A Study and Comparative analysis of Conditional Random Fields for Intrusion detection
- 1. International Journal of Research in Computer Science eISSN 2249-8265 Volume 2 Issue 4 (2012) pp. 31-38 © White Globe Publications www.ijorcs.org A STUDY AND COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS FOR INTRUSION DETECTION Deepa Guleria1, M.K.Chavan2 1 PG Scholar, VPCOE Baramati Email: [email protected] 2 Asstt Professor, VPCOE Baramati Email:[email protected] Abstract: Intrusion detection systems are an important Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and the component of defensive measures protecting computer other is Host Intrusion Detection Systems systems and networks from abuse. Intrusion detection (HIDS).NIDS monitors the packets from the network plays one of the key roles in computer security and it is an independent platform that identifies techniques and is one of the prime areas of research. intrusion by examining the network traffic and Due to complex and dynamic nature of computer multiple hosts. HIDS analyzes the audit data of the networks and hacking techniques, detecting malicious operation system and monitors the inbound and activities remains a challenging task for security outbound packets from the device only. It alerts the experts, that is, currently available defense systems user or administrator of suspicious activity is detected suffer from low detection capability and high number [7].Intrusion detection systems can also be classified of false alarms. An intrusion detection system must as signature based or anomaly based depending upon reliably detect malicious activities in a network and the attack detection method. The signature-based must perform efficiently to cope with the large amount systems are trained by extracting specific patterns (or of network traffic. In this paper we study the Machine signatures from previously known attacks while the Learning and data mining techniques to solve anomaly-based systems learn from the normal data Intrusion Detection problems within computer collected when there is no anomalous activity. The networks and compare the various approaches with first approach is called as Misuse Detection and leads conditional random fields and address these two issues us towards Signature Based IDS while the second is of Accuracy and Efficiency using Conditional Random called as Anomaly Detection and leads us to Behavior Fields and Layered Approach. based IDS. The Signature based systems though have very high detection accuracy but they fail when an Keywords: Intrusion Detection System, Conditional attack is previously unseen. On the other hand, Random Fields, Network Security, Decision tree Behavior based IDS or anomaly based may have the I. INTRODUCTION ability to detect new unseen attacks but have the problem of low detection accuracy [7]. Another An intrusion detection system monitors the approach for detecting intrusions is to consider both activities of a given environment and decides whether the normal and the known anomalous patterns for these activities are malicious (intrusive) or legitimate training a system and then performing classification on (normal) based on system integrity, confidentiality and the test data. Such a system incorporates the the availability of information resources. Intrusion advantages of both the signature-based and the detection as defined by the Sysadmin, Audit, anomaly-based systems and is known as the Hybrid Networking, and Security (SANS) institute is the act of System. detecting actions that attempt to compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability of a resource Hybrid systems can be very efficient, subject to the [1]. Detecting intrusions in networks and applications classification method used, and can also be used to has become one of the most critical tasks to prevent label unseen or new instances as they assign one of the their misuse by attackers. The cost involved in known classes to every test instance. This is possible protecting these valuable resources is often negligible because during training the system learns features from when compared with the actual cost of a successful all the classes. The only concern with the hybrid intrusion, which strengthens the need to develop more method is the availability of labeled data. Further, a powerful intrusion detection systems. single system has limited attack detection coverage and it cannot detect a wide variety of attacks reliably. There are two types of IDS depending on their mode of deployment and data used for analysis. www.ijorcs.org
- 2. 32 Deepa Guleria, M.K.Chavan We introduce hybrid intrusion detection systems based involve computing a distance between numeric on conditional random fields which can detect a wide features and therefore they cannot easily deal with variety of attacks and which result in very few false symbolic attributes, resulting in inaccuracy. Addition, alarms. To improve the efficiency of the system, we clustering methods consider the features independently then integrate the layered framework. and are unable to capture the relationship between different features of a single record which results in II. APPROACHES TO IMPLEMENT IDS lower accuracy [9]. Intrusion detection has been an active field of Data Mining: Data mining (DM), also called research for starting in 1980s after the influential paper Knowledge-Discovery and Data Mining, is the process from Anderson [7]. Several researchers have proposed of automatically searching large volumes of data for various intrusion detection methods and frameworks patterns using association rules. Data mining which are available to protect a computer system or approaches derive association rules and frequent network from attacks. Various techniques such as episodes from available sample data, not from human association rules, clustering, Naïve Bayes, Support experts. Using these rules, Lee et. al. developed a data Vector Machines, Neural Networks, and others have mining framework for the purpose of intrusion been developed to detect intrusions. This section detection[8].In particular, system usage behaviors are provides a brief literature review on these technologies recorded and analyzed to generate rules which can and related frameworks. These methods can be broadly recognize misuse attacks. The drawback of such divided into three major categories: frameworks is that they tend to produce a large number of rules and thereby, increase the complexity of the A. Pattern Matching system. Pattern Matching is the simple type of attack Bayesian Classifiers: A Bayesian network is a model detection technique. It has the simple concept of string that encodes probabilistic relationships among matching. Using pattern matching technique, IDSs variables of interest. This technique is generally used generally match the text (audit records) or binary for intrusion detection in combination with statistical sequences against known attack signatures. A pattern schemes, a procedure that yields several advantages, matching technique basically looks for a specific including the capability of encoding interdependencies attack signature which may be presented in audit between variables and of predicting events, as well as record. The limitation of pattern matching approach is the ability to incorporate both prior knowledge and that it can recognize only known attacks. It requires data. However, a serious disadvantage of using continuous updates of attack signatures to identify new Bayesian networks is that their results are similar to attacks. Pattern matching approach is well suited for those derived from threshold-based systems, while misuse detection. Snort system is based upon pattern considerably higher computational effort is required. matching. Decision Trees: Decision trees are one of the most B. Statistical Methods commonly used supervised learning algorithms in IDS due to its simplicity, high detection accuracy and fast Statistical modeling is among the earliest methods adaptation. Decision trees used for intrusion detection used for detecting intrusions in electronic information select the best features for each decision node during systems. It is assumed that an intruder’s behavior is tree construction based on some well-defined criteria noticeably different from that of a normal user, and [11]. One such criterion is the gain ratio which is used statistical models are used to aggregate the user’s in C4.5. behavior and distinguish an attacker from a normal user. The techniques are applicable to other subjects, A decision tree is composed of three basic elements: such as user groups and programs. Two statistical 1. A decision node specifying a test attributes. models that have been proposed for anomaly detection: 2. An edge or a branch corresponding to the one of NIDES/STAT and Haystack. the possible attribute values which means one of the test attribute outcomes. C. Data Mining and Machine Learning 3. A leaf which is also named an answer node Data mining and machine learning methods focus contains the class to which the object belongs. on analyzing the properties of the audit patterns rather than identifying the process which generated them. Artificial Neural Networks: Neural networks are These methods include approaches for mining known for good performance in learning system-call association rules, classification and cluster analysis. sequences. Once the neural net is trained on a set of representative command sequences of a user, the net constitutes the profile of the user, and the Clustering: For unsupervised intrusion detection, data fraction of incorrectly predicted events then clustering methods can be applied. These methods measures, in some sense, the variance of the user www.ijorcs.org
- 3. A Study and Comparative Analysis of Conditional Random Fields for Intrusion Detection 33 behavior from his profile. They can work effectively specific requirements of the environment where it with noisy data but they require large amount of data is deployed. for training and it is often hard to select the best possible architecture for the neural network [12]. IV. CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS Support Vector Machines: Support vector map real A. Conditional Probability valued input feature vector to higher dimensional Conditional probability is used to compute feature space through nonlinear mapping and have probability of an event Y given some other event X. been used for detecting intrusions. They can provide 𝑃(𝑋 ∩ 𝑌) Formally it is defined as: 𝑃(𝑌 | 𝑋) = real-time attack detection capability, deal with large 𝑃(𝑋) dimensionality of data and perform multi class classification. Similar to the pattern matching and statistical methods, these methods assume independence among consecutive events and hence do Where P(X) > 0. From this definition we can read that not consider the order of occurrence of events for if the occurrence of the event X takes place in the same attack detection [17]. space as the event Y, and there are no other events that may act the occurrence of the event Y, then the Markov Models: Markov chains and hidden Markov conditional probability of the occurrence of the event model is a set of states that are interconnected through Y given the event X is the relative proportion of certain transition probabilities, which determine the outcomes that satisfy Y among those that satisfy X. topology and the capabilities of the model. During a first training phase, the probabilities associated to the B. Conditional Random Field Framework transitions are estimated from the normal behavior of Conditional random fields [15] (CRFs) are a the target system. The detection of anomalies is then probabilistic framework for labeling and segmenting carried out by comparing the anomaly score sequential data, based on the conditional approach (associated probability) obtained for the observed described in the previous paragraph. A CRF is a form sequences with a fixed threshold. Markov chains and of undirected graphical model that defines a single log- hidden Markov models can be used when dealing with linear distribution over label sequences given a sequential representation of audit patterns. Hidden particular observation sequence. The primary Markov models have been shown to be effective in advantage of CRFs over hidden Markov models is modeling sequences of system calls of a privileged their conditional nature, resulting in the relaxation of process, which can be used to detect anomalous traces [13] the independence assumptions required by HMMs in . However, modeling system calls alone may not order to ensure tractable inference. Additionally, CRFs always provide accurate classification as various avoid the label bias problem [14], a weakness connection level features are ignored. Further, hidden exhibited by maximum entropy Markov models [16] Markov models cannot model long range dependencies (MEMMs) and other conditional Markov models between the observations. based on directed graphical models. CRFs outperform both MEMMs and HMMs on a number of real-world III. CHALLENGES AND REQUIREMENT FOR sequence labeling tasks. INTRUSION DETECTION SYSTEM It is important intrusion detection must detect CRF was firstly proposed by Lafferty and his attacks at an early stage in order to minimize their colleagues in 2001, [15] whose model idea mainly impact. The major challenges and requirements for came from MEMM (Maximum Entropy Markov building intrusion detection systems are: Model).The critical difference between CRFs and MEMMs is that a MEMM uses per-state exponential i. The system must be able to detect as many models for the conditional probabilities of next states attacks as possible without giving false alarms i.e given the current state, while a CRF has a single the system must be accurate in detecting attacks. exponential model for the joint probability of the entire ii. The system must be able to handle large amount sequence of labels given the observation sequence. of data without affecting performance and Therefore, the weights of different features at different without dropping data. states can be traded off against each other. Conditional iii. A system must not only detect an attack, but also models are probabilistic systems that are used to model able to identify the type of attack. the conditional distribution over a set of random iv. A system must be resistant to attacks since, a variables. Such models have been extensively used in system that can be exploited during an attack may the natural language processing tasks. Conditional not be able to detect attacks reliably. models offer a better framework as they do not make v. The challenge is to build a system which is any unwarranted assumptions on the observations and scalable and can be easily customized as per the can be used to model rich overlapping features among the visible observations [6]. www.ijorcs.org
- 4. 34 Deepa Guleria, M.K.Chavan Lafferty, McCallum and Pereira define a CRF on distribution, using the Bayes rule, requires marginal observations and random variables as follows: distribution p(x) which is difficult to estimate as the amount of training data is limited and the observation x Let X be the random variable over data sequence to contains highly dependent features. As a result strong be labeled and Y the corresponding label sequence. independence assumptions are made to reduce In addition, let G = (V , E ) be a graph such that Y is complexity. This results in reduced accuracy. indexed by the vertices of G . Then, ( X , Y ) is a attack attack attack attack attack CRF, when conditioned on X , the random variables v obey the Markov property with respect to the Y graph: p (Yv | X , Yw, w ≠ v ) =Yv | X , Yw, w v ) p( where w ~ v means that w and v are neighbors in G , duratio protocol n=0 service= flag= src_byt i.e., a CRF is a random field globally conditioned on =icmp echo_i SF e= 8 X . For a simple sequence (or chain) modeling, as in our case, the joint distribution over the label (a) Attack event sequence Y given X has the following form: pθ ( y x ) α exp ∑ λ kfk ( e, y e , x ) + ∑ µ kgk ( v, y v , x ) , (1) normal normal normal normal normal e∈E ,k v∈V ,k where x is the data sequence, y is a label sequence, and Y S is the set of components of y associated with the vertices or edges in subgraph S. In addition, the features fk and gk are assumed to be given and fixed. duratio protocol service n=0 flag= src_byte = tcp = smtp Further, the parameter estimation problem is to find SF = 4854 the parameters θ = ( λ 1, λ 2,....; µ 1, µ 2....) from the (b) Normal event D = ( x' , yi ) N training data with the empirical i =1 Figure 2: Conditional Random Fields for Network distribution p ( y, x ) Intrusion Detection In the figure 2, observation features ‘duration’, labels y1 y2 y3 y4 ‘protocol’, ‘service’, ‘flag’ and ‘source bytes’ are used to discriminate between (att) attack and (nor) normal events. The features take some possible value for every connection which are then used to determine the most likely sequence of labels < attack, attack, attack, attack, attack > or < normal, normal, normal, normal, Observations x1 normal >. During training, feature weights are learnt x2 x3 x4 and during testing, features are evaluated for the given Figure 1: Graphical Representation of a CRF observation which is then labeled accordingly. It is evident from the figure that every input feature is The graphical structure of a conditional random connected to every label which indicates that all the field is represented in Figure1 where x1, x2, x3, x4 features in an observation determine the final labeling represents an observed sequence of length four and of the entire sequence. Thus, a conditional random every event in the sequence is correspondingly labeled field can model dependencies among different features as y1, y2, y3, y4.The prime advantage of conditional in an observation. Present intrusion detection systems random fields is that they are discriminative models do not consider such relationships. which directly model the conditional distribution p ( y | x ) .Generative models such as the Markov chains, The task of intrusion detection can be compared to many problems in machine learning, natural language hidden Markov models and joint distribution have two processing, and bioinformatics. The CRFs have proven disadvantages. First, the joint distribution is not to be very successful in such tasks, as they do not required since the observations are completely visible make any unwarranted assumptions about the data. and the interest is in finding the correct class which is Hence, we explore the suitability of CRFs for building the conditional distribution p ( y | x ) .Second, inferring efficient and accurate intrusion detection. conditional probability p ( y | x ) from the joint www.ijorcs.org
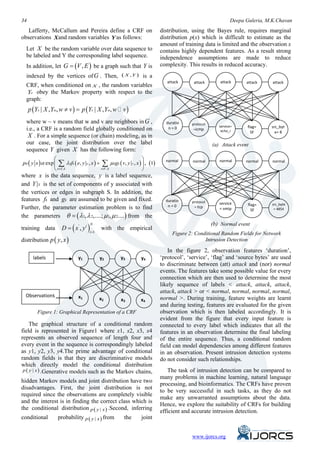
- 5. A Study and Comparative Analysis of Conditional Random Fields for Intrusion Detection 35 C. Inference in CRF D. Detecting network intrusions using layered Approach For general graphs, the problem of exact inference in CRFs is intractable. However there exist special Researchers are motivated to propose different cases for which exact inference is feasible: approaches seeing the low detection rates caused by the imbalanced network intrusion dataset. Current • If the graph is a chain or a tree, message passing research work proposes a staged or layered approach algorithms yield exact solutions. The algorithms to detect network intrusions efficiently. The recent used in these cases are analogous to the forward- research work of Gupta and Nath [6], considered the backward and Viterbi algorithm for the case of attack categories as layers and different features were HMMs. selected for each layer. The dataset was, therefore, • If the CRF only contains pair-wise potentials and divided into five attack categories for training and the energy is submodular, combinatorial min testing purposes of each layer. The test data passed cut/max flow algorithms yield exact solutions. through the cascaded layers to determine the category All Features Yes Yes Probe Layer DoS Layer Normal Normal Feature Selection Feature Selection No No Block Block Yes Yes R2L Layer U2R Layer Normal Normal Allow Feature Selection Feature Selection No No Block Block Figure 3: Integrating the Layered Framework a record that belonged to Conditional Random Fields V. EXPERIMENTAL METHODOLOGY (CRFs) were used in the layered approach as proposed by the researcher [6]. The three layer system to ensure The Data Set complete security viz. availability, confidentiality and integrity, each layer corresponding to one aspect of The data set used for the entire course of research is security. In the system, every layer is trained the DARPA KDD99 benchmark data set [4], also separately with the normal instances and with the known as “DARPA Intrusion Detection Evaluation attack instances belonging to a single attack class. data set” that not only includes a large quantity of Here the features involved were different in each layer. network traffic but also collects a wide variety of Explanation of which features should be used or not be attacks. They setup an environment to collect TCP/IP used was given in the paper. However, the complete dump from a host located on a simulated military feature list for each layer was not presented in the network. Each TCP/IP connection is described by 41 paper. The above staged and layered approaches used discrete and continuous features and labeled as either classifiers of the same type or of different types for the normal or as an attack. Attacks fall into following detecting network intrusions. The approaches handled four main classes: the attacks separately to minimize the attack categories from affecting each other in classification or detection A. Denial of service (DOS) tasks. Since every layer in Layered framework is In this type of attack an attacker makes some independent, feature sets for all the four layers are not computing or memory resources too busy or too full to disjoint. The final goal is to improve both the attack handle legitimate requests or denies legitimate users detection accuracy and the efficiency of the system. access to a machine. Examples are Apache2, Back, Hence, by integrating the CRFs and the Layered Land, Smurf, Teardrop. Approach can build efficient and accurate single system. www.ijorcs.org
- 6. 36 Deepa Guleria, M.K.Chavan B. Remote to user (R2L) difficult to choose a particular method to implement an intrusion detection system over the other. This paper In this type of attack an attacker who does not have has drawn the conclusions on the basis of an account on a remote machine sends packets to that implementations performed using various techniques. machine over a network and exploits some New techniques keep emerging which will remove the vulnerability to gain local access as a user of that drawbacks of the previous methods of implementation. machine. Examples are Dictionary, Ftp_write, Guest, In this paper, a new efficient and robust hybrid Imap, Named. intrusion detection systems using conditional random C. User to root (U2R) field was discussed. The CRFs are very effective in improving the attack detection rate and decreasing the In this type of attacks an attacker starts out with FAR. Feature selection and implementing the Layered access to a normal user account on the system and is framework significantly reduce the time required to able to exploit system vulnerabilities to gain root train and test the model. The sequence labeling access to the system. Examples are Eject, Loadmo methods such as the CRFs can be very effective in dule, Ps, Xterm, Perl. detecting attacks and decreasing the false alarm rate. Compared approach with some well-known methods D. Probing and found that most of the present methods for In this type of attacks an attacker scans a network intrusion detection fail to reliably detect R2L and U2R of computers to gather information or find known attacks, while integrated system can effectively and vulnerabilities. Examples are Ipsweep, Mscan, Satan, efficiently detect such attacks Finally, system has the Nmap. advantage that the number of layers can be increased VI. CONCLUSION or decreased depending upon the environment in which the system is deployed, giving flexibility to the Thus we conclude that there are various approaches network administrators. The areas for future research and techniques to implement an intrusion detection include the use of Layered CRF method for extracting system based on its type and mode of deployment. features that can aid in the development of signatures Each of the approaches to implement an intrusion for signature-based systems. This can further be detection system has its own advantages and extended to implement pipelining of layers in disadvantages. This is apparent from the discussion of multicore processors, which is likely to result in very comparison among the various methods. Thus it is high performance. Techniques Method Parameters Advantages Disadvantages A support vector The effectiveness of SVM 1. Able to model complex 1. High algorithmic machine constructs a lies in the selection of nonlinear decision complexity and hyper plane or set of kernel and soft margin boundaries. extensive memory hyper planes in a high parameters. For kernels, 2. Highly accurate. requirements of the or infinite dimensional different pairs of (C, γ) 3. Provide real-time required quadratic Support space, which can be values are tried and the one detection capability programming in Vector used for classification, with the best cross- 4. Deal with large large-scale tasks. Machine regression or other validation accuracy is dimensionality of 2. The choice of the tasks. picked. Trying data. kernel is difficult exponentially growing 5. Can be used for binary-class 3. The speed is slow sequences of C is a as well as multiclass both in training and practical method to classification. testing. identify good parameters. The cluster with the Convert d based on the Can work in near linear time. 1. Observation must be shortest distance is statistical information of numeric. selected, and if that the training set from which 2. Consider the features distance is less than the clusters were created. independently and are some constant W 1. Let d1 be the instance unable to capture the (cluster width) then after conversion. relationship between the instance is 2. Find a cluster which is different features of a Clustering assigned to that closest to d1 under the single record which cluster. metric M (i.e. a cluster in results in lower the cluster set, such that accuracy. for all C1 in S, dist (C, d1) <= dist (C1, d1). 3. Classify d1 according to the label of C(either Normal or anomalous. www.ijorcs.org
- 7. A Study and Comparative Analysis of Conditional Random Fields for Intrusion Detection 37 An ANN is an ANN uses the cost function 1. Able to implicitly detect 1. Greater computational adaptive system that C is an important concept complex nonlinear burden. changes its structure in learning, as it is a relationships between 2. Requires long training Artificial based on external or measure of how far away a dependent and independent time. Neural internal information particular solution is from variables. 3. Hard to select the best Network that flows through the an optimal solution to the 2. High tolerance to noisy possible architecture network during the problem to be solved. data. for a neural network. learning phase. 3. Availability of multiple 4. Require large amount training algorithms. of data for training. Based on the rule, In Bayes, all model 1. Exhibit high accuracy and 1. Make strict using the joint parameters (i.e., class speed when applied to independence between probabilities of sample priors and feature large databases. the features in observations and probability distributions) 2. Capability of encoding observations results classes, the algorithm can be approximated with interdependences between lower attack detection attempts to estimate relative frequencies from variable and of predicating accuracy. the conditional the training set. events. 2. Lack of available Bayesian probabilities of classes 3. Abiltity to incorporate probability data. Method given an observation. both prior knowledge and 3. A fully connected data. Bayesian network is complex and difficult to train. 4. 4.Higher computational effort is required. Decision tree builds a Decision Tree Induction 1. Construction does not 1. Output attribute must binary classification uses parameters like a set require any domain be categorical. tree. Each node of candidate attributes and knowledge. 2. Limited to one output corresponds to a an attribute selection 2. Can handle high attribute. binary predicate on method. dimensional data. 3. Decision tree one attribute; one 3. Representation is easy to algorithms are Decision branch corresponds to understand. unstable. Tree the positive instances 4. Able to process both 4. Trees created from of the predicate and numerical and categorical numeric datasets can the other to the data. be complex. negative instances. 5. High speed of operation and high attack detection accuracy. Markov chains and During a first training 1. Modeling the ordering 1. May not always hidden Markov phase, the probabilities property of events results provide accurate models can be used associated to the transitions higher detection accuracy. classification as when dealing with are estimated from the 2. Effective in modeling various connection sequential normal behavior of the sequences of system calls level features are representation of audit target system. The of a privileged process ignored Hidden patterns detection of anomalies is 2. HMMs become very Markov then carried out by complex for long Models comparing the anomaly range dependencies score (associated in observations. probability) obtained for 3. Results inaccuracy as the observed sequences the correlation among with a fixed threshold features is lost. Conditional Random • For training: 1. CRF do not assume 1. Computational Fields are – Forward Backward observation features to be expense of training. discriminative and algorithm is used which independent 2. Complete list of Layered undirected graphical has a complexity of 2. Not prohibitively expensive features for each level Conditional models which are used O(K2T), where K is the in testing. is not available. Random for sequence tagging. number of states and T is 3. CRF training is feasible for Fields They do not make any the length of the many real-world. unwarranted sequence 4. Integrated system (CRF & assumptions about the Layered) achieves data. www.ijorcs.org
- 8. 38 Deepa Guleria, M.K.Chavan • For testing: significant improvement, – Viterbi algorithm is used both, in the time required to which also has the same train and test the system and complexity also in the attack detection accuracy (F-value). 5. CRFs are robust to noise in training data. 6. CRFs avoid the label bias problem. 7. CRFs avoid a fundamental limitation of maximum entropy Markov models (MEMMs). VII. REFERENCES [13] Y. Du, H. Wang, and Y. Pang, “A Hidden Markov Models-Based Anomaly Intrusion Detection Method,” [1] SANS Institute—Intrusion Detection FAQ, Proc. Fifth World Congress on Intelligent Control and http://www.sans.org/ resources/idfaq/, 2010. Automation (WCICA ’04), vol. 5, pp. 4348-4351, [2] Autonomous Agents for Intrusion Detection, 2004. http://www.cerias.purdue.edu/research/aafid/, 2010. [14] A. McCallum, “Efficiently Inducing Features of [3] CRF++: Yet Another CRF Toolkit, Conditional Random Fields,” Proc. 19th Ann. Conf. http://crfpp.sourceforge.net/,2010. Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI ’03), pp. 403-410, 2003. [4] KDD Cup 1999 Intrusion Detection Data, http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup99.ht [15] J. Lafferty, A. McCallum, and F. Pereira, “Conditional ml, 2010. Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data,” Proc. 18th Int’l Conf. [5] Overview of Attack Trends, Machine Learning (ICML ’01), pp. 282-289, 2001. http://www.cert.org/archive/pdf/ attack_trends.pdf, 2002. [16] A. McCallum, D. Freitag, and F. Pereira, “Maximum Entropy Markov Models for Information Extraction and [6] Kapil Kumar Gupta, Baikunth Nath, Ramamohanarao Segmentation,” Proc. 17th Int’l Conf. Machine Kotagiri, "Layered Approach Using Conditional Learning (ICML ’00), pp. 591-598,2000. Random Fields for Intrusion Detection," IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing [17] D.S. Kim and J.S. Park, “Network-Based Intrusion (vol. 7 no. 1), pp. 3 5-49, 2010. Detection with Support Vector Machines,” Proc. Information Networking, networking Technologies for [7] J.P. Anderson, Computer Security Threat Monitoring Enhanced Internet Services Int’l Conf. (ICOIN ’03),pp. and Surveillance, 747-756, 2003. http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/history/ande80.pdf, 2010. [18] C. Sutton and A. McCallum, “An Introduction to Conditional Random Fields for Relational Learning,” [8] W. Lee and S. Stolfo, “Data Mining Approaches for Introduction to Statistical Relational Learning, 2006. Intrusion Detection,” Proc. Seventh USENIX Security Symp. (Security ’98), pp. 79-94, 1998. [9] H. Shah, J. Undercoffer, and A. Joshi, “Fuzzy Clustering for Intrusion Detection,” Proc. 12th IEEE Int’l Conf. Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE ’03), vol. 2, pp. 1274-1278, 2003. [10] C. Kruegel, D. Mutz, W. Robertson, and F. Valeur, “Bayesian Event Classification for Intrusion Detection,” Proc. 19th Ann. Computer Security Applications Conf. (ACSAC ’03), pp. 14-23, 2003. [11] N.B. Amor, S. Benferhat, and Z. Elouedi, “Naive Bayes vs. Decision Trees in Intrusion Detection Systems,” Proc. ACM Symp. Applied Computing (SAC ’04), pp. 420-424, 2004.[2] W. Lee and S. Stolfo, “Data Mining Approaches for Intrusion Detection,” Proc. Seventh USENIX Security Symp. (Security ’98), pp. 79-94, 1998. [12] H. Debar, M. Becke, and D. Siboni, “A Neural Network Component for an Intrusion Detection System,” Proc. IEEE Symp. Research in Security and Privacy (RSP ’92), pp. 240- 250, 1992. www.ijorcs.org
![International Journal of Research in Computer Science
eISSN 2249-8265 Volume 2 Issue 4 (2012) pp. 31-38
© White Globe Publications
www.ijorcs.org
A STUDY AND COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF
CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS FOR INTRUSION
DETECTION
Deepa Guleria1, M.K.Chavan2
1
PG Scholar, VPCOE Baramati
Email: deepa.guleria@gmail.com
2
Asstt Professor, VPCOE Baramati
Email:chavan_manik@yahoo.com
Abstract: Intrusion detection systems are an important Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and the
component of defensive measures protecting computer other is Host Intrusion Detection Systems
systems and networks from abuse. Intrusion detection (HIDS).NIDS monitors the packets from the network
plays one of the key roles in computer security and it is an independent platform that identifies
techniques and is one of the prime areas of research. intrusion by examining the network traffic and
Due to complex and dynamic nature of computer multiple hosts. HIDS analyzes the audit data of the
networks and hacking techniques, detecting malicious operation system and monitors the inbound and
activities remains a challenging task for security outbound packets from the device only. It alerts the
experts, that is, currently available defense systems user or administrator of suspicious activity is detected
suffer from low detection capability and high number [7].Intrusion detection systems can also be classified
of false alarms. An intrusion detection system must as signature based or anomaly based depending upon
reliably detect malicious activities in a network and the attack detection method. The signature-based
must perform efficiently to cope with the large amount systems are trained by extracting specific patterns (or
of network traffic. In this paper we study the Machine signatures from previously known attacks while the
Learning and data mining techniques to solve anomaly-based systems learn from the normal data
Intrusion Detection problems within computer collected when there is no anomalous activity. The
networks and compare the various approaches with first approach is called as Misuse Detection and leads
conditional random fields and address these two issues us towards Signature Based IDS while the second is
of Accuracy and Efficiency using Conditional Random called as Anomaly Detection and leads us to Behavior
Fields and Layered Approach. based IDS. The Signature based systems though have
very high detection accuracy but they fail when an
Keywords: Intrusion Detection System, Conditional
attack is previously unseen. On the other hand,
Random Fields, Network Security, Decision tree
Behavior based IDS or anomaly based may have the
I. INTRODUCTION ability to detect new unseen attacks but have the
problem of low detection accuracy [7]. Another
An intrusion detection system monitors the approach for detecting intrusions is to consider both
activities of a given environment and decides whether the normal and the known anomalous patterns for
these activities are malicious (intrusive) or legitimate training a system and then performing classification on
(normal) based on system integrity, confidentiality and the test data. Such a system incorporates the
the availability of information resources. Intrusion advantages of both the signature-based and the
detection as defined by the Sysadmin, Audit, anomaly-based systems and is known as the Hybrid
Networking, and Security (SANS) institute is the act of System.
detecting actions that attempt to compromise the
confidentiality, integrity or availability of a resource Hybrid systems can be very efficient, subject to the
[1]. Detecting intrusions in networks and applications classification method used, and can also be used to
has become one of the most critical tasks to prevent label unseen or new instances as they assign one of the
their misuse by attackers. The cost involved in known classes to every test instance. This is possible
protecting these valuable resources is often negligible because during training the system learns features from
when compared with the actual cost of a successful all the classes. The only concern with the hybrid
intrusion, which strengthens the need to develop more method is the availability of labeled data. Further, a
powerful intrusion detection systems. single system has limited attack detection coverage
and it cannot detect a wide variety of attacks reliably.
There are two types of IDS depending on their
mode of deployment and data used for analysis.
www.ijorcs.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vol2-iss4-06-a-study-and-comparative-analysis-of-conditional-random-fields-for-intrusion-detection-120714062024-phpapp01/85/A-Study-and-Comparative-analysis-of-Conditional-Random-Fields-for-Intrusion-detection-1-320.jpg)
![32 Deepa Guleria, M.K.Chavan
We introduce hybrid intrusion detection systems based involve computing a distance between numeric
on conditional random fields which can detect a wide features and therefore they cannot easily deal with
variety of attacks and which result in very few false symbolic attributes, resulting in inaccuracy. Addition,
alarms. To improve the efficiency of the system, we clustering methods consider the features independently
then integrate the layered framework. and are unable to capture the relationship between
different features of a single record which results in
II. APPROACHES TO IMPLEMENT IDS lower accuracy [9].
Intrusion detection has been an active field of Data Mining: Data mining (DM), also called
research for starting in 1980s after the influential paper Knowledge-Discovery and Data Mining, is the process
from Anderson [7]. Several researchers have proposed of automatically searching large volumes of data for
various intrusion detection methods and frameworks patterns using association rules. Data mining
which are available to protect a computer system or approaches derive association rules and frequent
network from attacks. Various techniques such as episodes from available sample data, not from human
association rules, clustering, Naïve Bayes, Support experts. Using these rules, Lee et. al. developed a data
Vector Machines, Neural Networks, and others have mining framework for the purpose of intrusion
been developed to detect intrusions. This section detection[8].In particular, system usage behaviors are
provides a brief literature review on these technologies recorded and analyzed to generate rules which can
and related frameworks. These methods can be broadly recognize misuse attacks. The drawback of such
divided into three major categories: frameworks is that they tend to produce a large number
of rules and thereby, increase the complexity of the
A. Pattern Matching system.
Pattern Matching is the simple type of attack Bayesian Classifiers: A Bayesian network is a model
detection technique. It has the simple concept of string that encodes probabilistic relationships among
matching. Using pattern matching technique, IDSs variables of interest. This technique is generally used
generally match the text (audit records) or binary for intrusion detection in combination with statistical
sequences against known attack signatures. A pattern schemes, a procedure that yields several advantages,
matching technique basically looks for a specific including the capability of encoding interdependencies
attack signature which may be presented in audit between variables and of predicting events, as well as
record. The limitation of pattern matching approach is the ability to incorporate both prior knowledge and
that it can recognize only known attacks. It requires data. However, a serious disadvantage of using
continuous updates of attack signatures to identify new Bayesian networks is that their results are similar to
attacks. Pattern matching approach is well suited for those derived from threshold-based systems, while
misuse detection. Snort system is based upon pattern considerably higher computational effort is required.
matching.
Decision Trees: Decision trees are one of the most
B. Statistical Methods commonly used supervised learning algorithms in IDS
due to its simplicity, high detection accuracy and fast
Statistical modeling is among the earliest methods
adaptation. Decision trees used for intrusion detection
used for detecting intrusions in electronic information
select the best features for each decision node during
systems. It is assumed that an intruder’s behavior is
tree construction based on some well-defined criteria
noticeably different from that of a normal user, and
[11]. One such criterion is the gain ratio which is used
statistical models are used to aggregate the user’s
in C4.5.
behavior and distinguish an attacker from a normal
user. The techniques are applicable to other subjects, A decision tree is composed of three basic elements:
such as user groups and programs. Two statistical 1. A decision node specifying a test attributes.
models that have been proposed for anomaly detection: 2. An edge or a branch corresponding to the one of
NIDES/STAT and Haystack. the possible attribute values which means one of
the test attribute outcomes.
C. Data Mining and Machine Learning
3. A leaf which is also named an answer node
Data mining and machine learning methods focus contains the class to which the object belongs.
on analyzing the properties of the audit patterns rather
than identifying the process which generated them. Artificial Neural Networks: Neural networks are
These methods include approaches for mining known for good performance in learning system-call
association rules, classification and cluster analysis. sequences. Once the neural net is trained on a set
of representative command sequences of a user,
the net constitutes the profile of the user, and the
Clustering: For unsupervised intrusion detection, data fraction of incorrectly predicted events then
clustering methods can be applied. These methods measures, in some sense, the variance of the user
www.ijorcs.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vol2-iss4-06-a-study-and-comparative-analysis-of-conditional-random-fields-for-intrusion-detection-120714062024-phpapp01/85/A-Study-and-Comparative-analysis-of-Conditional-Random-Fields-for-Intrusion-detection-2-320.jpg)
![A Study and Comparative Analysis of Conditional Random Fields for Intrusion Detection 33
behavior from his profile. They can work effectively specific requirements of the environment where it
with noisy data but they require large amount of data is deployed.
for training and it is often hard to select the best
possible architecture for the neural network [12]. IV. CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS
Support Vector Machines: Support vector map real A. Conditional Probability
valued input feature vector to higher dimensional Conditional probability is used to compute
feature space through nonlinear mapping and have probability of an event Y given some other event X.
been used for detecting intrusions. They can provide
𝑃(𝑋 ∩ 𝑌)
Formally it is defined as:
𝑃(𝑌 | 𝑋) =
real-time attack detection capability, deal with large
𝑃(𝑋)
dimensionality of data and perform multi class
classification. Similar to the pattern matching and
statistical methods, these methods assume
independence among consecutive events and hence do Where P(X) > 0. From this definition we can read that
not consider the order of occurrence of events for if the occurrence of the event X takes place in the same
attack detection [17]. space as the event Y, and there are no other events that
may act the occurrence of the event Y, then the
Markov Models: Markov chains and hidden Markov conditional probability of the occurrence of the event
model is a set of states that are interconnected through Y given the event X is the relative proportion of
certain transition probabilities, which determine the outcomes that satisfy Y among those that satisfy X.
topology and the capabilities of the model. During a
first training phase, the probabilities associated to the B. Conditional Random Field Framework
transitions are estimated from the normal behavior of
Conditional random fields [15] (CRFs) are a
the target system. The detection of anomalies is then
probabilistic framework for labeling and segmenting
carried out by comparing the anomaly score
sequential data, based on the conditional approach
(associated probability) obtained for the observed
described in the previous paragraph. A CRF is a form
sequences with a fixed threshold. Markov chains and
of undirected graphical model that defines a single log-
hidden Markov models can be used when dealing with
linear distribution over label sequences given a
sequential representation of audit patterns. Hidden
particular observation sequence. The primary
Markov models have been shown to be effective in
advantage of CRFs over hidden Markov models is
modeling sequences of system calls of a privileged
their conditional nature, resulting in the relaxation of
process, which can be used to detect anomalous traces
[13] the independence assumptions required by HMMs in
. However, modeling system calls alone may not
order to ensure tractable inference. Additionally, CRFs
always provide accurate classification as various
avoid the label bias problem [14], a weakness
connection level features are ignored. Further, hidden
exhibited by maximum entropy Markov models [16]
Markov models cannot model long range dependencies
(MEMMs) and other conditional Markov models
between the observations.
based on directed graphical models. CRFs outperform
both MEMMs and HMMs on a number of real-world
III. CHALLENGES AND REQUIREMENT FOR
sequence labeling tasks.
INTRUSION DETECTION SYSTEM
It is important intrusion detection must detect CRF was firstly proposed by Lafferty and his
attacks at an early stage in order to minimize their colleagues in 2001, [15] whose model idea mainly
impact. The major challenges and requirements for came from MEMM (Maximum Entropy Markov
building intrusion detection systems are: Model).The critical difference between CRFs and
MEMMs is that a MEMM uses per-state exponential
i. The system must be able to detect as many models for the conditional probabilities of next states
attacks as possible without giving false alarms i.e given the current state, while a CRF has a single
the system must be accurate in detecting attacks. exponential model for the joint probability of the entire
ii. The system must be able to handle large amount sequence of labels given the observation sequence.
of data without affecting performance and Therefore, the weights of different features at different
without dropping data. states can be traded off against each other. Conditional
iii. A system must not only detect an attack, but also models are probabilistic systems that are used to model
able to identify the type of attack. the conditional distribution over a set of random
iv. A system must be resistant to attacks since, a variables. Such models have been extensively used in
system that can be exploited during an attack may the natural language processing tasks. Conditional
not be able to detect attacks reliably. models offer a better framework as they do not make
v. The challenge is to build a system which is any unwarranted assumptions on the observations and
scalable and can be easily customized as per the can be used to model rich overlapping features among
the visible observations [6].
www.ijorcs.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vol2-iss4-06-a-study-and-comparative-analysis-of-conditional-random-fields-for-intrusion-detection-120714062024-phpapp01/85/A-Study-and-Comparative-analysis-of-Conditional-Random-Fields-for-Intrusion-detection-3-320.jpg)
![A Study and Comparative Analysis of Conditional Random Fields for Intrusion Detection 35
C. Inference in CRF D. Detecting network intrusions using layered
Approach
For general graphs, the problem of exact inference
in CRFs is intractable. However there exist special Researchers are motivated to propose different
cases for which exact inference is feasible: approaches seeing the low detection rates caused by
the imbalanced network intrusion dataset. Current
• If the graph is a chain or a tree, message passing
research work proposes a staged or layered approach
algorithms yield exact solutions. The algorithms
to detect network intrusions efficiently. The recent
used in these cases are analogous to the forward-
research work of Gupta and Nath [6], considered the
backward and Viterbi algorithm for the case of
attack categories as layers and different features were
HMMs.
selected for each layer. The dataset was, therefore,
• If the CRF only contains pair-wise potentials and
divided into five attack categories for training and
the energy is submodular, combinatorial min
testing purposes of each layer. The test data passed
cut/max flow algorithms yield exact solutions.
through the cascaded layers to determine the category
All Features
Yes Yes
Probe Layer DoS Layer
Normal Normal
Feature Selection Feature Selection
No No
Block Block
Yes Yes
R2L Layer U2R Layer
Normal Normal Allow
Feature Selection Feature Selection
No No
Block Block
Figure 3: Integrating the Layered Framework
a record that belonged to Conditional Random Fields V. EXPERIMENTAL METHODOLOGY
(CRFs) were used in the layered approach as proposed
by the researcher [6]. The three layer system to ensure The Data Set
complete security viz. availability, confidentiality and
integrity, each layer corresponding to one aspect of The data set used for the entire course of research is
security. In the system, every layer is trained the DARPA KDD99 benchmark data set [4], also
separately with the normal instances and with the known as “DARPA Intrusion Detection Evaluation
attack instances belonging to a single attack class. data set” that not only includes a large quantity of
Here the features involved were different in each layer. network traffic but also collects a wide variety of
Explanation of which features should be used or not be attacks. They setup an environment to collect TCP/IP
used was given in the paper. However, the complete dump from a host located on a simulated military
feature list for each layer was not presented in the network. Each TCP/IP connection is described by 41
paper. The above staged and layered approaches used discrete and continuous features and labeled as either
classifiers of the same type or of different types for the normal or as an attack. Attacks fall into following
detecting network intrusions. The approaches handled four main classes:
the attacks separately to minimize the attack categories
from affecting each other in classification or detection A. Denial of service (DOS)
tasks. Since every layer in Layered framework is In this type of attack an attacker makes some
independent, feature sets for all the four layers are not computing or memory resources too busy or too full to
disjoint. The final goal is to improve both the attack handle legitimate requests or denies legitimate users
detection accuracy and the efficiency of the system. access to a machine. Examples are Apache2, Back,
Hence, by integrating the CRFs and the Layered Land, Smurf, Teardrop.
Approach can build efficient and accurate single
system.
www.ijorcs.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vol2-iss4-06-a-study-and-comparative-analysis-of-conditional-random-fields-for-intrusion-detection-120714062024-phpapp01/85/A-Study-and-Comparative-analysis-of-Conditional-Random-Fields-for-Intrusion-detection-5-320.jpg)
![38 Deepa Guleria, M.K.Chavan
• For testing: significant improvement,
– Viterbi algorithm is used both, in the time required to
which also has the same train and test the system and
complexity also in the attack detection
accuracy (F-value).
5. CRFs are robust to noise in
training data.
6. CRFs avoid the label bias
problem.
7. CRFs avoid a fundamental
limitation of maximum
entropy Markov models
(MEMMs).
VII. REFERENCES [13] Y. Du, H. Wang, and Y. Pang, “A Hidden Markov
Models-Based Anomaly Intrusion Detection Method,”
[1] SANS Institute—Intrusion Detection FAQ, Proc. Fifth World Congress on Intelligent Control and
http://www.sans.org/ resources/idfaq/, 2010. Automation (WCICA ’04), vol. 5, pp. 4348-4351,
[2] Autonomous Agents for Intrusion Detection, 2004.
http://www.cerias.purdue.edu/research/aafid/, 2010. [14] A. McCallum, “Efficiently Inducing Features of
[3] CRF++: Yet Another CRF Toolkit, Conditional Random Fields,” Proc. 19th Ann. Conf.
http://crfpp.sourceforge.net/,2010. Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI ’03), pp.
403-410, 2003.
[4] KDD Cup 1999 Intrusion Detection Data,
http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup99.ht [15] J. Lafferty, A. McCallum, and F. Pereira, “Conditional
ml, 2010. Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting
and Labeling Sequence Data,” Proc. 18th Int’l Conf.
[5] Overview of Attack Trends,
Machine Learning (ICML ’01), pp. 282-289, 2001.
http://www.cert.org/archive/pdf/ attack_trends.pdf,
2002. [16] A. McCallum, D. Freitag, and F. Pereira, “Maximum
Entropy Markov Models for Information Extraction and
[6] Kapil Kumar Gupta, Baikunth Nath, Ramamohanarao
Segmentation,” Proc. 17th Int’l Conf. Machine
Kotagiri, "Layered Approach Using Conditional
Learning (ICML ’00), pp. 591-598,2000.
Random Fields for Intrusion Detection," IEEE
Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing [17] D.S. Kim and J.S. Park, “Network-Based Intrusion
(vol. 7 no. 1), pp. 3 5-49, 2010. Detection with Support Vector Machines,” Proc.
Information Networking, networking Technologies for
[7] J.P. Anderson, Computer Security Threat Monitoring
Enhanced Internet Services Int’l Conf. (ICOIN ’03),pp.
and Surveillance,
747-756, 2003.
http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/history/ande80.pdf,
2010. [18] C. Sutton and A. McCallum, “An Introduction to
Conditional Random Fields for Relational Learning,”
[8] W. Lee and S. Stolfo, “Data Mining Approaches for
Introduction to Statistical Relational Learning, 2006.
Intrusion Detection,” Proc. Seventh USENIX Security
Symp. (Security ’98), pp. 79-94, 1998.
[9] H. Shah, J. Undercoffer, and A. Joshi, “Fuzzy
Clustering for Intrusion Detection,” Proc. 12th IEEE
Int’l Conf. Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE ’03), vol. 2, pp.
1274-1278, 2003.
[10] C. Kruegel, D. Mutz, W. Robertson, and F. Valeur,
“Bayesian Event Classification for Intrusion Detection,”
Proc. 19th Ann. Computer Security Applications Conf.
(ACSAC ’03), pp. 14-23, 2003.
[11] N.B. Amor, S. Benferhat, and Z. Elouedi, “Naive Bayes
vs. Decision Trees in Intrusion Detection Systems,”
Proc. ACM Symp. Applied Computing (SAC ’04), pp.
420-424, 2004.[2] W. Lee and S. Stolfo, “Data
Mining Approaches for Intrusion Detection,” Proc.
Seventh USENIX Security Symp. (Security ’98), pp.
79-94, 1998.
[12] H. Debar, M. Becke, and D. Siboni, “A Neural Network
Component for an Intrusion Detection System,” Proc.
IEEE Symp. Research in Security and Privacy (RSP
’92), pp. 240- 250, 1992.
www.ijorcs.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vol2-iss4-06-a-study-and-comparative-analysis-of-conditional-random-fields-for-intrusion-detection-120714062024-phpapp01/85/A-Study-and-Comparative-analysis-of-Conditional-Random-Fields-for-Intrusion-detection-8-320.jpg)