focus( ) To reference an object's events use an underscore instead of a dot Button_Click, ListBox_TextChanged 7/13/2021 60
- 61. Naming Rules and Conventions Visual Basic automatically assigns a value to the Name property of each control, for example, Label1, Label2, Label3, or TextBox1, TextBox2, TextBox3, or Button1, Button2, Button3. However, it is difficult to remember the difference between Label1 and Label2 so: if you are going to later refer to the controls, it is best to rename them to a more meaningful name, if you are not going to refer to the controls later, then just use the assigned default name such as Label1. When you name an object such as a Label or TextBox or Button, you must follow these rules: An object name can begin with an alphabetic letter or the special “underscore” character. An object name can include letters, digits, and underscores. An object name CANNOT include a space or a punctuation mark. An object name CANNOT be a VB reserved word such as Button, Close, or TextBox. An object name can contain a VB reserved word – object names such as PrintButton, CloseButton, NameTextBox, and MajorTextBox are legal names. 7/13/2021 61
- 62. Pascal naming convention The rules are: Begin an object name with an uppercase alphabetic character. Capitalize each word that is part of an object name. Select object names that are meaningful. Append the full name of the control class to the end of the name. Avoid abbreviations unless they are standard abbreviations such as SSN (social security number). Examples of valid names: MajorTextBox, ResetButton, MessageLabel, TotalDueTextBox, and CloseButton. 7/13/2021 62
- 63. Camel Casing and Hungarian naming conventions Camel Casing and Hungarian Naming Conventions Control Type and Camel Casing Naming Suffix Example Camel Casing Control Names Hungarian Naming Prefix Example Hungarian Control Names TextBox NameTextBox, MajorTextBox txt txtName, txtMajor Button ShippingButton, ExitButton, ResetButton btn btnShipping, btnExit, btnReset Label NameLabel, OutputLabel lbl lblName, lblOutput Note: Label controls are often not renamed – they are not referred to later in writing computer code so the default assigned name is unchanged. 7/13/2021 63