Ad
What is sap security
- 2. Security SAP Security Components Security Solution Map Access control concepts PFCG Conclusion
- 3. SECURITY Prevent Unauthorized Access
- 6. An Overview of R/3 Security Services
- 7. Access control in SAP is composed of several concepts Program code Authorization fields ACTIVITY COMPANY_CODE Authorization objects Authorizations
- 8. Profiles Role Users
- 9. Program Code That calls an authorization check using the authority-check statement. This will look something like authority-check object id field Authorization fields: That define a scope of possible values. Examples of authorization fields would be ACTIVITY: defines the type of activity the user is doing with the data. Possible values are 'DISPLAY', 'MODIFY', 'DELETE', etc. COMPANY_CODE: possible values are any single value, or any range of values, or any combination thereof such as '0438' and '0600' thru '1100'
- 10. Authorization fields Authorization fields: That define a scope of possible values. Examples of authorization fields would be ACTIVITY: defines the type of activity the user is doing with the data. Possible values are 'DISPLAY', 'MODIFY', 'DELETE', etc. COMPANY_CODE: possible values are any single value, or any range of values, or any combination thereof such as '0438' and '0600' thru '1100'
- 11. Authorization objects Authorization objects that define a group of fields. For example, an authorization object called 'CO_MDATA', containing fields ACTIVITY and COMPANY_CODE, might used to control access to the company master data tables.
- 12. Authorizations Authorizations, each of which belong to exactly one authorization object, that define authorizationvalues (within the scopes defined by the authorizationobjects) to be granted to users. Note that an authorization is different from an authorizationobject!! Extending our previous examples, we might have an authorization, belonging to the authorizationobject 'CO_MDATA',called 'CO_MDATA_ALL', that grants all access to all company master data. Then 'CO_MDATA_ALL'would have the following values: FIELD VALUE ACTIVITY * COMPANY_CODE *
- 13. Profiles 1. Profiles, each of which may contain several authorizations or profiles. A simple profile contains a group of authorizations. A composite profile contains a group of profiles (simple or composite). [Profiles can be conceptualized as forming the structure of a tree, in which end nodes (leaves) are authorizations, and all other nodes are profiles. Simple profiles are nodes whose children are all end nodes, and composite profiles are nodes, other than end nodes, who have no end nodes for children.] Profiles are designed to define set or one or more functions or positions. For example, a functional profile might define all the authorizations that are required for doing a goods receipt, or for making a payment in the AP module. A position profile, on the other hand, might define all of the authorizations that are granted to an accountant, or to a warehouse supervisor. Often, a position profile is a composite profile consisting of several functional profiles.
- 14. Roles Roles are collectionsof activities which allow a user to use one or more business scenarios of an organization. According to the standard SAP role concept,roles containingaccess rights are assigned to users. These authorizationsare then checked when the user performs certain actions, such as starting a transaction. Assigning a Standard Role to a User Changing Standard Roles Creating Composite Roles Note: The term activity group was replaced with the term role in SAP R/3 Release 4.6C.
- 15. Composite roles Composite roles can simplify the user administration. They consist of single roles. Users who are assigned a composite role are automatically assigned the associated single roles during the compare. Composite roles do not themselves contain authorization data. Setting up composite roles are useful for example if some of your users need authorization for several roles. You can create a composite role and assign it to the users instead of putting each user in each required single role.
- 16. Derive Roles Derive Roles: There are two possible reasons for deriving a role from an existing role: The role menus are identical but the authorizations for the menu actions are different in the derived role. The menu and authorizations of the derived role are identical, but the organizational levels are different in the derived role.
- 17. What is PFCG The Profile Generator is a SAP tool. Can be used to automatically create profiles and assign them easily to users. Only selects and uses the necessary authorization objects, avoiding excessive validations in the system and thereby improving performance. Facilitates functional communication between security or the authorization administrator and end users or consultants. Makes defining and maintaining authorization profiles easier.
- 18. Configuring PFCG Beforeusing the PFGC for the first time, there are 4 steps that are required to configure and work with PFCG Tool. 1) Activate the PFCG Based on Instance Profile parameter “auth/no_check_in_some_cases=y 2) Set Up the Initial Copy of Profile Generator Configuration Tables (T-Code SU25) Transfer the SAP transactions and authorization objects from SAP tables USOBT and USOBX to customer USOBT_C and USOBX_C. You can then maintain these tables using T-Code SU24.
- 19. Table USOBT includes the relation between the transactions and the authorization objects. 3) Maintain the Scope of Authorizations Object Checks in Transactions (T-Code SU24) This is not a mandatory step, but can be used by customers to maintain their own authorizationobjects to custom transactions. 4) Generate the Company Menu Generate the SAP Standard menu and then the company menu.
- 20. Create Roles 1. Choose the pushbutton Create role or the transaction PFCG in the initial transaction SAP Easy Access. You go to the role maintenance. 2. Specify a name for the role. The roles delivered by SAP have the prefix 'SAP_'. Do not use the SAP namespace for your user roles. 3. SAP does not distinguish between the names of simple and composite roles. You should adopt your own naming convention to distinguish between simple and composite roles. 4. Choose Create.
- 21. 5. Enter a meaningful role description text. You can describe the activities in the role in detail. To assign Knowledge Warehouse documentation to the role, choose Utilities ® Info object ® Assign. The user of the role can then display the documentation.
- 22. MENU TAB 2. Assign transactions, programs and/or web addresses to the role in the MENU tab. The user menu which you create here is called automatically when the user to whom this role is assigned logs on to the SAP System. You can create the authorizations for the transactions in the role menu structure in the AUTHORIZATIONS tab.
- 23. MENU
- 24. SAP Menu You can copy complete menu branches from the SAP menu by clicking on the cross in front of it in the user menu. Expand the menu branch if you want to put lower-level nodes or individual transactions/programs in the user menu.
- 25. ABAB REPORT Choose a report and a variant. You can skip the selection screen. You can generate a transaction code automaticallyand copy the report description by setting checkboxes. Save and Move to Authorizations Tab.
- 26. Generating Authorizations To create authorizationsfor a role, choose AUTHORIZATIONS in the role maintenance. The AUTHORIZATIONS tab displays creation and change information as well as information on the authorization profile (includingthe profile name, profile text and status). Click on the change authorization
- 27. Choose Change Authorization Data 1. Choose the menu Click on the expand menu go to the respective authorization object and check the activity field assign the activity to be performed. 2. Save.
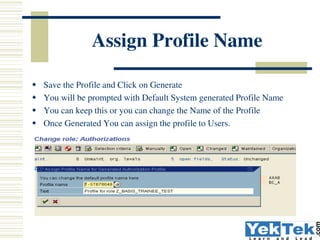
- 28. Assign Profile Name Save the Profile and Click on Generate You will be prompted with Default System generated Profile Name You can keep this or you can change the Name of the Profile Once Generated You can assign the profile to Users.
- 29. ASSIGN PROFILES TO USERS Assign Profile to USERS Comparing the new profile with existing profiles by using USER COMPARISION Old profile is overwritten by new profile. Save
- 30. MiniApps MiniApps for the role MiniApps are simple intuitive Web applications. The assignment of MiniApps to a role determines which MiniApps the user sees in his or her mySAP Workplace. Save and Exit
- 31. CONCLUSION It sounds complicated , but once you start working with authorizations, it's pretty easy.
- 32. About Approva Founded in 2001, Approva Corporation provides enterprise controls management software that enables Finance, IT, and
- 33. Audit to automate and strengthen business controls. Approva’s software product, BizRights, enables companies to perform:
- 34. Approva Provides Approva provides enterprise controls management software that enables Business, Finance, IT and Audit to automate and strengthen business controls.
- 36. What Is BizRights? BizRights is a web-based, cross-application, cross-platformenterprise controls application. This means that BizRights can monitor security and transactionaldata from any ERP system or platform, as well as multiple systems and platforms. Examples of what BizRights can tell you: If the same user performed the same transactions in two different SAP clients If user profiles for SAP and Oracle create a security risk or SegregationofDuties (SoD)violation If a user performed sensitive transactions that should be monitored If a user changedMasterData records
- 37. If a SAP client is configured to reduce risk If transactions were performed of an unusually high monetary value, such as purchase orders that exceeda million dollars What your business is doing, according to your business rules BizRights can monitor millions of records and thousands of transactions any time you want, as often as you want. BizRights is designedfor functional business professionals as wellas technical specialists, including: FinancialAuditors, Internal Controls staff, Compliance staff, Business Process Owners, IT Security Auditors, External Auditors More than just finding and fixing SoD violations, BizRights can monitorbusiness process transactions, including Procure-to-Pay, Financial Close, Order-to-Cash, and Payroll.
- 38. Segregation of Duties Segregation of duties is a basic, key internal control and one of the most difficult to achieve. It is used to ensure that errors or irregularities are prevented or detected on a timely basis by employees in the normal course of business. Segregation of duties provides two benefits: 1) a deliberate fraud is more difficult because it requires collusion of two or more persons, and 2) it is much more likely that innocent errors will be found. At the most basic level, it means that
- 39. no single individual should have control over two or more phases of a transaction or operation. Management should assign responsibilities to ensure a crosscheck of duties.
- 40. CATEGORIES There are four general categories of duties or responsibilities which are examined when segregation of duties are discussed: authorization, custody, record keeping and reconciliation. In an ideal system, different employees would perform each of these four major functions. In other words, no one person should have control of two or more of
- 41. these responsibilities. The more negotiable the asset, the greater the need for proper segregation of duties - especially when dealing with cash, negotiable checks and inventories
- 42. Authorization Authorization: the process of reviewing and approving transactions or operations. Some examples are: > Verifying cash collections and daily balancing reports.
- 43. > Approving purchase requisitions or purchase orders. > Approving time sheets, payroll certifications, leave requests and cumulative leave records. > Approving change orders, computer system design or programming changes.
- 44. Custody Having access to or control over any physical asset such as cash, checks, equipment, supplies, or materials. Some examples are: Access to any funds through the collectionof funds, or processingof payments.
- 45. > Access to safes, lock boxes, file cabinets or other places where money, checks or other assets are stored. > Custodianof a petty cash or change fund. > Receivingany goods or services. > Maintaining inventories. > Handlingor distributingpaychecks/advices, limited purchasechecks or other checks.
- 46. Record Keeping The process of creating and maintainingrecords of revenues, expenditures, inventories, and personnel transactions. These may be manual records or records maintainedin automatedcomputer systems. Some examples are:
- 47. > Preparingcash receipt back-ups or billings, purchase requisitions, payroll certifications, and leave records. > Entering charges or posting payments to an accounts receivablesystem. > Maintaining inventoryrecords.
- 48. Reconciliation Verifying the processing or recording of transactionsto ensure that all transactionsare valid, properlyauthorized and properlyrecorded on a timely basis. This includesfollowing up on any differences or discrepancies identified. Examples are: > Comparing billing documentsto billing summaries. > Comparing funds collectedto accountsreceivable postings.
- 49. > Comparing collectionsto deposits. > Performing surprise counts of funds. > Comparing payroll certifications to payroll summaries. > Performing physical inventory counts. > Comparing inventory changes to amounts purchased and sold. > Reconciling departmental records of revenue, expenditure, and payroll transactionsto the PeopleSoft management reports.
- 50. Pleasecontact













![Profiles
1. Profiles, each of which may contain several authorizations or profiles. A
simple profile contains a group of authorizations. A composite profile
contains a group of profiles (simple or composite). [Profiles can be
conceptualized as forming the structure of a tree, in which end nodes (leaves)
are authorizations, and all other nodes are profiles. Simple profiles are nodes
whose children are all end nodes, and composite profiles are nodes, other than
end nodes, who have no end nodes for children.]
Profiles are designed to define set or one or more functions or positions. For
example, a functional profile might define all the authorizations that are
required for doing a goods receipt, or for making a payment in the AP
module. A position profile, on the other hand, might define all of the
authorizations that are granted to an accountant, or to a warehouse supervisor.
Often, a position profile is a composite profile consisting of several functional
profiles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatissapsecurity-140623123745-phpapp01/85/What-is-sap-security-13-320.jpg)