Ad
VMworld 2014: Virtualize Active Directory, the Right Way!
- 1. Virtualize Active Directory, the Right Way! VAPP1340 Deji Akomolafe – @dejify Staff Solutions Architect, VMware Matt Liebowitz – @mattliebowitz Virtualization Discipline Lead, EMC
- 2. Disclaimer • This presentation may contain product features that are currently under development. • This overview of new technology represents no commitment from VMware to deliver these features in any generally available product. • Features are subject to change, and must not be included in contracts, purchase orders, or sales agreements of any kind. • Technical feasibility and market demand will affect final delivery. • Pricing and packaging for any new technologies or features discussed or presented have not been determined. CONFIDENTIAL 2
- 3. Agenda CONFIDENTIAL 3 1 Active Directory Overview 2 Why virtualize Active Directory? 3 Common Objections to Domain Controller Virtualization 4 Understanding Domain Controller Virtualization 5 Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers 6 New Features 7 DC “Safety” Considerations in DC Event 8 Protecting Active Directory with SRM – Conceptual Use Case
- 4. Active Directory Overview § This is not an Active Directory class § Windows Active Directory Multi-master Replication Conundrum – Write Originates from any Domain Controller • RODC is “special” - – Cannot perform write operations • Schema Update is “special” – Schema update operations happen on the Schema Master – Selective Partnership • The Case for Optimal Replication Topology – Changes MUST Converge • Eventually • Preferably On-Time § The Additional Complexity of Multi-Domain Infrastructure – The Infrastructure Master – The Global Catalog § Useful tool: Active Directory Replication Status Tool – http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=30005
- 5. Active Directory Overview § How Do They Do That? – Overview of AD Replication – The Directory Service Agent GUID • Unique to a Domain Controller • Persistent over the life of a Domain Controller • Used in USNs to track DC’s originating updates – The InvocationID • Used by DSA to identify a DC’s instance of the AD database • Can change over time (e.g. during a DC restore operation) – Update Sequence Number (USN), aka “Logical Clock” • Used by DCs to track updates sent or received • Increases per write transaction on each DC • Globally unique in Forest – USN + InvocationID => Replicable Transactions § What about Timestamps? – Conflict Resolution – Check the Stamps • Stamp = Version + Originating Time + Originating DSA
- 6. Why Virtualize Active Directory?
- 7. Why Virtualize AD? Active Directory virtualization is FULLY supported “Virtualize First” – the new normal No longer a “black magic” Virtualization is main-stream Active Directory characteristics are virtualization-friendly Domain Controllers are inter- changeable All roles are suitable candidates Can’t spell “Cloud” w/o “Virtual” Distributed, Multi-master Low I/O and resource requirements OK, maybe not the RODC J Facilitates rapid provisioning Physical Domain Controllers Waste Compute Resources $$$$ A single DC cannot utilize compute resources available on modern server hardware
- 8. Common Objections to DC Virtualization The fear of the “stolen vmdk” How about the “stolen server”? Or “stolen/copied backup tape”? Use array-, disk- or file-level encryption for added security Privilege Escalation* vCenter privileges do NOT elevate Windows or AD privileges Have to keep the xyz Operations Master role holder physical No technical reasoning for this Roles can be transferred or seized Deviates from our build process or standards Virtualization improves standardization Use templates for optimization
- 10. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers The “low-hanging fruit” • Deploy across multiple datacenters – Multiple geographical locations and AD Sites • Distribute the FSMO (Operations Masters) roles – First DC ALWAYS own all the roles • Can lead to high CPU utilization – Follow Microsoft Operations Master Role Placement Best Practices • http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754889.aspx • Use EFFECTIVE Role-Based Access Control – Grant Domain Admin rights only to trusted operators • A Domain Admin’s access CANNOT be restricted in the domain • Virtual infrastructure Admins do NOT require Domain Admin privileges • Domain Admins do NOT require Virtual infrastructure Admin privileges • Enforce Well-Defined Administrative Practices • To P2V or Not to P2V? • Follow our recommended practices http://kb.vmware.com/kb/1006996
- 11. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers Leverage VMware Availability Features • vSphere HA – Complements ADDS native high-availability features – Reduces downtime for critical Operations Master roles • vSphere DRS Rules – Efficient resource-balancing and utilization – Reduces resource wastage and improves consolidation • Use Anti-affinity rules to keep DCs separated – Avoids “eggs-in-one-basket” failure scenario • Use Host-Guest affinity rules to keep DCs on specific Hosts – Answers the “where’s my Domain Controller?” question • vMotion – True agility – Improves maintenance and patching procedure - without downtime
- 12. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers Domain Controller Sizing • Sizing domain controllers properly is key to good performance – Don’t assume DCs sit idle and don’t need a lot of resources. – Use capacity planning tools such as VMware Capacity Planner and/or Microsoft Assessment and Planning Toolkit to determine current state usage. – Resource requirements are highly dependent on total number of objects and rate of change in the environment. • CPU – Domain controllers are not typically heavy consumers of CPU resources. – Actual CPU usage varies by environment and by use case. • CPU usage in branch office serving primarily authentication function likely to be lower than in larger offices. – General sizing guidance: • 1 – 10,000 users = 1 vCPU. Greater than 10,000 users = 2 vCPU • If unsure, start with 2 vCPUs and scale up as needed.
- 13. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers Domain Controller Sizing • Memory – Domain controllers are similar to database servers – can cache AD database in RAM for faster read performance. – Monitor “Database/Database Cache % Hit” counter for “lsass” process to determine current cache usage. Low hit rate likely indicates DC needs more RAM. – Large forests with millions of objects can consume large amounts of memory. Not unusual to see DCs with 32GB of RAM for very large forests. • Networking – Domain controllers rely on replication to stay in sync. – Use VMXNET3 virtual NIC for best performance and lowest CPU utilization on domain controllers. • Storage – Need enough space to store AD database (plus room to grow), plus OS files & any other software. – DCs not particularly I/O intensive. Can offload read I/O to RAM.
- 14. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers What’s in a Name? • ~ 75% of AD-related support calls attributable to DNS “issues” • AD DEPENDS on effective name resolution – Clients and DCs reference objects by name/GUID – Internal AD processes depend on DNS • The “Initial Replication” conundrum – get your DNS right – DCs MUST perform successful “initial synchronization” on boot-up – DNS service will not start if not successful – DCs cannot synchronize if name resolution not working – The “Repl Perform Initial Synchronizations” Curse Word • Against Microsoft’s recommended practice – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2001093 – HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesNTDSParameters Value name: Repl Perform Initial Synchronizations Value type: REG_DWORD Value data: 0
- 15. Domain Controllers and DNS – Get it Right! DNS Service: 10.10.10.10 DC-1 What’s my IP? IP Address: 10.10.10.10 Hey, DNS! Who is DC-2.mydomain.local? Boots up What’s my DNS IP? DNS Address: 10.10.10.10 Must sync with DC-2.mydomain.local Must start DNS service I don’t know. I’m not Started.Hey, DNS Service! Please startI’m unable to start. You must sync first!
- 16. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers What’s in a Name? • Native AD DNS or IP Address Management Appliance? – Native AD DNS is “Free” – Physical IPAM can complicate DR testing – Solution must be AD-aware – Should support dynamic SRV records registration – not a MUST • Other Considerations – Avoid pointing DC to ONLY itself for DNS – see previous movie J – Distribute DNS servers across multiple sites – Include loopback (127.0.0.1) address in DNS list • Makes configuration and maintenance easier – Include ALL Suffixes in domain or forest – or use GlobalNames • Makes name resolution easier and more optimal • Depends on corporate administrative practices
- 17. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers It is about Time • ACCURATE timekeeping is essential to AD – Conflict resolution “tie breaker” – Kerberos authentication – W32Time is “good enough” • Operating Systems use timer interrupts (ticks) to track elapsed time – Relies on CPU availability for accuracy • Tickless timekeeping avoids problem of CPU saturation – Uses units of elapsed time since boot-up – Depends on fast, reliable “hardware counter” • Host resource over-allocation will lead to contention – Idle guests may not schedule timer interrupts – Guest unable to schedule CPU time for interrupts, leading to backlog and drift – Guest may over-compensate for “drift” by discarding backlogs – Ping-Pong!
- 18. Best Practices for Virtualizing Domain Controllers It is about Time • vSphere includes time-keeping mechanism • VMware Tools is the delivery vehicle – Resets Guest’s clock to match Host’s on boot-up • Even if Guest-Host clock synchronization is disabled – Reset Guest’s clock when resuming from suspension or snapshot restore • This behavior can be disabled • Synch with Host or Use Windows domain time hierarchy? – We have had a change of heart • Default guest time synchronization option changed in vSphere • Domain-joined Windows guests should use native time sync option • Domain Controllers should NOT be synced with vSphere hosts * – Unless when running VMKernel-hosted NTP daemon in vSphere (ESXi) • vSphere hosts should NOT be synced with virtualized DCs • Follow Microsoft’s time sync configuration best practices • VMtools STILL performs guest time correction during certain operations*
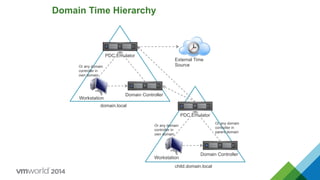
- 19. Domain Time Hierarchy PDC Emulator Domain Controller Workstation External Time Source PDC Emulator Domain Controller Workstation Or any domain controller in parent domain Or any domain controller in own domain Or any domain controller in own domain domain.local child.domain.local
- 20. Proper Time Keeping – For Visual Learners Stratum-1 Time Source Forest-root PDC Emulator http://support.microsoft.com/kb/816042 http://kb.vmware.com/kb/1318 http://www.vmware.com/files/pdf/techpaper/Timekeeping-In-VirtualMachines.pdf ESXi Host Or tools.syncTime = "0" Domain Controller Domain Members
- 21. Historical Problems with Virtualizing Domain Controllers • Virtual Disk – To cache or not to cache? – Not our problem a vSphere issue J – Force Unit Access – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/888794/en-us – Virtual Disk Corruption in Hyper-V – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2853952 • AD is a distributed directory service that relies on a clock-based replication scheme – Each domain controller keeps track of its own transactions and the transactions of every other domain controller via Update Sequence Numbers and InvocationIDs – A domain controller which has been reverted to a previously taken snapshot, or restored from a VM level backup will attempt to reuse USNs for new transactions – USN Rollback – The local DC will believe its transactions are legit, while other domain controllers know they are not and refuse to allow incoming replication • Why is USN Rollback so bad?
- 22. Way back when…… Why Some Fear Virtualizing DCs
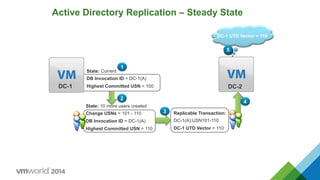
- 23. Active Directory Replication – Steady State 4 Replicable Transaction: DC-1(A);USN101-110 DC-1 UTD Vector = 110 3 DC-2 DC-1 UTD Vector = 100 15 DC-1 UTD Vector = 110 2 State: 10 more users created Change USNs = 101 - 110 DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 110 1 DC-1 State: Current DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 100
- 24. Users Created After VM Snapshot 4 Replicable Transaction: DC-1(A);USN111-120 DC-1 UTD Vector = 120 3 State: 10 more users created Change USNs = 111 - 120 DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 120 5 DC-2 1 DC-1 UTD Vector = 110DC-1 UTD Vector = 120 6 1 State: Current DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 110DC-1 State: Snapshot Created DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 110 2 DC-1
- 25. DC Reverted to Previous Snapshot State: Snapshot Reverted DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 2 DC-1 110 1 DC-1 State: Current (Snapshot Taken) DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 120
- 26. USN Rollback Effect after Reverting Snapshot 3 Replicable Transaction: DC-1(A);USN111-120 2 State: 10 more users created Change USNs = 111 - 120 DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) 4 1 DC-2 DC-1 UTD Vector = 120 DC-1 State: Snapshot Reverted DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 110 1 Bad DC! Off with You!!!
- 27. In the Present Time…… “Safely” Getting Over Your Fears
- 28. Introducing Domain Controller “Safety” Features
- 29. VM Generation ID • Windows Server 2012 provides a way for hypervisor vendors to expose a 128-bit generation ID counter to the VM guest – Generation ID is communicated from the hypervisor to the guest through the VM GenerationID Counter Driver (not VMware Tools) • VM GenerationID supported in vSphere 5.0 Update 2 and later – Exposed in VMX file as vm.genid or vm.genidx – Added to all VMs configured as Windows Server 2012 • VM GenerationID tracked via new Active Directory attribute on domain controller objects – msDS-GenerationId – Attribute is not replicated to other domain controllers • Changes in VM Generation ID is first line of defense against USN Rollback – Reverting snapshots triggers VM GenID changes – VM GenID changes triggers Domain Controller “Safety” mechanism • Provides 2 DISTINCT Benefits: – Safety – Cloning
- 30. Where is VM GenerationID Stored?
- 31. vSphere Operations that Trigger VMGenID Changes Scenario VM-Generation ID Change VMware vSphere vMotion®/VMware vSphere Storage vMotion No Virtual machine pause/resume No Virtual machine reboot No vSphere host reboot No Import virtual machine Yes Cold clone Yes Hot clone NOTE: Hot cloning of virtual domain controllers is not supported by either Microsoft or VMware. Do not attempt hot cloning under any circumstances. Yes New virtual machine from VMware Virtual Disk Development Kit (VMDK) copy Yes Cold snapshot revert (while powered off or while running and not taking a memory snapshot) Yes Hot snapshot revert (while powered on with a memory snapshot) Yes Restore from virtual machine level backup Yes Virtual machine replication (using both host-based and array-level replication) Yes CONFIDENTIAL
- 33. Domain Controller Cloning § DC Cloning enables fast, safer DC provisioning through clone operation – Includes regular VM cloning and manual VMDK copy operations § DC Cloning Sequence – Prepare Source DC for cloning • Add the DC to the cloneable domain controllers AD group • Check for non-cloneable software • Create the DCCloneConfig.xml configuration file – Shut down Source DC* – Clone Source DC VM, using hypervisor based cloning operations – Power on New DC • VM GenerationID is evaluated • New VM GenerationID triggers DC Safeguard – RID Pool is discarded – invocationID is reset • New VM checks for existence of file DCCloneConfig.xml – If exists, the cloning process proceeds • New DC is promoted using the existing AD database and SYSVOL contents
- 34. Domain Controller Cloning Example Source DC: msDS-GenerationId = 001 W2K12-DC02 192.168.11.41 vSphere Host W2K12-DC02: vm.genid = 001 Clone DC: msDS-GenerationId = 001 W2K12-DC02 192.168.11.41 Clone DC: msDS-GenerationId = 002 W2K12-DC02 192.168.11.41 Clone DC: msDS-GenerationId = 002 W2K12-DC03 192.168.11.42 vSphere Host W2K12-DC02: vm.genid = 001 W2K12-DC03: vm.genid = 002 VM GenerationID Counter Driver
- 36. Domain Controller Safeguard § DC Safeguard allows a DC that has been reverted from a snapshot, or restored from VM backup to continue to function as a member of the directory service • VM GenerationID is evaluated during boot sequence and before updates are committed to Active Directory § After revert/restore: • Boot-up or new AD update triggers VM GenerationID to be compared to value of msDS-GenerationId in local AD database • If the values differ: • The local RID pool is invalidated • New invocationID is set for the local AD database • New changes can be committed to the database and synchronized outbound • Changes lost due to revert/restore are synchronized back inbound § After VM Clone or Copy (without proper prep) • DC is rebooted into directory service restore mode (DSRM)
- 37. DC Safeguard Example DC01 VM GenID: 001 InvocationID: A Starting USN: 101 DC02 User 1 USN 101 InvID: A User 1 USN 101 InvID: DC01(A) Base DiskSnapshotBase Disk vSphere Host DC01 vm.genid = 001002 User 2 USN 101 InvID: B DC01 VM GenID: 002 InvocationID: B Starting USN: 101 User 2 USN 101 InvID: DC01(B) User 1 USN 101 InvID: A VM GenerationID Counter Driver Non-authoritative restore of differences
- 38. State: Snapshot Reverted DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 110 DC Reverted to Previous Snapshot with Safeguard 1 DC-1 State: Current (Snapshot Taken at USN=110) DB Invocation ID = DC-1(A) Highest Committed USN = 120 2 DC-1 ESXi Host State: New GenID Triggered VM: DC-1 vm.genid: <new value> 3 State: DC Safeguard Complete DB Invocation ID = DC-1(B) Highest Committed USN = 110 4 DC-1
- 39. 3 2 1 Replication after safeguard DC-1 State: Snapshot Reverted DB Invocation ID = DC-1(B) Highest Committed USN = 110 State: 10 more users created Change USNs = 111 - 120 DB Invocation ID = DC-1(B) Replicable Transaction: DC-1(B);USN111-120 DC-2 Non-authoritative restore: DC-1(A);USN111-120
- 40. Domain Controller Safeguard § Just because you can take/revert a snapshot of a domain controller, does that mean you should? § What are some valid reasons for using virtual machine snapshots with domain controllers? • Backup software that takes “image level” backups typically rely on snapshots to ensure consistent backups. • Need to install software on a virtualized domain controller and want the ability to revert in case there are issues. § Even with this ability, remember that snapshots are not backups. • It is often easier to deploy a new server & promote to domain controller rather than trying to restore a domain controller from a backup. § In general – it is unlikely you’ll frequently use this feature but good to know it’s there if you need it.
- 42. Considerations When Using DC Cloning Features • When performing DC Cloning operation: – Always shutdown reference domain controller prior to cloning • No Hot-clone! Besides, it’s not supported. – Ensure that the reference DC holds no Operations Master Role • Specifically, you can’t clone a RID-Master Role holder – You can clone the PDCe, but ….. • You must power on the reference DC before powering on the new clone – DNS MUST be reachable during the cloning process • When performing Mass DC cloning operation: – No “-CloneComputerName” or “-Static -IPv4Address” in dccloneconfig.xml – Ensure that DHCP is functional in the infrastructure – DON’T turn on the reference DC until you have finished all mass cloning • The dccloneconfig.xml file is automatically renamed as soon as Windows starts • Alternatively, convert the clone to a template and deploy new DCs from template – Re-usable template is only as good as the Tombstone Lifetime value of the domain • Do NOT perform “Guest Customization” when cloning a DC – It breaks the “safety” feature!!!
- 43. General Considerations for Cloning/Safeguard Features • Minimum vSphere/vCenter/ESXi version: 5.0 Update 2 • Guest Operating System version MUST be set to Windows Server 2012 – VM Generation ID will not be generated for any lower version • Leave “Cloneable Domain Controllers” AD security group empty in- between clone operations – Helps prevent unintended DC cloning – Helps enforce RBAC • Domain Admin populate group, vSphere Admin performs cloning, etc. • Validate all software (think management/backup agents) for cloning – VMware Tools is safe for cloning • If using Windows Backup, delete backup history on the clone, and take a fresh backup ASAP • Clone DC Templates will become stale – think “Tombstone” • Incorrect preparation will put clone in DSRM “Jail” • See - DC cloning fails and server restarts in DSRM (MS KB 2742844)
- 44. Key Take Aways… § Dangers which were once present when virtualizing DCs have mostly been resolved in Windows Server 2012 § Domain Controller virtualization is 100% supported § Multi-master, distributed, and low resource utilization characteristics of Active Directory make domain controllers virtualization-friendly § Physical and virtual Domain Controller best practices are identical § Same considerations around Time, Security, DNS, Availability, etc – Physical Servers can experience clock drift, too § Active Directory is natively highly available – vSphere High Availability complements it and help mitigate hardware failures § Upgrade to Windows Server 2012 to bring domain controller safeguard and cloning to the party.
- 45. Effects of DC “Safety” on Disaster Recovery • Special considerations required for site-wide Disaster Recovery plan • Disaster connotes complete site (or AD) outage • Must recover multiple DCs or entire AD infrastructure • Recovery could be from backup or orchestrated (e.g. VMware SRM) • Remember “DC Safety” workflow logic during a DC “recovery” – Hypervisor changes VM Generation ID of recovered DC • What if one of the recovered DCs is the RID-Master? – RID Pool cannot be obtained while RID Master is down – RID Master cannot issue RID pools until it has replicated with other DCs • Avoiding the conundrum • Always have DCs in multiple sites • Replicate RID-Master and PDCe (at least) to DR site as part of DR Plan • Restart Directory Service on RID-Master – Use the Powershell command (restart-service NTDS -force) – Then force replication to another DC not impacted by outage (if available) • Reboot RID-Master AFTER all other DCs have started • Or, just wait ….. For a sufficiently long time …. Yeah Right!
- 46. Protecting Active Directory with SRM
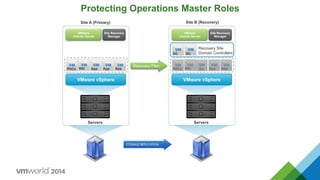
- 47. Protecting Operations Master Roles VMware vSphere VMware vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager Servers PDCe RID App App App VMware vSphere VMware vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager Servers PDCe RID App App Site A (Primary) Site B (Recovery) Recovery Plan DC DC Recovery Site Domain Controllers DC
- 48. Using Primary Site DC During DR Testing VMware vSphere VMware vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager Servers App App App App App DC-1 VMware vSphere VMware vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager Servers App App App App App DC-1 Site A (Primary) Site B (Recovery) Recovery Plan Test Only DC-2
- 49. Cloning Recovery Site DC During RP Testing VMware vSphere VMware vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager Servers App App App App App DC-1 VMware vSphere VMware vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager Servers App App App App App DC-2 Site A (Primary) Site B (Recovery) Recovery Plan Test Only DC-2
- 50. Shameless Plug • Virtualizing Microsoft Business Critical Applications on VMware vSphere – Authors: Matt Liebowitz, Alex Fontana • Covers Active Directory, Exchange Server 2013, SQL Server 2012, and SharePoint Server 2013 • Not just technical – covers building a business case, objection handling, & more! • Book signing – Tuesday at 12:00PM in VMworld Bookstore. 50
- 51. Thank You
- 52. Fill out a survey Every completed survey is entered into a drawing for a $25 VMware company store gift certificate
- 53. Virtualize Active Directory, the Right Way! VAPP1340 Deji Akomolafe, VMware Matt Liebowitz, EMC Corporation



















































































![Kb 40 kevin_klineukug_reading20070717[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/kb40kevinklineukugreading200707171-101026100915-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






















































