WINSEM2022-23_BECE204L_TH_VL2022230500861_2023-02-10_Reference-Material-I.pptx
- 2. Migrating from 8-/16-bit to 32 bit • Data width • n-bit ALU • Arithmetic Operations • Form factor • Data types • Speed and memory
- 3. Instruction Set category • What is RISC? • What is CISC? • What is EPIC? • RISC vs CISC • Any advantages of RISC based architectures? • Examples of RISC and CISC.
- 4. 4 • What is an Embedded System? Embedded System=Hardware + Software Definition: It is a computational engine, employing hardware and software, designed to perform specific function/s. The software is used for providing features and flexibility. The hardware is used for performance and sometimes security.
- 5. 5 ARM Embedded Systems • Key component of many 32 – bit embedded systems • Portable Consumer devices • ARM1 prototype in 1985 • One of the ARM’s most successful cores is the ARM7TDMI,provides high code density and low power consumption.
- 6. 6 The RISC Design Philosophy • ARM Core uses a RISC architecture • ARM licenses its cores out and other companies make processors based on its cores
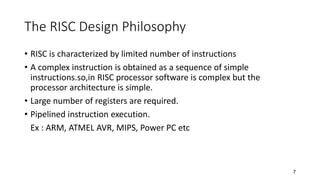
- 7. 7 The RISC Design Philosophy • RISC is characterized by limited number of instructions • A complex instruction is obtained as a sequence of simple instructions.so,in RISC processor software is complex but the processor architecture is simple. • Large number of registers are required. • Pipelined instruction execution. Ex : ARM, ATMEL AVR, MIPS, Power PC etc
- 8. 8 The CISC Design Philosophy • CISC is characterized by large instruction set. • The aim of designing CISC processors is to reduce software complexity by increasing the complexity of processor architecture. • Very small number of registers are available. Ex : Intel X86 family,Motorola 68000 series.
- 9. 9 CISC vs. RISC Compiler Processor Code Generation Greater Complexity CISC Compiler Processor Code Generation Greater Complexity RISC
- 10. 10 RISC – 4 major design rules • Instructions • Reduced Number of Instructions • Execute in a single cycle • The compiler synthesizes complicated operations • Each instruction is a fixed length
- 11. 11 RISC – 4 major design rules • Pipelines • The processing of instructions is broken down into smaller units that can be executed in parallel by pipelines • Pipeline advances by one step on each cycle for maximum throughput
- 12. 12 RISC – 4 major design rules • Registers • Have a large general purpose register set • Any register can contain either data or address • CISC has dedicated registers for specific purposes.
- 13. 13 RISC – 4 major design rules • Load – Store Architecture • Separate load and store instructions transfers data between the register bank and external memory
- 14. 14 The ARM Design Philosophy • Reduce power consumption • High code density • Reduce the area of the die taken up by the embedded processor • Incorporated hardware debug technology
- 15. 15 Instruction set for Embedded Systems • Variable cycle execution for certain instructions • Inline barrel shifter leading to more complex instructions • Thumb 16 – bit instructions • Conditional execution • Enhanced Instructions
- 17. 17 Agenda • Registers • CPSR • Pipeline • Exceptions, Interrupts and the Vector Table • Core Extensions • Architecture Revisions • ARM Processor Families • Summary
- 18. 18 ARM core dataflow model Incrementer Address Register ALU Barrel Shifter MAC Register File r0 – r15 Sign Extend Instruction Decoder Read Data A B Acc Rd Result B A r15 pc Rn Rm N Address
- 19. 19 ARM core dataflow model • Functional units connected by data buses • Data Bus Data or Instruction • Von Neumann architecture Data and instruction share the same bus • Load Store Architecture • Register File – 32 bit registers • ARM instruction has 2 source and 1 destination register • L/S inst: use the ALU to generate an address to be held in the address reg. and broadcast on the Address Bus • Result Bus
- 20. 20 Registers – User Mode r0 r1 r2 r3 r4 r5 r6 r7 r8 r9 r10 r11 r12 r13 sp r14 lr r15 pc cpsr - • 32 bit in size • Hold either data or address • 16 data registers(r0 – r15) and 2 processor status register (cpsr & spsr) • r13, r14, r15 – Special functions • r13 (sp) –stores the head of the stack in the current processor mode • r14 (lr) – the core puts the return address whenever it calls a subroutine • r15 (pc) – contains the address of the next instruction to be fetched by the processor • Which register are visible to the programmer depend upon the current mode of the processor
- 21. 21 Current Program Status Register • To monitor and control internal operations • Some ARM Processor core have extra bits allocated N Z C V I F T Mode 31 30 29 28 7 6 5 4 0 Condition Flags Processor Mode Interrupt Masks Thumb State Function Bit Fields Flags Status Extension Control
- 22. 22 Processor Modes • Determines which registers are active and the access rights to the cpsr register itself • Privileged & Nonprivileged • Abort • Fast Interrupt Request • Interrupt Request • Supervisor • System • Undefined • User Privileged-R/W access to CPSR Nonprivileged-R Access to CF,R/W access to ConditionFlags
- 23. 23 Processor Modes • Abort – Failed attempt to access memory • FIQ IRQ – Two interrupt levels available on the ARM processor • Supervisor – OS kernel operates • System – Special version of user mode that allows full R/W access to the cpsr • Undefined – processor encounters an instruction that is undefined • User – used in programs & applications • When a power is applied to the core it starts in supervisor mode.
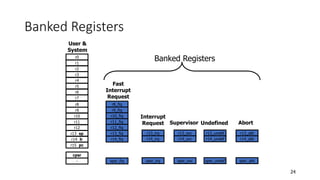
- 24. 24 Banked Registers r0 r1 r2 r3 r4 r5 r6 r7 r8 r9 r10 r11 r12 r13 sp r14 lr r15 pc cpsr - r8_fiq r9_fiq r10_fiq r11_fiq r12_fiq r13_fiq r14_fiq spsr_fiq r13_irq r14_irq spsr_irq r13_svc r14_svc spsr_svc r13_undef r14_undef spsr_undef r13_abt r14_abt spsr_abt Fast Interrupt Request Interrupt Request Supervisor Undefined Abort User & System Banked Registers
- 25. 25 Banked Registers • Banked registers are available only when the processor is in a particular mode • Every processor mode except user mode can change mode by writing directly to the mode bits of the cpsr • Banked registers are a subset of the main 16 registers • If we change processor mode, a banked register from the new mode will replace an existing register • Exceptions and Interrupts cause a mode change
- 26. 26 Changing mode on an exception r0 r1 r2 r3 r4 r5 r6 r7 r8 r9 r10 r11 r12 r13 sp r14 lr r15 pc cpsr - User Mode r13_irq r14_irq spsr_irq Interrupt Request Mode • This change causes user register r13 and r14 to be banked • The user registers are replaced with registers r13_irq and r14_irq • spsr stores the previous mode cpsr
- 27. 27 Processor Mode Mode Abbr: Privileged Mode[4:0] Abort abt yes 10111 Fast Interrupt Request fiq yes 10001 Interrupt Request irq yes 10010 Supervisor svc yes 10011 System sys yes 11111 Undefined und yes 11011 User usr no 10000 cpsr is not copied into the spsr when a mode change is forced due to a program writing directly to the cpsr.
- 28. 28 State and Instruction Sets • There are three instruction sets • ARM • Thumb • Jazelle The Jazelle instruction set is a closed instruction set and is not openly available. To take advantage of Jazelle extra software has to be licensed from both ARM Limited and Sun Microsystems.
- 29. 29 State and Instruction Sets ARM (cpsr T = 0) Thumb (cpsr T = 1) Instruction Size 32 bit 16 bit Core Instruction 58 30 Conditional Execution Most Only branch instructions Data Processing Instructions Access to barrel shifter and ALU Separate barrel and ALU instructions Program Status Register R/W in privileged mode No direct access Register Usage 15 GPR + PC 8 GPR + 7 high registers + PC
- 30. 30 State and Instruction Sets Jazelle (cpsr T = 0, J = 1) Instruction Size 8 bit Core Instruction Over 60% of the java bytecodes are implemented in hardware; the rest of the codes are implemented in software
- 31. 31 Interrupt Masks • Are used to stop specific interrupt requests from interrupting the processor • IRQ • FIQ • The I bit masks IRQ when set to binary 1, and F bit masks FIQ when set to binary 1
- 32. 32 Condition Flags Flag Flag Name Set when Q Saturation The result causes an overflow and / or saturation V oVerflow The result causes a signed overflow C Carry The result causes an unsigned carry Z Zero The result is zero, frequently used to indicate the equality N Negative Bit 31 of the result is a binary 1
- 33. 33 Condition Flags • Condition flags are updated by comparisons and the result of ALU operations that specify the S instruction suffix • If SUBS results in a register value of zero, then the Z flag in the cpsr is set
- 34. 34 Condition Flags – Eg 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 10011 31 30 29 28 7 6 5 4 0 nzCvq svc i F t Function Bit Fields Flags Status Extension Control 0 24 0 27 j cpsr = nzCvqjiFt_SVC
- 35. 35 Conditional Execution • Conditional execution controls whether or not the core will execute an instruction • Most instructions have a condition attribute that determines if the core will execute it based on the setting of the condition flags • Prior to execution, the processor compares the condition attribute with the condition flags in the cpsr • If they match, then the instruction is executed, otherwise the instruction is ignored • When a condition mnemonic is not present, the default behaviour is set to always (AL) execute
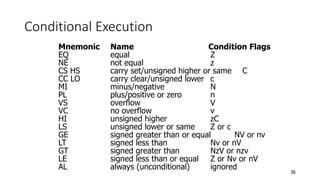
- 36. 36 Conditional Execution Mnemonic Name Condition Flags EQ equal Z NE not equal z CS HS carry set/unsigned higher or same C CC LO carry clear/unsigned lower c MI minus/negative N PL plus/positive or zero n VS overflow V VC no overflow v HI unsigned higher zC LS unsigned lower or same Z or c GE signed greater than or equal NV or nv LT signed less than Nv or nV GT signed greater than NzV or nzv LE signed less than or equal Z or Nv or nV AL always (unconditional) ignored
- 37. 37 Pipeline • Is a mechanism a RISC processor uses to execute instructions • Using a pipeline speeds up execution by fetching the next instruction while other instructions are being decoded and executed
- 38. 38 ARM7 Three stage pipeline • Fetch loads an instruction from memory • Decode identifies the instruction to be executed • Execute processes the instruction and writes the result back to a register Fetch Decode Execute
- 39. 39 Pipelined instruction sequence ADD SUB ADD CMP SUB ADD Fetch Decode Execute Cycle 1 Cycle 2 Cycle 3 Time • Filling the pipeline • Allows the core to execute an instruction every cycle
- 40. 40 ARM9 Five stage pipeline Fetch Decode Execute Memory Write • Higher operating frequency higher performance • Latency increases • Increase in instruction throughput by around 13% in 5 stage pipeline • 1.1 Dhrystone MIPS per MHz
- 41. 41 ARM9 Five stage pipeline • Fetch • The instruction is fetched from memory and placed in the instruction pipeline • Decode • The instruction is decoded and register operands read from the register file • Execute • An operand is shifted and the ALU result generated • Memory (Buffer/Data) • Data memory is accessed if required. Otherwise the ALU result is buffered for one clock cycle to give the same pipeline flow for all instructions • Write (Write-Back) • The results generated by the instruction are written back to the register file, including any data loaded from memory
- 42. 42 ARM10 Six stage pipeline Fetch Decode Execute Memory Write Issue • Increase in instruction throughput by around 34% in 6 stage pipeline • 1.3 Dhrystone MIPS per MHz • Code written for the ARM7 will execute on ARM9 and ARM10
- 43. 43 ARM Instruction Sequence MSR ADD AND SUB MSR ADD AND MSR ADD cpsr IFt_SVC cpsr IFt_SVC cpsr iFt_SVC Fetch Decode Execute Cycle 1 Cycle 2 Cycle 3 Time Cycle 4
- 44. 44 Pipeline Characteristics • An instruction in the execute stage will complete even though an interrupt has been raised • The execution of a branch instruction or branching by the direct modification of the PC causes the ARM core to flush its pipeline
- 45. 45 Exceptions, Interrupts, and the Vector Table • When an exception or interrupt occurs, the processor set the PC to a specific memory address • The address is within a special address range called the vector table • The entries in the vector table are instructions that branch to specific routines designed to handle a particular exception or interrupt • When an exception or interrupt occurs,the processor suspends normal execution and starts loading instructions from the exception vector table.
- 46. 46 Exceptions, Interrupts, and the Vector Table Exception / Interrupt Shorthand Address High Address Reset RESET 0x00000000 0xffff0000 Undefined Instruction UNDEF 0x00000004 0xffff0004 Software Interrupt SWI 0x00000008 0xffff0008 Prefetch Abort PABT 0x0000000C 0xffff000C Data Abort DABT 0x000000010 0xffff0010 Reserved - 0x000000014 0xffff0014 Interrupt Request IRQ 0x000000018 0xffff0018 Fast Interrupt Request FIQ 0x00000001C 0xffff001C
- 47. 47 Exceptions, Interrupts, and the Vector Table • RESET – when power is applied, branches to initialization code • UNDEF – when the processor cannot decode an instruction • SWI – when a SWI instruction is called • PABT – attempts to fetch an instruction from an address without the correct access permissions • DABT –attempts to access data memory without the correct access permissions • IRQ – by external hardware • FIQ – by external hardware requiring faster response time
- 48. 48 Core Extensions • Standard components placed next to the ARM core • Improve performance, manage resources, provide extra functionality • Three hardware extensions • Caches • Memory Management • Coprocessors
- 49. 49 Caches • Cache is a block of fast memory placed between main memory and the core • Cache provides an overall increase in performance • ARM has two forms of cache • Single unified cache for data and instruction • Separate caches for data and instruction
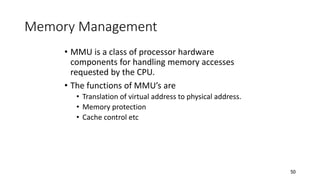
- 50. 50 Memory Management • MMU is a class of processor hardware components for handling memory accesses requested by the CPU. • The functions of MMU’s are • Translation of virtual address to physical address. • Memory protection • Cache control etc
- 51. 51 Coprocessors • Coprocessors can be attached to the ARM processor • A separate chip,that performs lot of calculations for the microprocessor,relieving the CPU some of its work and thus enhancing overall speed of system. • A secondary processor used to speed up operation by taking over a specific part of main processors work. • The ARM processor uses coprocessor 15 registers to control cache, TCMs, and memory management
- 52. 52 Architecture Revisions • Every ARM processor implementation executes a specific instruction set architecture (ISA) • ISA have more than one processor implementation
- 53. 53 Nomenclature • ARM{x}{y}{z}{T}{D}{M}{I}{E}{J}{F}{-S} x - family y – memory management / protection unit z - cache T – Thumb 16 – bit decoder D – JTAG debug M – fast multiplier I – EmbeddedICE macrocell E – Enhanced instructions (assumes TDMI) J - Jazelle F – vector floating point unit S – Synthesizible version
- 54. 54 Revision History Revision Example core Implementation ISA enhancement ARMv1 ARM1 First ARM Processor 26 – bit addressing ARMv2 ARM2 32 – bit multiplier 32 – bit coprocessor support ARMv2a ARM3 On chip cache Atomic swap instruction ARMv3 ARM6 & ARM7DI 32 – bit addressing Separate cpsr & spsr Coprocessor 15 for cache management New modes – UNDEF, ABORT MMU support – virtual memory ARMv3M ARM7M Signed & unsigned long multiply inst. ARMv4 StrongARM Load – store instruction New Mode – system 26 bit addressing mode no longer supported
- 55. 55 Revision History Revision Example core Implementation ISA enhancement ARMv4T ARM7TDMI & ARM9T Thumb ARMv5TE ARM9E & ARM10E Superset of the ARMv4T Extra inst. added for changing state between ARM & Thumb Enhanced multiply instructions Extra DSP type instructions Faster multiply accumulate ARMv5TEJ ARM7EJ & ARM926EJ Java acceleration ARMv6 ARM11 Improved multiprocessor instructions Unaligned and mixed endian data handling New multimedia instructions
- 56. 56 Description of cpsr Description Parts Bits Architecture Mode 4:0 all processor mode T 5 ARMv4T Thumb state I & F 7:6 all interrupt masks J 24 ARMv5TEJ Jazelle state Q 27 ARMv5TE condition flag V 28 all condition flag C 29 all condition flag Z 30 all condition flag N 31 all condition flag
- 57. 57 ARM processor families • ARM7, ARM9, ARM10 and ARM11 • 7, 9, 10, 11 indicate different core designs
- 58. 58 ARM family attribute comparison (+ cache) ARM11 eight-stage 335 0.4 mW/MHz 1.2 Harvard 16 x 32 ARM7 three-stage 80 0.06 mW/MHz 0.97 Von Neumann 8 x 32 ARM10 six-stage 260 0. 5 mW/MHz 1.3 Harvard 16 x 32 (+ cache) ARM9 five-stage 150 0.19 mW/MHz 1.1 Harvard 8 x 32 (+ cache) Pipeline depth Typical MHz MIPS/MHz Multiplier Architecture mW/MHz
- 59. 59 ARM processor variants E no yes Jazelle no ISA v4T yes Thumb yes v5TEJ yes CPU Core MMU /MPU Cache ARM7TDMI none none ARM7EJ-S none none no v4T no ARM720T MMU unified – 8K cache yes no v4T no ARM920T MMU separate – 16K/16K yes D + I cache v4T no ARM922T MMU separate – 8K/8K yes D + I cache no v5TEJ yes ARM926EJ-S MMU separate – cache yes TCM configurable yes v4T no ARM940T MPU separate – 4K/4K yes D + I cache no v5TE no ARM946E-S MPU separate – cache yes TCM configurable yes v5TE no ARM966E-S none separate – TCM yes configurable no
- 60. 60 ARM processor variants E yes Jazelle no ISA v5TE Thumb yes CPU Core MMU /MPU Cache ARM1020E MMU D + I cache separate – 32K/32K yes no v5TE yes ARM1022E MMU D + I cache separate – 16K/16K yes yes v5TE yes ARM1026EJ-S MMU MPU TCM configurable separate – cache yes yes v6 yes ARM1136J-S MMU TCM configurable separate – cache yes yes v6 yes ARM1136F-S MMU TCM configurable separate – cache
- 61. 61 Cortex Family • ARM Cortex-A Series - Application processors for complex OS and user applications • ARM Cortex-A8, ARM Cortex-A9 • ARM Cortex-R Series - Embedded processors for real-time systems • ARM Cortex-R4(F) • ARM Cortex-M Series – Embedded processors optimized for cost sensitive applications, as Mobile devices • ARM Cortex-M0, ARM Cortex-M1, ARM Cortex-M3
- 62. 62 Specialized Processors • StrongARM • Digital Semiconductor + Intel • PDAs • Low power consumption • Harvard Architecture • 5 stage pipeline • No thumb support
- 63. 63 Summary • Data flow in an ARM core. • 3 instruction sets • Register file • Extensions • Caches • Memory Management • Coprocessors • ISA
























![27
Processor Mode
Mode Abbr: Privileged Mode[4:0]
Abort abt yes 10111
Fast Interrupt Request fiq yes 10001
Interrupt Request irq yes 10010
Supervisor svc yes 10011
System sys yes 11111
Undefined und yes 11011
User usr no 10000
cpsr is not copied into the spsr when a mode
change is forced due to a program writing directly
to the cpsr.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/winsem2022-23bece204lthvl20222305008612023-02-10reference-material-i-230428193803-22c34ee0/85/WINSEM2022-23_BECE204L_TH_VL2022230500861_2023-02-10_Reference-Material-I-pptx-27-320.jpg)