Word2vec ultimate beginner
- 1. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space Tomas Mikolov, Kai Chen, Greg Corrado, Jeffrey Dean in Google Brain[2013] University of Gothenburg Master in Language Technology Sung Min Yang [email protected] 2017 – 05 - 29
- 2. Basic Distributed representation Rangan Majumder, Works at Microsoft https://www.quora.com/Deep-Learning-What-is-meant-by-a-distributed-representation sparse representations “one hot” vector A distributed representation is dense 1.One concept is represented by more than one neuron firing 2.One neuron represents more than one concept
- 3. Rangan Majumder, Works at Microsoft https://www.quora.com/Deep-Learning-What-is-meant-by-a-distributed-representation Make new shape with a sparse representation, we would have to increase the dimensionality. With distributed representation, we can represent a new shape with the existing dimensionality. e.g., Because of this efficient reuse, Distributed representations are used more than sparse representations. Distributed representation Basic
- 4. Background knowledge required - Negative-sampling, Subsampling - Neural Network (we don’t need recurrent concept here) *SGD(Stochastic gradient decent) + Backpropagation[these two techniques are important in word2vec] - We can interpret as “Updating weight” for now. - Softmax, Cross-entropy, Activation-function(ReLU) Background
- 5. Introduction Why so popular? Because they(Google brain tem)made a real tool and release it. Which is not heavy but quicker, simpler than previous works
- 6. Main : word2vec is not a single algorithm. Word2vec has two different Model [Architectures] (CBOW and skip-gram) It means each Model uses “a lot of algorithms” Why word2vec? because previous works for finding “word vectors”base on Neural Network were computationally expensive [ RAM, time, etc] Goal of word2vec? Computing continuous vector representation of words from 1. VERY LARGE data set 2. Quickly Introduction https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/
- 7. Main : word2vec is not a single algorithm. Word2vec has two different Model [Architectures] (CBOW and skip-gram) It means each Model uses “a lot of algorithms” Why word2vec? because previous works for finding “word vectors”base on Neural Network were computationally expensive [ RAM, time, etc] Goal of word2vec? Computing continuous vector representation of words from 1. VERY LARGE data set 2. Quickly Introduction
- 9. Inside of word2vec CBOW ( Continuous Bag of Words) Input : The, quick, brown, fox Goal : Predict Next word by given Context Output : runs, eats, jumps, chases, goes … Inside word2vec
- 10. Inside of word2vec CBOW ( Continuous Bag of Words) Let’s say we got two sentence already [whole data we got] 1. “the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog” 2. “the dog runs and chases mouse then it goes not well, so dog eats nothing” Input : Goal : Predict Next word by given Context Output : runs, eats, jumps, chases, goes … The quick brown fox Inside word2vec
- 11. Inside of word2vec Skip-gram : with one word, predict surrounding words Let’s say we got two sentence already [whole data we got] 1. “the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog” 2. “the dog runs and chases mouse then it goes not well, so dog eats nothing” [ Here, we consider surrounding words as just before and after the target word] Input : fox Goal : predict surrounding words by given Context Output : brown, eats, jumps, chases, goes the, quick, dog, then, jumps, … Inside word2vec
- 12. word2vec is not Deep learning both Model CBOW and skip-gram are "shallow" neural models Difference Deep learning(Neural Network with many hidden layers) “shallow(1 Hidden layer)” Neural Network Models https://codesachin.wordpress.com/2015/10/09/generating-a-word2vec-model-from-a-block-of-text-using-gensim-python/ Origin of word2vec
- 13. Authors(team) of word2vec belonged to has been investing a number of teams for A.I Thanks to huge amount of data own they can use “Neural Network” with a lot of Hidden Layer – a.k.a. Deep Learning the study of artificial neural networks and related machine learning algorithm that contain more than one hidden layer -wikipedia Then released open Neural Network library https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/word2vec Origin of word2vec
- 14. Shortly, Word2vec was made to be implemented into But we can build exact same word2vec tool with specific algorithms, This is where word2vec supported by other project. –from Google Origin of word2vec - One-Hot Encoding, Negative-sampling, SGD(Stochastic gradient decent) Backpropagation, hierarchical softmax, Cross-entropy, Activation- function(ReLU), logistic classifier, tSNE(not SVD) Drop- Out, etc. https://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning--ud730 Word2vec in Python by Radim Rehurek in gensim (plus tutorial and demo that uses the above model trained on Google News). Word2vec in Java as part of the deeplearning4j project. Another Java version from Medallia here. Word2vec implementation in Spark MLlib. https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/
- 15. Okay, So where can we use it? To capture Similarity! http://www.sadanduseless.com/2015/09/hilariously-similar-things/ Where to use
- 16. Many faces of Similarity ( a.k.a. degrees of Similarity) Yoav Goldberg Bar Ilan University https://www.slideshare.net/hustwj/word-embeddings-what-how-and-whither ?? Where to use
- 17. Many faces of Similarity ( a.k.a. degrees of Similarity) Yoav Goldberg Bar Ilan University https://www.slideshare.net/hustwj/word-embeddings-what-how-and-whither Related Subject Where to use
- 18. Okay, So where can we use it? To capture Similarity! Where to use [1]Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Spacehttps://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning--ud730
- 19. Okay,how to build? First concept is, word2vec use “Random” values for weight. Initial weight value is not important, because our “Neural Network” – Unsupervised Machine Learning will fix it for us. Inside of Code : `hashfxn` = hash function to use to randomly initialize weights, for increased training reproducibility. -gensim Randomly Initiated Randomly Initiated how to build
- 20. Suppose that we have only 3 sentences. “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Then we have alphabetically sorted bag of words {1. a 2. cat 3. chased 4. climbed 5. dog 6. saw 7. the 8. tree} Suppose we have 3 dimensions vectors for each word[1,2,…8] (a.k.a. vector dimensionality, Hidden neurons) now, We have randomly initiated input matrix, output matrix.( each element in matrix is called “weight”) Note. Word “dimension(ality)” will be called as “Neurons” or “Number of Neurons in hidden layer” in many papers. The fact is, writer of original word2vec paper never used term “neuron” in his papers. Don’t get confused. dimension1 dimension2 dimension3 the dog saw a cat https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ tree chased climbed dimension1 dimension2 dimension3 a thedog sawcat treechased climbed Randomly Initiated In other words, 3 hidden neurons how to build
- 21. Suppose that our target word is “cat” We can select cat by dot product [0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0] with WI(weight Input) dimension1 dimension2 dimension3 the dog saw a cat https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/tree chased climbed dimension1 dimension2 dimension3 a thedog sawcat treechased climbed “cat”[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0] how to build
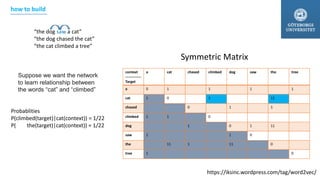
- 22. We have given data word-word occurrence frequency matrix. Suppose that we have window size 1 (one left, one right word of target word) Then we have this matrix https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ Output ------------- Target a cat chased climbed dog saw the tree a 0 1 1 1 1 cat 1 0 1 11 chased 0 1 1 climbed 1 1 0 dog 1 0 1 11 saw 1 1 0 the 11 1 11 0 tree 1 0 “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” how to build
- 23. https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ context ------------- Target a cat chased climbed dog saw the tree a 0 1 1 1 1 cat 1 0 1 11 chased 0 1 1 climbed 1 1 0 dog 1 0 1 11 saw 1 1 0 the 11 1 11 0 tree 1 0 “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Probablities P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22 P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22 Suppose we want the network to learn relationship between the words “cat” and “climbed” Symmetric Matrix how to build
- 24. dimension1 dimension2 dimension3 a thedog sawcat treechased climbed https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Suppose we want the network to learn relationship between the words “cat” and “climbed” “cat”[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0] [0.100934 -0.309331 -0.122361 -0.151399 0.143463 -0.051262 -0.079686 0.112928] Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext) P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045 P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22 how to build
- 25. dimension1 dimension2 dimension3 a thedog sawcat treechased climbed https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext) P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045 P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22 Suppose we want the network to learn relationship between the words “cat” and “climbed” [0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0] [0.100934 -0.309331 -0.122361 -0.151399 0.143463 -0.051262 -0.079686 0.112928] Selecting “climbed” [0.143073 0.094925 0.114441 0.111166 0.149289 0.122874 0.119431 0.144800] Nothing but making elements real number to Probability [a.k.a multinomial logistic regression ] “climbed” https://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning--ud730 how to build
- 26. https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext) P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045 P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22 Suppose we want the network to learn relationship between the words “cat” and “climbed” [0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0] Selecting “climbed”[0.143073 0.094925 0.114441 0.111166 0.149289 0.122874 0.119431 0.144800] “climbed” 0.111166 Is this proper probability? Yes => Okay. Doing nothing No => is this high? => Make it lower No => is this low? => make it higher 1 2 Sum up to 1 (probability) P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) how to build
- 27. https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/ “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext) P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045 P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22 Suppose we want the network to learn relationship between the words “cat” and “climbed” How to make it lower(than 1/22=0.045)? => by changing values of 0.111166 P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) Okay, So how? Answer is using “Backpropagation + SGD(Stochastic gradient descent)” Shortly, we update “WI” and “Wo” to reduce “error” (0.111166 – 0.0045 in this case) how to build
- 28. “the dog saw a cat” “the dog chased the cat” “the cat climbed a tree” Suppose we want the network to learn relationship between the words “cat” and “climbed” The goal of backpropagation is to optimize the weights so that the neural network can learn how to correctly map arbitrary inputs to outputs. Nice blog : https://mattmazur.com/2015/03/17/a-step-by-step- backpropagation-example/ Changed Changed 1 2 3 4 Repeat how to build
- 29. [('woman', 1.0000000000000002), ('man', 0.93929068644269287), ('girl', 0.89133962858176452), ('child', 0.89053309984881468), ('boy', 0.8668296321482909), ('friends', 0.84200637602356676), ('parents', 0.83820242065276596), ('herself', 0.83644761073062379), ('mother', 0.83537914209269237), ('person', 0.83160901738727488)] Goal of word2vec is finding High quality vectors representation of words. High quality?Low quality? Word2vec-gensimlab8 http://www.petrkeil.com/?p=1722 Woman Evaluation
- 30. Performance of word2vec how to build [1]Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space
- 31. Performance of word2vec how to build [1]Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space
- 32. Compositionality Further Sweden = [ 0.2, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7 ] currency = [ 0.8, 0.4, 0.2, 0.7 ] Krona = [ 0.1, 0,1, 0,1, 0,1 ] Suppose there is “currency” relation between “Sweden” and “Krona”. Then we can get Krona = Sweden 𝕴 currency by calculation. Let’s say we have a good 𝕴 operator, then we can find currency with “Japan, USA, Denmark, etc.” (+*?%... proper calculation ) [2] Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality.
- 33. Further Translation Linear Relationships Between Languages we noticed that the vector representations of similar words in different languages were related by a linear transformation. For instance, Figure 1 shows that the word vectors for English numbers one to five and the corresponding Spanish words uno to cinco have similar geometric arrangements. The relationship between vector spaces that represent these two languages can thus possibly be captured by linear mapping (namely, a rotation and scaling). Thus, if we know the translation of one and four from English to Spanish, we can learn the transformation matrix that can help us to translate even the other numbers to Spanish. [3 "Exploiting similarities among languages for machine translation."
- 34. Okay, So observing similarity for what? Real Application field? Does it useful? word2vec doc2vec paragraph 2vec item2vec etc Application
- 35. tweet_w2v.most_similar('good') Out[52]: [(u'goood', 0.7355118989944458), (u'great', 0.7164269685745239), (u'rough', 0.656904935836792), (u'gd', 0.6395257711410522), (u'goooood', 0.6351571083068848), (u'tough', 0.6336284875869751), (u'fantastic', 0.6223267316818237), (u'terrible', 0.6179217100143433), (u'gooood', 0.6099461317062378), (u'gud', 0.6096700429916382)] Application https://www.slideshare.net/PradeepPujari/sais-20431863
- 36. In Out [ 0.2, 0.4, 0,1, …… ] [ 0.2, 0.3, 0,1, ……] [ 0.2, 0.7, 0,2, ……] [ 0.2, 0.5, 0,6, ……] Etc … A nice application of Word2Vec is item recommendations e.g. movies, music, games, market basket analysis etc. Contextis Event history of users Data set of What items all users clicked, selected, and installed it. Item1 -> item2 (change) Item2 -> item14(change) item14(select – after searched item5) item15(install – after searched item8) context is history In [5] Item2Vec: Neural Item Embedding for Collaborative Relation Item1 item2 Item1 item2 . . Application
- 37. • “Tomas Mikolov told me that the whole idea behind word2vec was to demonstrate that you can get better word representations if you trade the model's complexity for efficiency, i.e. the ability to learn from much bigger datasets.” Omer Levy, at MIT in machine learning. https://www.quora.com/How-does-word2vec-work Final
- 39. [1] Mikolov, T., Corrado, G., Chen, K., & Dean, J. “Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2013), 1–12. (2013) [2] Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. “Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality.” NIPS, 1–9. 2013. [3] Mikolov, Tomas, Quoc V. Le, and Ilya Sutskever. "Exploiting similarities among languages for machine translation." arXiv preprint arXiv:1309.4168 (2013). [4] Levy, Omer, Yoav Goldberg, and Israel Ramat-Gan. "Linguistic Regularities in Sparse and Explicit Word Representations." CoNLL. 2014. [5] Barkan, Oren, and Noam Koenigstein. "Item2vec: neural item embedding for collaborative filtering." Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), 2016 IEEE 26th International Workshop on. IEEE, 2016. References
![Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space
Tomas Mikolov, Kai Chen, Greg Corrado, Jeffrey Dean in Google Brain[2013]
University of Gothenburg
Master in Language Technology
Sung Min Yang
sungmin.nlp@gmail.com
2017 – 05 - 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-1-320.jpg)


![Background knowledge required
- Negative-sampling, Subsampling
- Neural Network (we don’t need recurrent concept here)
*SGD(Stochastic gradient decent) + Backpropagation[these two techniques are important in word2vec]
- We can interpret as “Updating weight” for now.
- Softmax, Cross-entropy, Activation-function(ReLU)
Background](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-4-320.jpg)

![Main : word2vec is not a single algorithm.
Word2vec has two different Model [Architectures] (CBOW and skip-gram)
It means each Model uses “a lot of algorithms”
Why word2vec?
because previous works
for finding “word vectors”base on Neural Network
were computationally expensive [ RAM, time, etc]
Goal of word2vec?
Computing continuous vector representation of words from
1. VERY LARGE data set
2. Quickly
Introduction
https://code.google.com/archive/p/word2vec/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-6-320.jpg)
![Main : word2vec is not a single algorithm.
Word2vec has two different Model [Architectures] (CBOW and skip-gram)
It means each Model uses “a lot of algorithms”
Why word2vec?
because previous works
for finding “word vectors”base on Neural Network
were computationally expensive [ RAM, time, etc]
Goal of word2vec?
Computing continuous vector representation of words from
1. VERY LARGE data set
2. Quickly
Introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-7-320.jpg)


![Inside of word2vec
CBOW ( Continuous Bag of Words)
Let’s say we got two sentence already [whole data we got]
1. “the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog”
2. “the dog runs and chases mouse then it goes not well, so dog eats nothing”
Input :
Goal : Predict Next word by given Context
Output : runs, eats, jumps, chases, goes …
The quick brown fox
Inside word2vec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-10-320.jpg)
![Inside of word2vec
Skip-gram : with one word, predict surrounding words
Let’s say we got two sentence already [whole data we got]
1. “the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog”
2. “the dog runs and chases mouse then it goes not well, so dog eats nothing”
[ Here, we consider surrounding words as just before and after the target word]
Input : fox
Goal : predict surrounding words by given Context
Output : brown, eats, jumps, chases, goes
the, quick, dog, then, jumps, …
Inside word2vec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-11-320.jpg)






![Okay, So where can we use it?
To capture Similarity!
Where to use
[1]Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Spacehttps://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning--ud730](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-18-320.jpg)

![Suppose that we have only 3 sentences.
“the dog saw a cat”
“the dog chased the cat”
“the cat climbed a tree”
Then we have alphabetically sorted bag of words {1. a 2. cat 3. chased 4. climbed 5. dog 6. saw 7. the 8. tree}
Suppose we have 3 dimensions vectors for each word[1,2,…8] (a.k.a. vector dimensionality, Hidden neurons)
now, We have randomly initiated input matrix, output matrix.( each element in matrix is called “weight”)
Note. Word “dimension(ality)” will be called as “Neurons”
or “Number of Neurons in hidden layer” in many papers.
The fact is, writer of original word2vec paper never used
term “neuron” in his papers. Don’t get confused.
dimension1 dimension2 dimension3
the
dog
saw
a
cat
https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/
tree
chased
climbed
dimension1
dimension2
dimension3
a thedog sawcat treechased climbed
Randomly
Initiated
In other words, 3 hidden neurons
how to build](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-20-320.jpg)
![Suppose that our target word is “cat”
We can select cat by dot product [0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0] with WI(weight Input)
dimension1 dimension2 dimension3
the
dog
saw
a
cat
https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/tree
chased
climbed
dimension1
dimension2
dimension3
a thedog sawcat treechased climbed
“cat”[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
how to build](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-21-320.jpg)

![dimension1
dimension2
dimension3
a thedog sawcat treechased climbed
https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/
“the dog saw a cat”
“the dog chased the cat”
“the cat climbed a tree”
Suppose we want the network
to learn relationship between
the words “cat” and “climbed”
“cat”[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
[0.100934 -0.309331 -0.122361 -0.151399 0.143463 -0.051262 -0.079686 0.112928]
Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext)
P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045
P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22
how to build](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-24-320.jpg)
![dimension1
dimension2
dimension3
a thedog sawcat treechased climbed
https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/
“the dog saw a cat”
“the dog chased the cat”
“the cat climbed a tree”
Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext)
P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045
P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22
Suppose we want the network
to learn relationship between
the words “cat” and “climbed”
[0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0]
[0.100934 -0.309331 -0.122361 -0.151399 0.143463 -0.051262 -0.079686 0.112928]
Selecting “climbed”
[0.143073 0.094925 0.114441 0.111166 0.149289 0.122874 0.119431 0.144800]
Nothing but making
elements real number to
Probability [a.k.a
multinomial logistic
regression ]
“climbed”
https://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning--ud730
how to build](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-25-320.jpg)
![https://iksinc.wordpress.com/tag/word2vec/
“the dog saw a cat”
“the dog chased the cat”
“the cat climbed a tree”
Pr(wordtarget|wordcontext)
P(climbed(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22=0.045
P( the(target)|cat(context)) = 1/22
Suppose we want the network
to learn relationship between
the words “cat” and “climbed”
[0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0]
Selecting “climbed”[0.143073 0.094925 0.114441 0.111166 0.149289 0.122874 0.119431 0.144800]
“climbed”
0.111166
Is this proper probability?
Yes => Okay. Doing nothing
No => is this high? => Make it lower
No => is this low? => make it higher
1
2
Sum up to 1 (probability)
P(climbed(target)|cat(context))
how to build](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-26-320.jpg)


![[('woman', 1.0000000000000002),
('man', 0.93929068644269287),
('girl', 0.89133962858176452),
('child', 0.89053309984881468),
('boy', 0.8668296321482909),
('friends', 0.84200637602356676),
('parents', 0.83820242065276596),
('herself', 0.83644761073062379),
('mother', 0.83537914209269237),
('person', 0.83160901738727488)]
Goal of word2vec is finding
High quality vectors representation of words.
High quality?Low quality?
Word2vec-gensimlab8
http://www.petrkeil.com/?p=1722
Woman
Evaluation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-29-320.jpg)
![Performance of word2vec
how to build
[1]Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-30-320.jpg)
![Performance of word2vec
how to build
[1]Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-31-320.jpg)
![Compositionality
Further
Sweden = [ 0.2, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7 ]
currency = [ 0.8, 0.4, 0.2, 0.7 ]
Krona = [ 0.1, 0,1, 0,1, 0,1 ]
Suppose there is “currency” relation between
“Sweden” and “Krona”. Then we can get
Krona = Sweden 𝕴 currency by calculation.
Let’s say we have a good 𝕴 operator, then we can
find currency with “Japan, USA, Denmark, etc.”
(+*?%... proper calculation )
[2] Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-32-320.jpg)


![tweet_w2v.most_similar('good')
Out[52]:
[(u'goood', 0.7355118989944458),
(u'great', 0.7164269685745239),
(u'rough', 0.656904935836792),
(u'gd', 0.6395257711410522),
(u'goooood', 0.6351571083068848),
(u'tough', 0.6336284875869751),
(u'fantastic', 0.6223267316818237),
(u'terrible', 0.6179217100143433),
(u'gooood', 0.6099461317062378),
(u'gud', 0.6096700429916382)]
Application
https://www.slideshare.net/PradeepPujari/sais-20431863](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-35-320.jpg)
![In
Out
[ 0.2, 0.4, 0,1, …… ]
[ 0.2, 0.3, 0,1, ……] [ 0.2, 0.7, 0,2, ……] [ 0.2, 0.5, 0,6, ……] Etc …
A nice application of Word2Vec is item recommendations
e.g. movies, music, games, market basket analysis etc.
Contextis
Event history of users
Data set of What items all users
clicked, selected, and installed it.
Item1 -> item2 (change)
Item2 -> item14(change)
item14(select – after searched item5)
item15(install – after searched item8)
context is history
In
[5] Item2Vec: Neural Item Embedding for Collaborative
Relation Item1 item2
Item1
item2
.
.
Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-36-320.jpg)


![[1] Mikolov, T., Corrado, G., Chen, K., & Dean, J. “Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space.”
Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2013), 1–12.
(2013)
[2] Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. “Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their
Compositionality.” NIPS, 1–9. 2013.
[3] Mikolov, Tomas, Quoc V. Le, and Ilya Sutskever. "Exploiting similarities among languages for machine translation."
arXiv preprint arXiv:1309.4168 (2013).
[4] Levy, Omer, Yoav Goldberg, and Israel Ramat-Gan. "Linguistic Regularities in Sparse and Explicit Word
Representations." CoNLL. 2014.
[5] Barkan, Oren, and Noam Koenigstein. "Item2vec: neural item embedding for collaborative filtering." Machine
Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), 2016 IEEE 26th International Workshop on. IEEE, 2016.
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vecsungminvt17semantic-170603144702/85/Word2vec-ultimate-beginner-39-320.jpg)